Goethe's Theory of Colours - Book by Johann, Wolfgang von Goethe
GOETHE'S
THEORY OF COLOURS;
TRANSLATED FROM THE GERMAN:
WITH NOTES BY
CHARLES LOCK EASTLAKE, R.A., F.R.S.
"Cicero varietatem propriè in coloribus nasci, hinc in
alienum migrare existimavit. Certè non alibi natura
copiosius aut majore lasciviâ opes suas commendavit.
Metalla, gemmas, marmora, flores, astra, omnia denique quæ
progenuit suis etiam coloribus distinxit; ut venia debeatur
si quis in tam numerosâ rerum sylvâ caligaverit."
CELIO CALCAGNINI.
LONDON:
JOHN MURRAY, ALBEMARLE STREET.
1840
JEREMIAH HARMAN, Esq.
Dear Sir,
I dedicate to you the following translation as a testimony
of my sincere gratitude and respect; in doing so, I but
follow the example of Portius, an Italian writer, who
inscribed his translation of Aristotle's Treatise on Colours
to one of the Medici.
I have the honour to be,
Dear Sir,
Your most obliged and obedient Servant,
C. L. EASTLAKE.
English writers who have spoken of Goethe's "Doctrine of Colours,"[1]
have generally confined their remarks to those parts of the work in
which he has undertaken to account for the colours of the prismatic
spectrum, and of refraction altogether, on principles different
from the received theory of Newton. The less questionable merits
of the treatise consisting of a well-arranged mass of observations
and experiments, many of which are important and interesting, have
thus been in a great measure overlooked. The translator, aware of
the opposition which the theoretical views alluded to have met with,
intended at first to make a selection of such of the experiments as
seem more directly applicable to the theory and practice of painting.
Finding, however, that the alterations this would have involved would
have been incompatible with a clear and connected view of the author's
statements, he preferred giving the theory itself entire, reflecting,
at the same time, that some scientific readers may be curious to hear
the author speak for himself even on the points at issue.
In reviewing the history and progress of his opinions and researches,
Goethe tells us that he first submitted his views to the public
in two short essays entitled "Contributions to Optics." Among the
circumstances which he supposes were unfavourable to him on that
occasion, he mentions the choice of his title, observing that by a
reference to optics he must have appeared to make pretensions to a
knowledge of mathematics, a science with which he admits he was very
imperfectly acquainted. Another cause to which he attributes the severe
treatment he experienced, was his having ventured so openly to question
the truth of the established theory: but this last provocation could
not be owing to mere inadvertence on his part; indeed the larger work,
in which he alludes to these circumstances,[Pg ix] is still more remarkable
for the violence of his objections to the Newtonian doctrine.
There can be no doubt, however, that much of the opposition Goethe met
with was to be attributed to the manner as well as to the substance
of his statements. Had he contented himself with merely detailing his
experiments and showing their application to the laws of chromatic
harmony, leaving it to others to reconcile them as they could with the
pre-established system, or even to doubt in consequence, the truth of
some of the Newtonian conclusions, he would have enjoyed the credit
he deserved for the accuracy and the utility of his investigations.
As it was, the uncompromising expression of his convictions only
exposed him to the resentment or silent neglect of a great portion
of the scientific world, so that for a time he could not even obtain
a fair hearing for the less objectionable or rather highly valuable
communications contained in his book. A specimen of his manner of
alluding to the Newtonian theory will be seen in the preface.
It was quite natural that this spirit should call forth a somewhat
vindictive feeling, and with it not a little uncandid as well as
unsparing criticism. "The Doctrine of Colours" met[Pg x] with this reception
in Germany long before it was noticed in England, where a milder and
fairer treatment could hardly be expected, especially at a time when,
owing perhaps to the limited intercourse with the continent, German
literature was far less popular than it is at present. This last fact,
it is true, can be of little importance in the present instance,
for although the change of opinion with regard to the genius of an
enlightened nation must be acknowledged to be beneficial, it is to be
hoped there is no fashion in science, and the translator begs to state
once for all, that in advocating the neglected merits of the "Doctrine
of Colours," he is far from undertaking to defend its imputed errors.
Sufficient time has, however, now elapsed since the publication of this
work (in 1810) to allow a calmer and more candid examination of its
claims. In this more pleasing task Germany has again for some time led
the way, and many scientific investigators have followed up the hints
and observations of Goethe with a due acknowledgment of the acuteness
of his views.[2]
[Pg xi]
It may require more magnanimity in English scientific readers to do
justice to the merits of one who was so open and, in many respects, it
is believed, so mistaken an opponent of Newton; but it must be admitted
that the statements of Goethe contain more useful principles in all
that relates to harmony of colour than any that have been derived from
the established doctrine. It is no derogation of the more important
truths of the Newtonian theory to say, that the views it contains
seldom appear in a form calculated for direct application to the arts.
The principle of contrast, so universally exhibited in nature, so
apparent in the action and re-action of the eye itself, is scarcely
hinted at. The equal pretensions of seven colours, as[Pg xii] such, and the
fanciful analogies which their assumed proportions could suggest, have
rarely found favour with the votaries of taste,—indeed they have
long been abandoned even by scientific authorities.[3] And here the
translator stops: he is quite aware that the defects which make the
Newtonian theory so little available for æsthetic application, are
far from invalidating its more important conclusions in the opinion
of most scientific men. In carefully abstaining therefore from any
comparison between the two theories in these latter respects, he may
still be permitted to advocate the clearness and fulness of Goethe's
experiments. The German philosopher reduces the colours to their[Pg xiii]
origin and simplest elements; he sees and constantly bears in mind, and
sometimes ably elucidates, the phenomena of contrast and gradation,
two principles which may be said to make up the artist's world, and to
constitute the chief elements of beauty. These hints occur mostly in
what may be called the scientific part of the work. On the other hand,
in the portion expressly devoted to the æsthetic application of the
doctrine, the author seems to have made but an inadequate use of his
own principles.
In that part of the chapter on chemical colours which relates to the
colours of plants and animals, the same genius and originality which
are displayed in the Essays on Morphology, and which have secured
to Goethe undisputed rank among the investigators of nature, are
frequently apparent.
But one of the most interesting features of Goethe's theory, although
it cannot be a recommendation in a scientific point of view, is, that
it contains, undoubtedly with very great improvements, the general
doctrine of the ancients and of the Italians at the revival of letters.
The translator has endeavoured, in some notes, to point out the
connexion between this theory and the practice of the Italian painters.
[Pg xiv]
The "Doctrine of Colours," as first published in 1810, consists of
two volumes in 8vo., and sixteen plates, with descriptions, in 4to.
It is divided into three parts, a didactic, a controversial, and an
historical part; the present translation is confined to the first of
these, with such extracts from the other two as seemed necessary,
in fairness to the author, to explain some of his statements. The
polemical and historical parts are frequently alluded to in the
preface and elsewhere in the present work, but it has not been thought
advisable to omit these allusions. No alterations whatever seem to
have been made by Goethe in the didactic portion in later editions,
but he subsequently wrote an additional chapter on entoptic colours,
expressing his wish that it might be inserted in the theory itself at
a particular place which he points out. The form of this additional
essay is, however, very different from that of the rest of the work,
and the translator has therefore merely given some extracts from it in
the appendix. The polemical portion has been more than once omitted in
later editions.
In the two first parts the author's statements are arranged
numerically, in the style of Bacon's Natural History. This, we are
told, was for the[Pg xv] convenience of reference; but many passages are
thus separately numbered which hardly seem to have required it. The
same arrangement is, however, strictly followed in the translation to
facilitate a comparison with the original where it may be desired; and
here the translator observes, that although he has sometimes permitted
himself to make slight alterations, in order to avoid unnecessary
repetition, or to make the author's meaning clearer, he feels that an
apology may rather be expected from him for having omitted so little.
He was scrupulous on this point, having once determined to translate
the whole treatise, partly, as before stated, from a wish to deal
fairly with a controversial writer, and partly because many passages,
not directly bearing on the scientific views, are still characteristic
of Goethe. The observations which the translator has ventured to add
are inserted in the appendix: these observations are chiefly confined
to such of the author's opinions and conclusions as have direct
reference to the arts; they seldom interfere with the scientific
propositions, even where these have been considered most vulnerable.
It may naturally be asked whether, in proposing to treat of colours,
light itself should not first engage our attention: to this we briefly
and frankly answer that since so much has already been said on the
subject of light, it can hardly be desirable to multiply repetitions by
again going over the same ground.
Indeed, strictly speaking, it is useless to attempt to express the
nature of a thing abstractedly. Effects we can perceive, and a complete
history of those effects would, in fact, sufficiently define the
nature of the thing itself. We should try in vain to describe a man's
character, but let his acts be collected and an idea of the character
will be presented to us.
The colours are acts of light; its active and passive modifications:
thus considered we may expect from them some explanation respecting
light itself. Colours and light, it is true, stand in the most intimate
relation to each other, but[Pg xviii] we should think of both as belonging to
nature as a whole, for it is nature as a whole which manifests itself
by their means in an especial manner to the sense of sight.
The completeness of nature displays itself to another sense in a
similar way. Let the eye be closed, let the sense of hearing be
excited, and from the lightest breath to the wildest din, from the
simplest sound to the highest harmony, from the most vehement and
impassioned cry to the gentlest word of reason, still it is Nature that
speaks and manifests her presence, her power, her pervading life and
the vastness of her relations; so that a blind man to whom the infinite
visible is denied, can still comprehend an infinite vitality by means
of another organ.
And thus as we descend the scale of being, Nature speaks to other
senses—to known, misunderstood, and unknown senses: so speaks she with
herself and to us in a thousand modes. To the attentive observer she
is nowhere dead nor silent; she has even a secret agent in inflexible
matter, in a metal, the smallest portions of which tell us what
is passing in the entire mass. However manifold, complicated, and
unintelligible this language may often seem to us, yet its elements
remain ever the same. With light poise[Pg xix] and counterpoise, Nature
oscillates within her prescribed limits, yet thus arise all the
varieties and conditions of the phenomena which are presented to us in
space and time.
Infinitely various are the means by which we become acquainted with
these general movements and tendencies: now as a simple repulsion and
attraction, now as an upsparkling and vanishing light, as undulation
in the air, as commotion in matter, as oxydation and de-oxydation; but
always, uniting or separating, the great purpose is found to be to
excite and promote existence in some form or other.
The observers of nature finding, however, that this poise and
counterpoise are respectively unequal in effect, have endeavoured to
represent such a relation in terms. They have everywhere remarked and
spoken of a greater and lesser principle, an action and resistance,
a doing and suffering, an advancing and retiring, a violent and
moderating power; and thus a symbolical language has arisen, which,
from its close analogy, may be employed as equivalent to a direct and
appropriate terminology.
To apply these designations, this language of Nature to the subject
we have undertaken: to enrich and amplify this language by means of[Pg xx]
the theory of colours and the variety of their phenomena, and thus
facilitate the communication of higher theoretical views, was the
principal aim of the present treatise.
The work itself is divided into three parts. The first contains the
outline of a theory of colours. In this, the innumerable cases which
present themselves to the observer are collected under certain leading
phenomena, according to an arrangement which will be explained in
the Introduction; and here it may be remarked, that although we have
adhered throughout to experiment, and throughout considered it as our
basis, yet the theoretical views which led to the arrangement alluded
to, could not but be stated. It is sometimes unreasonably required by
persons who do not even themselves attend to such a condition, that
experimental information should be submitted without any connecting
theory to the reader or scholar, who is himself to form his conclusions
as he may list. Surely the mere inspection of a subject can profit us
but little. Every act of seeing leads to consideration, consideration
to reflection, reflection to combination, and thus it may be said that
in every attentive look on nature we already theorise. But in order to
guard against the possible[Pg xxi] abuse of this abstract view, in order that
the practical deductions we look to should be really useful, we should
theorise without forgetting that we are so doing, we should theorise
with mental self-possession, and, to use a bold word, with irony.
In the second part[1] we examine the Newtonian theory; a theory which
by its ascendancy and consideration has hitherto impeded a free inquiry
into the phenomena of colours. We combat that hypothesis, for although
it is no longer found available, it still retains a traditional
authority in the world. Its real relations to its subject will require
to be plainly pointed out; the old errors must be cleared away, if the
theory of colours is not still to remain in the rear of so many other
better investigated departments of natural science. Since, however,
this second part of our work may appear somewhat dry as regards its
matter, and perhaps too vehement and excited in its manner, we may here
be permitted to introduce a sort of allegory in a lighter style, as a
prelude to that graver portion, and as some excuse for the earnestness
alluded to.
We compare the Newtonian theory of colours[Pg xxii] to an old castle, which
was at first constructed by its architect with youthful precipitation;
it was, however, gradually enlarged and equipped by him according
to the exigencies of time and circumstances, and moreover was still
further fortified and secured in consequence of feuds and hostile
demonstrations.
The same system was pursued by his successors and heirs: their
increased wants within, the harassing vigilance of their opponents
without, and various accidents compelled them in some places to build
near, in others in connexion with the fabric, and thus to extend the
original plan.
It became necessary to connect all these incongruous parts and
additions by the strangest galleries, halls and passages. All damages,
whether inflicted by the hand of the enemy or the power of time, were
quickly made good. As occasion required, they deepened the moats,
raised the walls, and took care there should be no lack of towers,
battlements, and embrasures. This care and these exertions gave rise
to a prejudice in favour of the great importance of the fortress,
and still upheld that prejudice, although the arts of building and
fortification were by this time very much advanced, and people had[Pg xxiii]
learnt to construct much better dwellings and defences in other cases.
But the old castle was chiefly held in honour because it had never
been taken, because it had repulsed so many assaults, had baffled so
many hostile operations, and had always preserved its virgin renown.
This renown, this influence lasts even now: it occurs to no one that
the old castle is become uninhabitable. Its great duration, its costly
construction, are still constantly spoken of. Pilgrims wend their
way to it; hasty sketches of it are shown in all schools, and it is
thus recommended to the reverence of susceptible youth. Meanwhile,
the building itself is already abandoned; its only inmates are a few
invalids, who in simple seriousness imagine that they are prepared for
war.
Thus there is no question here respecting a tedious siege or a
doubtful war; so far from it we find this eighth wonder of the world
already nodding to its fall as a deserted piece of antiquity, and
begin at once, without further ceremony, to dismantle it from gable
and roof downwards; that the sun may at last shine into the old nest
of rats and owls, and exhibit to the eye of the wondering traveller
that labyrinthine, incongruous style of building, with its scanty,[Pg xxiv]
make-shift contrivances, the result of accident and emergency, its
intentional artifice and clumsy repairs. Such an inspection will,
however, only be possible when wall after wall, arch after arch, is
demolished, the rubbish being at once cleared away as well as it can be.
To effect this, and to level the site where it is possible to do
so, to arrange the materials thus acquired, so that they can be
hereafter again employed for a new building, is the arduous duty
we have undertaken in this Second Part. Should we succeed, by a
cheerful application of all possible ability and dexterity, in razing
this Bastille, and in gaining a free space, it is thus by no means
intended at once to cover the site again and to encumber it with a new
structure; we propose rather to make use of this area for the purpose
of passing in review a pleasing and varied series of illustrative
figures.
The third part is thus devoted to the historical account of early
inquirers and investigators. As we before expressed the opinion that
the history of an individual displays his character, so it may here be
well affirmed that the history of science is science itself. We cannot
clearly be aware of what we possess till we have the means of knowing
what others possessed[Pg xxv] before us. We cannot really and honestly rejoice
in the advantages of our own time if we know not how to appreciate
the advantages of former periods. But it was impossible to write, or
even to prepare the way for a history of the theory of colours while
the Newtonian theory existed; for no aristocratic presumption has ever
looked down on those who were not of its order, with such intolerable
arrogance as that betrayed by the Newtonian school in deciding on
all that had been done in earlier times and all that was done around
it. With disgust and indignation we find Priestley, in his History
of Optics, like many before and after him, dating the success of all
researches into the world of colours from the epoch of a decomposed ray
of light, or what pretended to be so; looking down with a supercilious
air on the ancient and less modern inquirers, who, after all, had
proceeded quietly in the right road, and who have transmitted to us
observations and thoughts in detail which we can neither arrange better
nor conceive more justly.
We have a right to expect from one who proposes to give the history of
any science, that he inform us how the phenomena of which it treats
were gradually known, and what was imagined,[Pg xxvi] conjectured, assumed,
or thought respecting them. To state all this in due connexion is by
no means an easy task; need we say that to write a history at all is
always a hazardous affair; with the most honest intention there is
always a danger of being dishonest; for in such an undertaking, a
writer tacitly announces at the outset that he means to place some
things in light, others in shade. The author has, nevertheless, long
derived pleasure from the prosecution of his task: but as it is the
intention only that presents itself to the mind as a whole, while the
execution is generally accomplished portion by portion, he is compelled
to admit that instead of a history he furnishes only materials for
one. These materials consist in translations, extracts, original and
borrowed comments, hints, and notes; a collection, in short, which, if
not answering all that is required, has at least the merit of having
been made with earnestness and interest. Lastly, such materials,—not
altogether untouched it is true, but still not exhausted,—may be more
satisfactory to the reflecting reader in the state in which they are,
as he can easily combine them according to his own judgment.
This third part, containing the history of the[Pg xxvii] science, does not,
however, thus conclude the subject: a fourth supplementary portion[2]
is added. This contains a recapitulation or revision; with a view
to which, chiefly, the paragraphs are headed numerically. In the
execution of a work of this kind some things may be forgotten, some
are of necessity omitted, so as not to distract the attention, some
can only be arrived at as corollaries, and others may require to be
exemplified and verified: on all these accounts, postscripts, additions
and corrections are indispensable. This part contains, besides, some
detached essays; for example, that on the atmospheric colours; for as
these are introduced in the theory itself without any classification,
they are here presented to the mind's eye at one view. Again, if this
essay invites the reader to consult Nature herself, another is intended
to recommend the artificial aids of science by circumstantially
describing the apparatus which will in future be necessary to assist
researches into the theory of colours.
In conclusion, it only remains to speak of the[Pg xxviii] plates which are added
at the end of the work;[3] and here we confess we are reminded of that
incompleteness and imperfection which the present undertaking has,
in common with all others of its class; for as a good play can be in
fact only half transmitted to writing, a great part of its effect
depending on the scene, the personal qualities of the actor, the powers
of his voice, the peculiarities of his gestures, and even the spirit
and favourable humour of the spectators; so it is, in a still greater
degree, with a book which treats of the appearances of nature. To be
enjoyed, to be turned to account, Nature herself must be present to
the reader, either really, or by the help of a lively imagination.
Indeed, the author should in such cases communicate his observations
orally, exhibiting the phenomena he describes—as a text, in the
first instance,—partly as they appear to us unsought, partly as they
may be presented by contrivance to serve in particular illustration.
Explanation and description could not then fail to produce a lively
impression.
The plates which generally accompany works like the present are thus
a most inadequate substitute[Pg xxix] for all this; a physical phenomenon
exhibiting its effects on all sides is not to be arrested in lines
nor denoted by a section. No one ever dreams of explaining chemical
experiments with figures; yet it is customary in physical researches
nearly allied to these, because the object is thus found to be in
some degree answered. In many cases, however, such diagrams represent
mere notions; they are symbolical resources, hieroglyphic modes of
communication, which by degrees assume the place of the phenomena and
of Nature herself, and thus rather hinder than promote true knowledge.
In the present instance we could not dispense with plates, but we have
endeavoured so to construct them that they may be confidently referred
to for the explanation of the didactic and polemical portions. Some of
these may even be considered as forming part of the apparatus before
mentioned.
We now therefore refer the reader to the work itself; first, only
repeating a request which many an author has already made in vain, and
which the modern German reader, especially, so seldom grants:—
Si quid novisti rectius istis
Candidus imperti; si non, his utere mecum.
[Pg xxxi]
| INTRODUCTION | xxxvii |
|---|
PART I.
PHYSIOLOGICAL COLOURS. |
|---|
| I. | Effects of Light and Darkness on the Eye | 2 |
| II. | Effects of Black and White Objects on the Eye | 5 |
| III. | Grey Surfaces and Objects | 14 |
| IV. | Dazzling Colourless Objects | 16 |
| V. | Coloured Objects | 20 |
| VI. | Coloured Shadows | 29 |
| VII. | Faint Lights | 38 |
| VIII. | Subjective Halos | 40 |
| | Pathological Colours—Appendix | 45 |
PART II.
PHYSICAL COLOURS. |
|---|
| IX. | Dioptrical Colours | 59 |
| X. | Dioptrical Colours of the First Class | 60 |
| XI. | Dioptrical Colours of the Second Class
—Refraction | 74 |
| | Subjective Experiments | 80 |
| XII. | Refraction without the Appearance of Colour | 80 |
| XIII. | Conditions of the Appearance of Colour | 81 |
| XIV. | Conditions under which the Appearance of |
| | Colour increases | 86 |
| XV. | Explanation of the foregoing Phenomena | 90 |
| XVI. | Decrease of the Appearance of Colour | 100 |
| XVII. | Grey Objects displaced by Refraction | 103 |
| XVIII. | Coloured Objects displaced by Refraction | 106 |
| XIX. | Achromatism and Hyperchromatism | 118
[Pg xxxii] |
| XX. | Advantages of Subjective Experiments
—Transition to the Objective | 123 |
| | Objective Experiments | 125 |
| XXI. | Refraction without the Appearance of Colour | 121 |
| XXII. | Conditions of the Appearance of Colour | 128 |
| XXIII. | Conditions of the Increase of Colour | 134 |
| XXIV. | Explanation of the foregoing Phenomena | 139 |
| XXV. | Decrease of the Appearance of Colour | 141 |
| XXVI. | Grey Objects | 142 |
| XXVII. | Coloured Objects | 143 |
| XXVIII. | Achromatism and Hyperchromatism | 145 |
| XXIX. | Combination of Subjective and Objective
Experiments | 147 |
| XXX. | Transition | 150 |
| XXXI. | Catoptrical Colours | 154 |
| XXXII. | Paroptical Colours | 163 |
| XXXIII. | Epoptical Colours | 177 |
PART III.
CHEMICAL COLOURS. |
|---|
| XXXIV. | Chemical Contrast | 202 |
| XXXV. | White | 203 |
| XXXVI. | Black | 205 |
| XXXVII. | First Excitation of Colour | 206 |
| XXXVIII. | Augmentation of Colour | 212 |
| XXXIX. | Culmination | 214 |
| XL. | Fluctuation | 217 |
| XLI. | Passage through the Whole Scale | 218 |
| XLII. | Inversion | 220 |
| XLIII. | Fixation | 221 |
| XLIV. | Intermixture, Real | 223 |
| XLV. | Intermixture, Apparent | 226 |
| XLVI. | Communication, Actual | 230 |
| XLVII. | Communication, Apparent | 235 |
| XLVIII. | Extraction | 237 |
| XLIX. | Nomenclature | 242 |
| L. | Minerals | 245
[Pg xxxiii] |
| LI. | Plants | 247 |
| LII. | Worms, Insects, Fishes | 252 |
| LIII. | Birds | 259 |
| LIV. | Mammalia and Human Beings | 262 |
| LV. | Physical and Chemical Effects of the
Transmission
of Light through Coloured Mediums | 266 |
| LVI. | Chemical Effect in Dioptrical Achromatism | 270 |
PART IV.
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS.
The Facility with which Colour appears 274
The Definite Nature of Colour 276
Combination of the Two Principles 277
Augmentation to Red 277
Junction of the Two Augmented Extremes 278
Completeness the Result of Variety in Colour 279
Harmony of the Complete State 280
Facility with which Colour may be made to tend either to
the Plus or Minus side 281
Evanescence of Colour 281
Permanence of Colour 282
PART V.
RELATION TO OTHER PURSUITS.
Relation to Philosophy 283
Relation to Mathematics 286
Relation to the Technical Operations of the Dyer 289
Relation to Physiology and Pathology 291
Relation to Natural History 292
Relation to General Physics 293
Relation to the Theory of Music 298
Concluding Observations on Terminology 300
PART VI.
EFFECT OF COLOUR WITH REFERENCE
TO MORAL ASSOCIATIONS.
[Pg xxxiv]
Yellow 306
Red-Yellow 308
Yellow-Red 309
Blue 310
Red-Blue 312
Blue-Red 313
Red 313
Green 316
Completeness and Harmony 316
Characteristic Combinations 321
Yellow and Blue 322
Yellow and Red 322
Blue and Red 322
Yellow-Red and Blue-Red 323
Combinations Non-Characteristic 324
Relation of the Combinations to Light and Dark 325
Considerations derived from the Evidence of Experience
and History 326
Æsthetic Influence 330
Chiaro-Scuro 331
Tendency to Colour 334
Keeping 335
Colouring 337
Colour in General Nature 337
Colour of Particular Objects 338
Characteristic Colouring 339
Harmonious Colouring 341
Genuine Tone 342
False Tone 342
Weak Colouring 343
The Motley 344
Dread of Theory 344
Ultimate Aim 345
Grounds 345
Pigments 348
Allegorical, Symbolical, Mystical Application of Colour 350
Concluding Observations 352
[Pg xxxv]
"Si vera nostra sunt aut falsa, erunt talia, licet nostra
per vitam defendimus. Post fata nostra pueri qui nunc ludunt
nostri judices erunt."
[Pg xxxvii]
The desire of knowledge is first stimulated in us when remarkable
phenomena attract our attention. In order that this attention be
continued, it is necessary that we should feel some interest in
exercising it, and thus by degrees we become better acquainted with the
object of our curiosity. During this process of observation we remark
at first only a vast variety which presses indiscriminately on our
view; we are forced to separate, to distinguish, and again to combine;
by which means at last a certain order arises which admits of being
surveyed with more or less satisfaction.
To accomplish this, only in a certain degree, in any department,
requires an unremitting and close application; and we find, for this
reason, that men prefer substituting a general theoretical view, or
some system of explanation, for the facts themselves, instead of taking
the trouble to make themselves first acquainted with cases in detail
and then constructing a whole.
The attempt to describe and class the phenomena of colours has been
only twice made: first by Theophrastus,[1] and in modern times by[Pg xxxviii]
Boyle. The pretensions of the present essay to the third place will
hardly be disputed.
Our historical survey enters into further details. Here we merely
observe that in the last century such a classification was not to be
thought of, because Newton had based his hypothesis on a phenomenon
exhibited in a complicated and secondary state; and to this the other
cases that forced themselves on the attention were contrived to be
referred, when they could not be passed over in silence; just as an
astronomer would do, if from whim he were to place the moon in the
centre of our system; he would be compelled to make the earth, sun, and
planets revolve round the lesser body, and be forced to disguise and
gloss over the error of his first assumption by ingenious calculations
and plausible statements.
In our prefatory observations we assumed the reader to be acquainted
with what was known respecting light; here we assume the same with
regard to the eye. We observed that all nature manifests itself by
means of colours to the sense of sight. We now assert, extraordinary as
it may in some degree appear, that the eye sees no form, inasmuch as
light, shade, and colour together constitute that which to our vision
distinguishes object from object, and the parts of an object from each
other. From these three, light, shade, and colour, we construct the
visible[Pg xxxix] world, and thus, at the same time, make painting possible,
an art which has the power of producing on a flat surface a much more
perfect visible world than the actual one can be.
The eye may be said to owe its existence to light, which calls forth,
as it were, a sense that is akin to itself; the eye, in short, is
formed with reference to light, to be fit for the action of light; the
light it contains corresponding with the light without.
We are here reminded of a significant adage in constant use with the
ancient Ionian school—"Like is only known by Like;" and again, of the
words of an old mystic writer, which may be thus rendered, "If the eye
were not sunny, how could we perceive light? If God's own strength
lived not in us, how could we delight in Divine things?" This immediate
affinity between light and the eye will be denied by none; to consider
them as identical in substance is less easy to comprehend. It will be
more intelligible to assert that a dormant light resides in the eye,
and that it may be excited by the slightest cause from within or from
without. In darkness we can, by an effort of imagination, call up the
brightest images; in dreams objects appear to us as in broad daylight;
awake, the slightest external action of light is perceptible, and if
the organ suffers an actual shock, light and colours spring forth.[Pg xl]
Here, however, those who are wont to proceed according to a certain
method, may perhaps observe that as yet we have not decidedly explained
what colour is. This question, like the definition of light and the
eye, we would for the present evade, and would appeal to our inquiry
itself, where we have circumstantially shown how colour is produced.
We have only therefore to repeat that colour is a law of nature in
relation with the sense of sight. We must assume, too, that every one
has this sense, that every one knows the operation of nature on it, for
to a blind man it would be impossible to speak of colours.
That we may not, however, appear too anxious to shun such an
explanation, we would restate what has been said as follows: colour is
an elementary phenomenon in nature adapted to the sense of vision; a
phenomenon which, like all others, exhibits itself by separation and
contrast, by commixture and union, by augmentation and neutralization,
by communication and dissolution: under these general terms its nature
may be best comprehended.
We do not press this mode of stating the subject on any one. Those
who, like ourselves, find it convenient, will readily adopt it; but we
have no desire to enter the lists hereafter in its defence. From time
immemorial it has been dangerous to treat of colour; so much so, that[Pg xli]
one of our predecessors ventured on a certain occasion to say, "The ox
becomes furious if a red cloth is shown to him; but the philosopher,
who speaks of colour only in a general way, begins to rave."
Nevertheless, if we are to proceed to give some account of our work, to
which we have appealed, we must begin by explaining how we have classed
the different conditions under which colour is produced. We found three
modes in which it appears; three classes of colours, or rather three
exhibitions of them all. The distinctions of these classes are easily
expressed.
Thus, in the first instance, we considered colours, as far as they
may be said to belong to the eye itself, and to depend on an action
and re-action of the organ; next, they attracted our attention as
perceived in, or by means of, colourless mediums; and lastly, where
we could consider them as belonging to particular substances. We have
denominated the first, physiological, the second, physical, the third,
chemical colours. The first are fleeting and not to be arrested; the
next are passing, but still for a while enduring; the last may be made
permanent for any length of time.
Having separated these classes and kept them as distinct as possible,
with a view to a clear, didactic exposition, we have been enabled at[Pg xlii]
the same time to exhibit them in an unbroken series, to connect the
fleeting with the somewhat more enduring, and these again with the
permanent hues; and thus, after having carefully attended to a distinct
classification in the first instance, to do away with it again when a
larger view was desirable.
In a fourth division of our work we have therefore treated generally
what was previously detailed under various particular conditions, and
have thus, in fact, given a sketch for a future theory of colours. We
will here only anticipate our statements so far as to observe, that
light and darkness, brightness and obscurity, or if a more general
expression is preferred, light and its absence, are necessary to the
production of colour. Next to the light, a colour appears which we call
yellow; another appears next to the darkness, which we name blue. When
these, in their purest state, are so mixed that they are exactly equal,
they produce a third colour called green. Each of the two first-named
colours can however of itself produce a new tint by being condensed or
darkened. They thus acquire a reddish appearance which can be increased
to so great a degree that the original blue or yellow is hardly to
be recognised in it: but the intensest and purest red, especially in
physical cases, is produced when the two extremes of the yellow-red
and blue-red are[Pg xliii] united. This is the actual state of the appearance
and generation of colours. But we can also assume an existing red in
addition to the definite existing blue and yellow, and we can produce
contrariwise, by mixing, what we directly produced by augmentation or
deepening. With these three or six colours, which may be conveniently
included in a circle, the elementary doctrine of colours is alone
concerned. All other modifications, which may be extended to infinity,
have reference more to the application,—have reference to the
technical operations of the painter and dyer, and the various purposes
of artificial life. To point out another general quality, we may
observe that colours throughout are to be considered as half-lights, as
half-shadows, on which account if they are so mixed as reciprocally to
destroy their specific hues, a shadowy tint, a grey, is produced.
In the fifth division of our inquiry we had proposed to point out
the relations in which we should wish our doctrine of colours to
stand to other pursuits. Important as this part of our work is, it
is perhaps on this very account not so successful as we could wish.
Yet when we reflect that strictly speaking these relations cannot be
described before they exist, we may console ourselves if we have in
some degree failed in endeavouring for the first time to define them.
For undoubtedly we should first[Pg xliv] wait to see how those whom we have
endeavoured to serve, to whom we have intended to make an agreeable and
useful offering, how such persons, we say, will accept the result of
our utmost exertion: whether they will adopt it, whether they will make
use of it and follow it up, or whether they will repel, reject, and
suffer it to remain unassisted and neglected.
Meanwhile, we venture to express what we believe and hope. From the
philosopher we believe we merit thanks for having traced the phenomena
of colours to their first sources, to the circumstances under which
they simply appear and are, and beyond which no further explanation
respecting them is possible. It will, besides, be gratifying to him
that we have arranged the appearances described in a form that admits
of being easily surveyed, even should he not altogether approve of the
arrangement itself.
The medical practitioner, especially him whose study it is to watch
over the organ of sight, to preserve it, to assist its defects and to
cure its disorders, we reckon to make especially our friend. In the
chapter on the physiological colours, in the Appendix relating to those
that are more strictly pathological, he will find himself quite in his
own province. We are not without hopes of seeing the physiological
phenomena,—a hitherto neglected, and, we may add, most important
branch of the theory of[Pg xlv] colours,—completely investigated through the
exertions of those individuals who in our own times are treating this
department with success.
The investigator of nature should receive us cordially, since we
enable him to exhibit the doctrine of colours in the series of other
elementary phenomena, and at the same time enable him to make use of a
corresponding nomenclature, nay, almost the same words and designations
as under the other rubrics. It is true we give him rather more trouble
as a teacher, for the chapter of colours is not now to be dismissed
as heretofore with a few paragraphs and experiments; nor will the
scholar submit to be so scantily entertained as he has hitherto been,
without murmuring. On the other hand, an advantage will afterwards
arise out of this: for if the Newtonian doctrine was easily learnt,
insurmountable difficulties presented themselves in its application.
Our theory is perhaps more difficult to comprehend, but once known, all
is accomplished, for it carries its application along with it.
The chemist who looks upon colours as indications by which he may
detect the more secret properties of material things, has hitherto
found much inconvenience in the denomination and description of
colours; nay, some have been induced after closer and nicer examination
to look upon colour as an uncertain and fallacious criterion[Pg xlvi] in
chemical operations. Yet we hope by means of our arrangement and the
nomenclature before alluded to, to bring colour again into credit,
and to awaken the conviction that a progressive, augmenting, mutable
quality, a quality which admits of alteration even to inversion, is not
fallacious, but rather calculated to bring to light the most delicate
operations of nature.
In looking a little further round us, we are not without fears
that we may fail to satisfy another class of scientific men. By an
extraordinary combination of circumstances the theory of colours
has been drawn into the province and before the tribunal of the
mathematician, a tribunal to which it cannot be said to be amenable.
This was owing to its affinity with the other laws of vision which the
mathematician was legitimately called upon to treat. It was owing,
again, to another circumstance: a great mathematician had investigated
the theory of colours, and having been mistaken in his observations as
an experimentalist, he employed the whole force of his talent to give
consistency to this mistake. Were both these circumstances considered,
all misunderstanding would presently be removed, and the mathematician
would willingly co-operate with us, especially in the physical
department of the theory.
To the practical man, to the dyer, on the other hand, our labour must
be altogether acceptable;[Pg xlvii] for it was precisely those who reflected on
the facts resulting from the operations of dyeing who were the least
satisfied with the old theory: they were the first who perceived the
insufficiency of the Newtonian doctrine. The conclusions of men are
very different according to the mode in which they approach a science
or branch of knowledge; from which side, through which door they
enter. The literally practical man, the manufacturer, whose attention
is constantly and forcibly called to the facts which occur under his
eye, who experiences benefit or detriment from the application of his
convictions, to whom loss of time and money is not indifferent, who
is desirous of advancing, who aims at equalling or surpassing what
others have accomplished,—such a person feels the unsoundness and
erroneousness of a theory much sooner than the man of letters, in whose
eyes words consecrated by authority are at last equivalent to solid
coin; than the mathematician, whose formula always remains infallible,
even although the foundation on which it is constructed may not square
with it. Again, to carry on the figure before employed, in entering
this theory from the side of painting, from the side of æsthetic[2]
colouring generally, we shall be[Pg xlviii] found to have accomplished a
most thank-worthy office for the artist. In the sixth part we have
endeavoured to define the effects of colour as addressed at once to
the eye and mind, with a view to making them more available for the
purposes of art. Although much in this portion, and indeed throughout,
has been suffered to remain as a sketch, it should be remembered that
all theory can in strictness only point out leading principles, under
the guidance of which, practice may proceed with vigour and be enabled
to attain legitimate results.
PHYSIOLOGICAL COLOURS.
1.
We naturally place these colours first, because they belong altogether,
or in a great degree, to the subject[1]—to the eye itself. They
are the foundation of the whole doctrine, and open to our view the
chromatic harmony on which so much difference of opinion has existed.
They have been hitherto looked upon as extrinsic and casual, as
illusion and infirmity: their appearances have been known from ancient
date; but, as they were too evanescent to be arrested, they were
banished into the region of phantoms, and under this idea have been
very variously described.
2.
Thus they are called colores adventicii by Boyle; imaginarii and
phantastici by Rizetti; by Buffon, couleurs accidentelles; by
Scherfer, scheinfarben (apparent colours); ocular illusions and
deceptions of sight[Pg 2] by many; by Hamberger, vitia fugitiva; by
Darwin, ocular spectra.
3.
We have called them physiological because they belong to the eye in a
healthy state; because we consider them as the necessary conditions
of vision; the lively alternating action of which, with reference to
external objects and a principle within it, is thus plainly indicated.
4.
To these we subjoin the pathological colours, which, like all
deviations from a constant law, afford a more complete insight into the
nature of the physiological colours.
I
EFFECTS OF LIGHT AND DARKNESS ON THE EYE.
5.
The retina, after being acted upon by light or darkness, is found to be
in two different states, which are entirely opposed to each other.
6.
If we keep the eyes open in a totally dark place, a certain sense of
privation is experienced. The organ is abandoned to itself; it retires
into itself. That stimulating and grateful contact is wanting by means
of which it is connected with the external world, and becomes part of a
whole.
[Pg 3]
7.
If we look on a white, strongly illumined surface, the eye is dazzled,
and for a time is incapable of distinguishing objects moderately
lighted.
8.
The whole of the retina is acted on in each of these extreme states,
and thus we can only experience one of these effects at a time. In
the one case (6) we found the organ in the utmost relaxation and
susceptibility; in the other (7) in an overstrained state, and scarcely
susceptible at all.
9.
If we pass suddenly from the one state to the other, even without
supposing these to be the extremes, but only, perhaps, a change from
bright to dusky, the difference is remarkable, and we find that the
effects last for some time.
10.
In passing from bright daylight to a dusky place we distinguish nothing
at first: by degrees the eye recovers its susceptibility; strong eyes
sooner than weak ones; the former in a minute, while the latter may
require seven or eight minutes.
11.
The fact that the eye is not susceptible to faint[Pg 4] impressions of
light, if we pass from light to comparative darkness, has led to
curious mistakes in scientific observations. Thus an observer, whose
eyes required some time to recover their tone, was long under the
impression that rotten wood did not emit light at noon-day, even in a
dark room. The fact was, he did not see the faint light, because he was
in the habit of passing from bright sunshine to the dark room, and only
subsequently remained so long there that the eye had time to recover
itself.
The same may have happened to Doctor Wall, who, in the daytime, even in
a dark room, could hardly perceive the electric light of amber.
Our not seeing the stars by day, as well as the improved appearance of
pictures seen through a double tube, is also to be attributed to the
same cause.
12.
If we pass from a totally dark place to one illumined by the sun, we
are dazzled. In coming from a lesser degree of darkness to light that
is not dazzling, we perceive all objects clearer and better: hence eyes
that have been in a state of repose are in all cases better able to
perceive moderately distinct appearances.
Prisoners who have been long confined in darkness acquire so great
a susceptibility of the retina, that even in the dark (probably a
darkness[Pg 5] very slightly illumined) they can still distinguish objects.
13.
In the act which we call seeing, the retina is at one and the same time
in different and even opposite states. The greatest brightness, short
of dazzling, acts near the greatest darkness. In this state we at once
perceive all the intermediate gradations of chiaro-scuro, and all the
varieties of hues.
14.
We will proceed in due order to consider and examine these elements of
the visible world, as well as the relation in which the organ itself
stands to them, and for this purpose we take the simplest objects.
EFFECTS OF BLACK AND WHITE OBJECTS ON THE EYE.
15.
In the same manner as the retina generally is affected by brightness
and darkness, so it is affected by single bright or dark objects.
If light and dark produce different results on the whole retina, so
black and white objects seen at[Pg 6] the same time produce the same states
together which light and dark occasioned in succession.
16.
A dark object appears smaller than a bright one of the same size. Let
a white disk be placed on a black ground, and a black disk on a white
ground, both being exactly similar in size; let them be seen together
at some distance, and we shall pronounce the last to be about a fifth
part smaller than the other. If the black circle be made larger by so
much, they will appear equal.[1]
17.
Thus Tycho de Brahe remarked that the moon in conjunction (the darker
state) appears about a fifth part smaller than when in opposition
(the bright full state). The first crescent appears to belong to a
larger disk than the remaining dark portion, which can sometimes be
distinguished at the period of the new moon. Black dresses make people
appear smaller than light ones. Lights seen behind an edge make an
apparent notch in it. A ruler, behind which the flame of a light just
appears, seems to us indented. The rising or setting sun appears to
make a notch in the horizon.
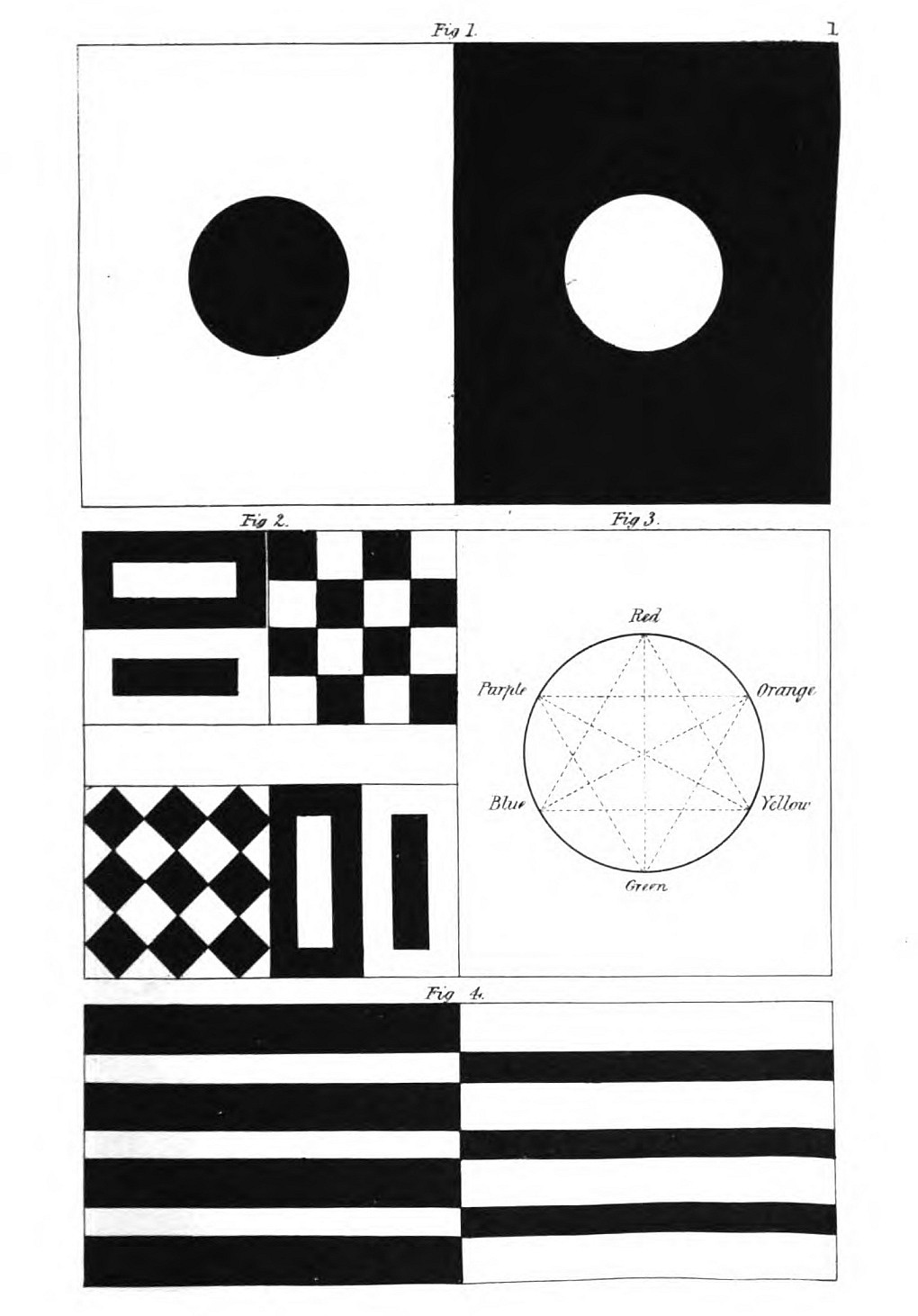
Plate 1.
18.
Black, as the equivalent of darkness, leaves[Pg 7] the organ in a state of
repose; white, as the representative of light, excites it. We may,
perhaps, conclude from the above experiment (16) that the unexcited
retina, if left to itself, is drawn together, and occupies a less space
than in its active state, produced by the excitement of light.
Hence Kepler says very beautifully: "Certum est vel in retinâ caussâ
picturæ, vel in spiritibus caussâ impressionis, exsistere dilatationem
lucidorum."—Paralip. in Vitellionem, p. 220. Scherfer expresses a
similar conjecture.—Note A.
19.
However this may be, both impressions derived from such objects remain
in the organ itself, and last for some time, even when the external
cause is removed. In ordinary experience we scarcely notice this, for
objects are seldom presented to us which are very strongly relieved
from each other, and we avoid looking at those appearances that dazzle
the sight. In glancing from one object to another, the succession of
images appears to us distinct; we are not aware that some portion of
the impression derived from the object first contemplated passes to
that which is next looked at.
20.
If in the morning, on waking, when the eye is very susceptible, we look
intently at the bars[Pg 8] of a window relieved against the dawning sky, and
then shut our eyes or look towards a totally dark place, we shall see a
dark cross on a light ground before us for some time.
21.
Every image occupies a certain space on the retina, and of course a
greater or less space in proportion as the object is seen near or at a
distance. If we shut the eyes immediately after looking at the sun we
shall be surprised to find how small the image it leaves appears.
22.
If, on the other hand, we turn the open eye towards the side of a
room, and consider the visionary image in relation to other objects,
we shall always see it larger in proportion to the distance of the
surface on which it is thrown. This is easily explained by the laws of
perspective, according to which a small object near covers a great one
at a distance.
23.
The duration of these visionary impressions varies with the powers
or structure of the eye in different individuals, just as the time
necessary for the recovery of the tone of the retina varies in passing
from brightness to darkness (10): it can be measured by minutes and
seconds,[Pg 9] indeed much more exactly than it could formerly have been
by causing a lighted linstock to revolve rapidly, so as to appear a
circle.—Note B.
24.
But the force with which an impinging light impresses the eye is
especially worthy of attention. The image of the sun lasts longest;
other objects, of various degrees of brightness, leave the traces of
their appearance on the eye for a proportionate time.
25.
These images disappear by degrees, and diminish at once in distinctness
and in size.
26.
They are reduced from the contour inwards, and the impression on some
persons has been that in square images the angles become gradually
blunted till at last a diminished round image floats before the eye.
27.
Such an image, when its impression is no more observable, can,
immediately after, be again revived on the retina by opening and
shutting the eye, thus alternately exciting and resting it.
[Pg 10]
28.
Images may remain on the retina in morbid affections of the eye for
fourteen, seventeen minutes, or even longer. This indicates extreme
weakness of the organ, its inability to recover itself; while visions
of persons or things which are the objects of love or aversion indicate
the connexion between sense and thought.
29.
If, while the image of the window-bars before mentioned lasts, we
look upon a light grey surface, the cross will then appear light
and the panes dark. In the first case (20) the image was like the
original picture, so that the visionary impression also could continue
unchanged; but in the present instance our attention is excited by a
contrary effect being produced. Various examples have been given by
observers of nature.
30.
The scientific men who made observations in the Cordilleras saw a
bright appearance round the shadows of their heads on some clouds. This
example is a case in point; for, while they fixed their eyes on the
dark shadow, and at the same time moved from the spot, the compensatory
light image appeared to float round the[Pg 11] real dark one. If we look at
a black disk on a light grey surface, we shall presently, by changing
the direction of the eyes in the slightest degree, see a bright halo
floating round the dark circle.
A similar circumstance happened to myself: for while, as I sat in the
open air, I was talking to a man who stood at a little distance from me
relieved on a grey sky, it appeared to me, as I slightly altered the
direction of my eyes, after having for some time looked fixedly at him,
that his head was encircled with a dazzling light.
In the same way probably might be explained the circumstance that
persons crossing dewy meadows at sunrise see a brightness round each
other's heads[2]; the brightness in this case may be also iridescent,
as the phenomena of refraction come into the account.
Thus again it has been asserted that the shadows of a balloon thrown on
clouds were bordered with bright and somewhat variegated circles.
Beccaria made use of a paper kite in some experiments on electricity.
Round this kite appeared a small shining cloud varying in size; the
same brightness was even observed round part of the string. Sometimes
it disappeared,[Pg 12] and if the kite moved faster the light appeared to
float to and fro for a few moments on the place before occupied. This
appearance, which could not be explained by those who observed it at
the time, was the image which the eye retained of the kite relieved as
a dark mass on a bright sky; that image being changed into a light mass
on a comparatively dark background.
In optical and especially in chromatic experiments, where the observer
has to do with bright lights whether colourless or coloured, great care
should be taken that the spectrum which the eye retains in consequence
of a previous observation does not mix with the succeeding one, and
thus affect the distinctness and purity of the impression.
31.
These appearances have been explained as follows: That portion of the
retina on which the dark cross (29) was impressed is to be considered
in a state of repose and susceptibility. On this portion therefore the
moderately light surface acted in a more lively manner than on the rest
of the retina, which had just been impressed with the light through
the panes, and which, having thus been excited by a much stronger
brightness, could only view the grey surface as a dark.
[Pg 13]
32.
This mode of explanation appears sufficient for the cases in question,
but, in the consideration of phenomena hereafter to be adduced, we are
forced to trace the effects to higher sources.
33.
The eye after sleep exhibits its vital elasticity more especially by
its tendency to alternate its impressions, which in the simplest form
change from dark to light, and from light to dark. The eye cannot for a
moment remain in a particular state determined by the object it looks
upon. On the contrary, it is forced to a sort of opposition, which, in
contrasting extreme with extreme, intermediate degree with intermediate
degree, at the same time combines these opposite impressions, and thus
ever tends to a whole, whether the impressions are successive, or
simultaneous and confined to one image.
34.
Perhaps the peculiarly grateful sensation which we experience in
looking at the skilfully treated chiaro-scuro of colourless pictures
and similar works of art arises chiefly from the simultaneous
impression of a whole, which by the organ itself is sought, rather than
arrived at, in succession, and which, whatever may be the result, can
never be arrested.
GREY SURFACES AND OBJECTS.
35.
A moderate light is essential to many chromatic experiments. This can
be presently obtained by surfaces more or less grey, and thus we have
at once to make ourselves acquainted with this simplest kind of middle
tint, with regard to which it is hardly necessary to observe, that
in many cases a white surface in shadow, or in a low light, may be
considered equivalent to a grey.
36.
Since a grey surface is intermediate between brightness and darkness,
it admits of our illustrating a phenomenon before described (29) by an
easy experiment.
37.
Let a black object be held before a grey surface, and let the
spectator, after looking steadfastly at it, keep his eyes unmoved while
it is taken away: the space it occupied appears much lighter. Let a
white object be held up in the same manner: on taking it away the space
it occupied will appear much darker than the[Pg 15] rest of the surface. Let
the spectator in both cases turn his eyes this way and that on the
surface, the visionary images will move in like manner.
38.
A grey object on a black ground appears much brighter than the same
object on a white ground. If both comparisons are seen together the
spectator can hardly persuade himself that the two greys are identical.
We believe this again to be a proof of the great excitability of the
retina, and of the silent resistance which every vital principle is
forced to exhibit when any definite or immutable state is presented to
it. Thus inspiration already presupposes expiration; thus every systole
its diastole. It is the universal formula of life which manifests
itself in this as in all other cases. When darkness is presented to
the eye it demands brightness, and vice versâ: it shows its vital
energy, its fitness to receive the impression of the object, precisely
by spontaneously tending to an opposite state.
[Pg 16]
DAZZLING COLOURLESS OBJECTS.
39.
If we look at a dazzling, altogether colourless object, it makes a
strong lasting impression, and its after-vision is accompanied by an
appearance of colour.
40.
Let a room be made as dark as possible; let there be a circular opening
in the window-shutter about three inches in diameter, which may be
closed or not at pleasure. The sun being suffered to shine through this
on a white surface, let the spectator from some little distance fix his
eyes on the bright circle thus admitted. The hole being then closed,
let him look towards the darkest part of the room; a circular image
will now be seen to float before him. The middle of this circle will
appear bright, colourless, or somewhat yellow, but the border will at
the same moment appear red.
After a time this red, increasing towards the centre, covers the whole
circle, and at last the bright central point. No sooner, however, is
the whole circle red than the edge begins to be blue, and the blue
gradually encroaches inwards[Pg 17] on the red. When the whole is blue
the edge becomes dark and colourless. This darker edge again slowly
encroaches on the blue till the whole circle appears colourless. The
image then becomes gradually fainter, and at the same time diminishes
in size. Here again we see how the retina recovers itself by a
succession of vibrations after the powerful external impression it
received. (25, 26.)
41.
By several repetitions similar in result, I found the comparative
duration of these appearances in my own case to be as follows:—
I looked on the bright circle five seconds, and then, having closed
the aperture, saw the coloured visionary circle floating before me.
After thirteen seconds it was altogether red; twenty-nine seconds
next elapsed till the whole was blue, and forty-eight seconds till
it appeared colourless. By shutting and opening the eye I constantly
revived the image, so that it did not quite disappear till seven
minutes had elapsed.
Future observers may find these periods shorter or longer as their
eyes may be stronger or weaker (23), but it would be very remarkable
if, notwithstanding such variations, a corresponding proportion as to
relative duration should be found to exist.
[Pg 18]
42.
But this remarkable phenomenon no sooner excites our attention than we
observe a new modification of it.
If we receive the impression of the bright circle as before, and then
look on a light grey surface in a moderately lighted room, an image
again floats before us; but in this instance a dark one: by degrees it
is encircled by a green border that gradually spreads inwards over the
whole circle, as the red did in the former instance. As soon as this
has taken place a dingy yellow appears, and, filling the space as the
blue did before, is finally lost in a negative shade.
43.
These two experiments may be combined by placing a black and a white
plane surface next each other in a moderately lighted room, and then
looking alternately on one and the other as long as the impression of
the light circle lasts: the spectator will then perceive at first a red
and green image alternately, and afterwards the other changes. After a
little practice the two opposite colours may be perceived at once, by
causing the floating image to fall on the junction of the two planes.
This can be more conveniently done if the planes are at some distance,
for the spectrum then appears larger.
[Pg 19]
44.
I happened to be in a forge towards evening at the moment when a
glowing mass of iron was placed on the anvil; I had fixed my eyes
steadfastly on it, and, turning round, I looked accidentally into an
open coal-shed: a large red image now floated before my eyes, and, as I
turned them from the dark opening to the light boards of which the shed
was constructed, the image appeared half green, half red, according as
it had a lighter or darker ground behind it. I did not at that time
take notice of the subsequent changes of this appearance.
45.
The after-vision occasioned by a total dazzling of the retina
corresponds with that of a circumscribed bright object. The red colour
seen by persons who are dazzled with snow belongs to this class of
phenomena, as well as the singularly beautiful green colour which dark
objects seem to wear after looking long on white paper in the sun. The
details of such experiments may be investigated hereafter by those
whose young eyes are capable of enduring such trials further for the
sake of science.
46.
With these examples we may also class the black letters which in the
evening light appear[Pg 20] red. Perhaps we might insert under the same
category the story that drops of blood appeared on the table at which
Henry IV. of France had seated himself with the Duc de Guise to play at
dice.
COLOURED OBJECTS.
47.
We have hitherto seen the physiological colours displayed in the
after-vision of colourless bright objects, and also in the after-vision
of general colourless brightness; we shall now find analogous
appearances if a given colour be presented to the eye: in considering
this, all that has been hitherto detailed must be present to our
recollection.
48.
The impression of coloured objects remains in the eye like that of
colourless ones, but in this case the energy of the retina, stimulated
as it is to produce the opposite colour, will be more apparent.
49.
Let a small piece of bright-coloured paper or silk stuff be held before
a moderately lighted white surface; let the observer look steadfastly[Pg 21]
on the small coloured object, and let it be taken away after a time
while his eyes remain unmoved; the spectrum of another colour will then
be visible on the white plane. The coloured paper may be also left in
its place while the eye is directed to another part of the white plane;
the same spectrum will be visible there too, for it arises from an
image which now belongs to the eye.
50.
In order at once to see what colour will be evoked by this contrast,
the chromatic circle[1] may be referred to. The colours are here
arranged in a general way according to the natural order, and the
arrangement will be found to be directly applicable in the present
case; for the colours diametrically opposed to each other in this
diagram are those which reciprocally evoke each other in the eye. Thus,
yellow demands purple; orange, blue; red, green; and vice versâ: thus
again all intermediate gradations reciprocally evoke each other; the
simpler colour demanding the compound, and vice versâ.—Note C.
51.
The cases here under consideration occur oftener than we are aware in
ordinary life; indeed,[Pg 22] an attentive observer sees these appearances
everywhere, while, on the other hand, the uninstructed, like our
predecessors, consider them as temporary visual defects, sometimes
even as symptoms of disorders in the eye, thus exciting serious
apprehensions. A few remarkable instances may here be inserted.
52.
I had entered an inn towards evening, and, as a well-favoured girl,
with a brilliantly fair complexion, black hair, and a scarlet bodice,
came into the room, I looked attentively at her as she stood before me
at some distance in half shadow. As she presently afterwards turned
away, I saw on the white wall, which was now before me, a black face
surrounded with a bright light, while the dress of the perfectly
distinct figure appeared of a beautiful sea-green.
53.
Among the materials for optical experiments, there are portraits with
colours and shadows exactly opposite to the appearance of nature. The
spectator, after having looked at one of these for a time, will see the
visionary figure tolerably true to nature. This is conformable to the
same principles, and consistent with experience, for, in the former
instance, a negress with a white head-dress would have given me a
white face surrounded with black. In the case[Pg 23] of the painted figures,
however, which are commonly small, the parts are not distinguishable by
every one in the after-image.
54.
A phenomenon which has before excited attention among the observers of
nature is to be attributed, I am persuaded, to the same cause.
It has been stated that certain flowers, towards evening in summer,
coruscate, become phosphorescent, or emit a momentary light. Some
persons have described their observation of this minutely. I had often
endeavoured to witness it myself, and had even resorted to artificial
contrivances to produce it.
On the 19th of June, 1799, late in the evening, when the twilight was
deepening into a clear night, as I was walking up and down the garden
with a friend, we very distinctly observed a flame-like appearance
near the oriental poppy, the flowers of which are remarkable for their
powerful red colour. We approached the place and looked attentively
at the flowers, but could perceive nothing further, till at last, by
passing and repassing repeatedly, while we looked sideways on them, we
succeeded in renewing the appearance as often as we pleased. It proved
to be a physiological phenomenon, such as others we have described, and
the apparent[Pg 24] coruscation was nothing but the spectrum of the flower in
the compensatory blue-green colour.
In looking directly at a flower the image is not produced, but it
appears immediately as the direction of the eye is altered. Again, by
looking sideways on the object, a double image is seen for a moment,
for the spectrum then appears near and on the real object.
The twilight accounts for the eye being in a perfect state of repose,
and thus very susceptible, and the colour of the poppy is sufficiently
powerful in the summer twilight of the longest days to act with
full effect and produce a compensatory image. I have no doubt these
appearances might be reduced to experiment, and the same effect
produced by pieces of coloured paper. Those who wish to take the most
effectual means for observing the appearance in nature—suppose in a
garden—should fix the eyes on the bright flowers selected for the
purpose, and, immediately after, look on the gravel path. This will
be seen studded with spots of the opposite colour. The experiment is
practicable on a cloudy day, and even in the brightest sunshine, for
the sun-light, by enhancing the brilliancy of the flower, renders it
fit to produce the compensatory colour sufficiently distinct to be
perceptible even in a bright light. Thus, peonies produce beautiful
green, marigolds vivid blue spectra.
[Pg 25]
55.
As the opposite colour is produced by a constant law in experiments
with coloured objects on portions of the retina, so the same effect
takes place when the whole retina is impressed with a single colour. We
may convince ourselves of this by means of coloured glasses. If we look
long through a blue pane of glass, everything will afterwards appear
in sunshine to the naked eye, even if the sky is grey and the scene
colourless. In like manner, in taking off green spectacles, we see all
objects in a red light. Every decided colour does a certain violence to
the eye, and forces the organ to opposition.
56.
We have hitherto seen the opposite colours producing each other
successively on the retina: it now remains to show by experiment
that the same effects can exist simultaneously. If a coloured object
impinges on one part of the retina, the remaining portion at the same
moment has a tendency to produce the compensatory colour. To pursue
a former experiment, if we look on a yellow piece of paper placed
on a white surface, the remaining part of the organ has already a
tendency to produce a purple hue on the colourless surface: in this
case the small portion of yellow is not powerful enough to produce[Pg 26]
this appearance distinctly, but, if a white paper is placed on a yellow
wall, we shall see the white tinged with a purple hue.
57.
Although this experiment may be made with any colours, yet red and
green are particularly recommended for it, because these colours seem
powerfully to evoke each other. Numerous instances occur in daily
experience. If a green paper is seen through striped or flowered
muslin, the stripes or flowers will appear reddish. A grey building
seen through green pallisades appears in like manner reddish. A
modification of this tint in the agitated sea is also a compensatory
colour: the light side of the waves appears green in its own colour,
and the shadowed side is tinged with the opposite hue. The different
direction of the waves with reference to the eye produces the same
effect. Objects seen through an opening in a red or green curtain
appear to wear the opposite hue. These appearances will present
themselves to the attentive observer on all occasions, even to an
unpleasant degree.
58.
Having made ourselves acquainted with the simultaneous exhibition of
these effects in direct cases, we shall find that we can also observe
them by indirect means. If we place a piece of[Pg 27] paper of a bright
orange colour on the white surface, we shall, after looking intently
at it, scarcely perceive the compensatory colour on the rest of the
surface: but when we take the orange paper away, and when the blue
spectrum appears in its place, immediately as this spectrum becomes
fully apparent, the rest of the surface will be overspread, as if by a
flash, with a reddish-yellow light, thus exhibiting to the spectator
in a lively manner the productive energy of the organ, in constant
conformity with the same law.
59.
As the compensatory colours easily appear, where they do not exist in
nature, near and after the original opposite ones, so they are rendered
more intense where they happen to mix with a similar real hue. In a
court which was paved with grey limestone flags, between which grass
had grown, the grass appeared of an extremely beautiful green when
the evening clouds threw a scarcely perceptible reddish light on the
pavement. In an opposite case we find, in walking through meadows,
where we see scarcely anything but green, the stems of trees and the
roads often gleam with a reddish hue. This tone is not uncommon in
the works of landscape painters, especially those who practice in
water-colours: they probably see it in[Pg 28] nature, and thus, unconsciously
imitating it, their colouring is criticised as unnatural.
60.
These phenomena are of the greatest importance, since they direct our
attention to the laws of vision, and are a necessary preparation for
future observations on colours. They show that the eye especially
demands completeness, and seeks to eke out the colorific circle in
itself. The purple or violet colour suggested by yellow contains red
and blue; orange, which responds to blue, is composed of yellow and
red; green, uniting blue and yellow, demands red; and so through all
gradations of the most complicated combinations. That we are compelled
in this case to assume three leading colours has been already remarked
by other observers.
61.
When in this completeness the elements of which it is composed are
still appreciable by the eye, the result is justly called harmony. We
shall subsequently endeavour to show how the theory of the harmony of
colours may be deduced from these phenomena, and how, simply through
these qualities, colours may be capable of being applied to æsthetic
purposes. This will be shown when we have gone through the whole circle
of our observations, returning to the point from which we started.
COLOURED SHADOWS.
62.
Before, however, we proceed further, we have yet to observe some very
remarkable cases of the vivacity with which the suggested colours
appear in the neighbourhood of others: we allude to coloured shadows.
To arrive at these we first turn our attention to shadows that are
colourless or negative.
63.
A shadow cast by the sun, in its full brightness, on a white surface,
gives us no impression of colour; it appears black, or, if a contrary
light (here assumed to differ only in degree) can act upon it, it is
only weaker, half-lighted, grey.
64.
Two conditions are necessary for the existence of coloured shadows:
first, that the principal light tinge the white surface with some hue;
secondly, that a contrary light illumine to a certain extent the cast
shadow.
65.
Let a short, lighted candle be placed at twilight on a sheet of white
paper. Between it and the declining daylight let a pencil be placed[Pg 30]
upright, so that its shadow thrown by the candle may be lighted, but
not overcome, by the weak daylight: the shadow will appear of the most
beautiful blue.
66.
That this shadow is blue is immediately evident; but we can only
persuade ourselves by some attention that the white paper acts as a
reddish yellow, by means of which the complemental blue is excited in
the eye.—Note D.
67.
In all coloured shadows, therefore, we must presuppose a colour excited
or suggested by the hue of the surface on which the shadow is thrown.
This may be easily found to be the case by attentive consideration, but
we may convince ourselves at once by the following experiment.
68.
Place two candles at night opposite each other on a white surface; hold
a thin rod between them upright, so that two shadows be cast by it;
take a coloured glass and hold it before one of the lights, so that
the white paper appear coloured; at the same moment the shadow cast by
the coloured light and slightly illumined by the colourless one will
exhibit the complemental hue.
[Pg 31]
69.
An important consideration suggests itself here, to which we shall
frequently have occasion to return. Colour itself is a degree of
darkness σκιερόν; hence Kircher is perfectly right in calling it
lumen opacatum. As it is allied to shadow, so it combines readily
with it; it appears to us readily in and by means of shadow the
moment a suggesting cause presents itself. We could not refrain from
adverting at once to a fact which we propose to trace and develop
hereafter.—Note E.
70.
Select the moment in twilight when the light of the sky is still
powerful enough to cast a shadow which cannot be entirely effaced by
the light of a candle. The candle may be so placed that a double shadow
shall be visible, one from the candle towards the daylight, and another
from the daylight towards the candle. If the former is blue the latter
will appear orange-yellow: this orange-yellow is in fact, however, only
the yellow-red light of the candle diffused over the whole paper, and
which becomes visible in shadow.
71.
This is best exemplified by the former experiment with two candles and
coloured glasses.
[Pg 32]
The surprising readiness with which shadow assumes a colour will again
invite our attention in the further consideration of reflections and
elsewhere.
72.
Thus the phenomena of coloured shadows may be traced to their cause
without difficulty. Henceforth let any one who sees an instance of
the kind observe only with what hue the light surface on which they
are thrown is tinged. Nay, the colour of the shadow may be considered
as a chromatoscope of the illumined surface, for the spectator may
always assume the colour of the light to be the opposite of that of the
shadow, and by an attentive examination may ascertain this to be the
fact in every instance.
73.
These appearances have been a source of great perplexity to former
observers: for, as they were remarked chiefly in the open air, where
they commonly appeared blue, they were attributed to a certain inherent
blue or blue colouring quality in the air. The inquirer can, however,
convince himself, by the experiment with the candle in a room, that no
kind of blue light or reflection is necessary to produce the effect
in question. The experiment may be made on a cloudy day with white
curtains drawn[Pg 33] before the light, and in a room where no trace of blue
exists, and the blue shadow will be only so much the more beautiful.
74.
De Saussure, in the description of his ascent of Mont Blanc, says, "A
second remark, which may not be uninteresting, relates to the colour of
the shadows. These, notwithstanding the most attentive observation, we
never found dark blue, although this had been frequently the case in
the plain. On the contrary, in fifty-nine instances we saw them once
yellowish, six times pale bluish, eighteen times colourless or black,
and thirty-four times pale violet. Some natural philosophers suppose
that these colours arise from accidental vapours diffused in the air,
which communicate their own hues to the shadows; not that the colours
of the shadows are occasioned by the reflection of any given sky colour
or interposition of any given air colour: the above observations seem
to favour this opinion." The instances given by De Saussure may be now
explained and classed with analogous examples without difficulty.
At a great elevation the sky was generally free from vapours, the sun
shone in full force on the snow, so that it appeared perfectly white
to the eye: in this case they saw the shadows quite colourless. If the
air was charged with a[Pg 34] certain degree of vapour, in consequence of
which the light snow would assume a yellowish tone, the shadows were
violet-coloured, and this effect, it appears, occurred oftenest. They
saw also bluish shadows, but this happened less frequently; and that
the blue and violet were pale was owing to the surrounding brightness,
by which the strength of the shadows was mitigated. Once only they
saw the shadow yellowish: in this case, as we have already seen (70),
the shadow is cast by a colourless light, and slightly illumined by a
coloured one.
75.
In travelling over the Harz in winter, I happened to descend from the
Brocken towards evening; the wide slopes extending above and below me,
the heath, every insulated tree and projecting rock, and all masses of
both, were covered with snow or hoar-frost. The sun was sinking towards
the Oder ponds[1]. During the day, owing to the yellowish hue of the
snow, shadows tending to violet had already been observable; these
might now be pronounced to be decidedly blue, as the illumined parts
exhibited a yellow deepening to orange.
But as the sun at last was about to set, and its rays, greatly
mitigated by the thicker vapours,[Pg 35] began to diffuse a most beautiful
red colour over the whole scene around me, the shadow colour changed
to a green, in lightness to be compared to a sea-green, in beauty to
the green of the emerald. The appearance became more and more vivid:
one might have imagined oneself in a fairy world, for every object had
clothed itself in the two vivid and so beautifully harmonising colours,
till at last, as the sun went down, the magnificent spectacle was lost
in a grey twilight, and by degrees in a clear moon-and-starlight night.
76.
One of the most beautiful instances of coloured shadows may be
observed during the full moon. The candle-light and moon-light may be
contrived to be exactly equal in force; both shadows may be exhibited
with equal strength and clearness, so that both colours balance each
other perfectly. A white surface being placed opposite the full moon,
and the candle being placed a little on one side at a due distance,
an opaque body is held before the white plane, A double shadow will
then be seen: that cast by the moon and illumined by the candle-light
will be a powerful red-yellow; and contrariwise, that cast by the
candle and illumined by the moon will appear of the most beautiful
blue. The shadow, composed of the union of the two shadows, where[Pg 36]
they cross each other, is black. The yellow shadow (74) cannot perhaps
be exhibited in a more striking manner. The immediate vicinity of
the blue and the interposing black shadow make the appearance the
more agreeable. It will even be found, if the eye dwells long on
these colours, that they mutually evoke and enhance each other, the
increasing red in the one still producing its contrast, viz. a kind of
sea-green.
77.
We are here led to remark that in this, and in all cases, a moment or
two may perhaps be necessary to produce the complemental colour. The
retina must be first thoroughly impressed with the demanding hue before
the responding one can be distinctly observable.
78.
When divers are under water, and the sunlight shines into the
diving-bell, everything is seen in a red light (the cause of which
will be explained hereafter), while the shadows appear green. The very
same phenomenon which I observed on a high mountain (75) is presented
to others in the depths of the sea, and thus Nature throughout is in
harmony with herself.
79.
Some observations and experiments which equally illustrate what has
been stated with regard[Pg 37] to coloured objects and coloured shadows may
be here added. Let a white paper blind be fastened inside the window
on a winter evening; in this blind let there be an opening, through
which the snow of some neighbouring roof can be seen. Towards dusk let
a candle be brought into the room; the snow seen through the opening
will then appear perfectly blue, because the paper is tinged with warm
yellow by the candle-light. The snow seen through the aperture is here
equivalent to a shadow illumined by a contrary light (76), and may also
represent a grey disk on a coloured surface (56).
80.
Another very interesting experiment may conclude these examples. If we
take a piece of green glass of some thickness, and hold it so that the
window bars be reflected in it, they will appear double owing to the
thickness of the glass. The image which is reflected from the under
surface of the glass will be green; the image which is reflected from
the upper surface, and which should be colourless, will appear red.
The experiment may be very satisfactorily made by pouring water into
a vessel, the inner surface of which can act as a mirror; for both
reflections may first be seen colourless while the water is pure, and
then by tinging it, they will exhibit two opposite hues.
FAINT LIGHTS.
81.
Light, in its full force, appears purely white, and it gives this
impression also in its highest degree of dazzling splendour. Light,
which is not so powerful, can also, under various conditions, remain
colourless. Several naturalists and mathematicians have endeavoured to
measure its degrees—Lambert, Bouguer, Rumford.
82.
Yet an appearance of colour presently manifests itself in fainter
lights, for in their relation to absolute light they resemble the
coloured spectra of dazzling objects (39).
83.
A light of any kind becomes weaker, either when its own force, from
whatever cause, is diminished, or when the eye is so circumstanced or
placed, that it cannot be sufficiently impressed by the action of the
light. Those appearances which may be called objective, come under the
head of physical colours. We will only advert here to the transition
from white to red heat in glowing iron. We may also observe[Pg 39] that the
flames of lights at night appear redder in proportion to their distance
from the eye.—Note F.
84.
Candle-light at night acts as yellow when seen near; we can perceive
this by the effect it produces on other colours. At night a pale yellow
is hardly to be distinguished from white; blue approaches to green, and
rose-colour to orange.
85.
Candle-light at twilight acts powerfully as a yellow light: this
is best proved by the purple blue shadows which, under these
circumstances, are evoked by the eye.
86.
The retina may be so excited by a strong light that it cannot perceive
fainter lights (11): if it perceive these they appear coloured: hence
candle-light by day appears reddish, thus resembling, in its relation
to fuller light, the spectrum of a dazzling object; nay, if at night we
look long and intently on the flame of a light, it appears to increase
in redness.
87.
There are faint lights which, notwithstanding their moderate lustre,
give an impression of a[Pg 40] white, or, at the most, of a light yellow
appearance on the retina; such as the moon in its full splendour.
Rotten wood has even a kind of bluish light. All this will hereafter be
the subject of further remarks.
88.
If at night we place a light near a white or greyish wall so that the
surface be illumined from this central point to some extent, we find,
on observing the spreading light at some distance, that the boundary of
the illumined surface appears to be surrounded with a yellow circle,
which on the outside tends to red-yellow. We thus observe that when
light direct or reflected does not act in its full force, it gives an
impression of yellow, of reddish, and lastly even of red. Here we find
the transition to halos which we are accustomed to see in some mode or
other round luminous points.
SUBJECTIVE HALOS.
89.
Halos may be divided into subjective and objective. The latter will
be considered under the physical colours; the first only belong here.
These are distinguished from the objective[Pg 41] halos by the circumstance
of their vanishing when the point of light which produces them on the
retina is covered.
90.
We have before noticed the impression of a luminous object on the
retina, and seen that it appears larger: but the effect is not at
an end here, it is not confined to the impression of the image; an
expansive action also takes place, spreading from the centre.
91.
That a nimbus of this kind is produced round the luminous image in the
eye may be best seen in a dark room, if we look towards a moderately
large opening in the window-shutter. In this case the bright image is
surrounded by a circular misty light. I saw such a halo bounded by a
yellow and yellow-red circle on opening my eyes at dawn, on an occasion
when I passed several nights in a bed-carriage.
92.
Halos appear most vivid when the eye is susceptible from having been in
a state of repose. A dark background also heightens their appearance.
Both causes account for our seeing them so strong if a light is
presented to the eyes[Pg 42] on waking at night. These conditions were
combined when Descartes after sleeping, as he sat in a ship, remarked
such a vividly-coloured halo round the light.
93.
A light must shine moderately, not dazzle, in order to produce the
impression of a halo in the eye; at all events the halos of dazzling
lights cannot be observed. We see a splendour of this kind round the
image of the sun reflected from the surface of water.
94.
A halo of this description, attentively observed, is found to be
encircled towards its edge with a yellow border: but even here the
expansive action, before alluded to, is not at an end, but appears
still to extend in varied circles.
95.
Several cases seem to indicate a circular action of the retina, whether
owing to the round form of the eye itself and its different parts, or
to some other cause.
96.
If the eye is pressed only in a slight degree from the inner corner,
darker or lighter circles[Pg 43] appear. At night, even without pressure, we
can sometimes perceive a succession of such circles emerging from, or
spreading over, each other.
97.
We have already seen that a yellow border is apparent round the white
space illumined by a light placed near it. This may be a kind of
objective halo. (88.)
98.
Subjective halos may be considered as the result of a conflict between
the light and a living surface. From the conflict between the exciting
principle and the excited, an undulating motion arises, which may be
illustrated by a comparison with the circles on water. The stone thrown
in drives the water in all directions; the effect attains a maximum,
it reacts, and being opposed, continues under the surface. The effect
goes on, culminates again, and thus the circles are repeated. If we
have ever remarked the concentric rings which appear in a glass of
water on trying to produce a tone by rubbing the edge; if we call to
mind the intermitting pulsations in the reverberations of bells, we
shall approach a conception of what may take place on the retina when
the image of a luminous object impinges on it, not to mention[Pg 44] that as
a living and elastic structure, it has already a circular principle in
its organisation.—Note G.
99.
The bright circular space which appears round the shining object
is yellow, ending in red: then follows a greenish circle, which is
terminated by a red border. This appears to be the usual phenomenon
where the luminous body is somewhat considerable in size. These halos
become greater the more distant we are from the luminous object.
100.
Halos may, however, appear extremely small and numerous when the
impinging image is minute, yet powerful, in its effect. The experiment
is best made with a piece of gold-leaf placed on the ground and
illumined by the sun. In these cases the halos appear in variegated
rays. The iridescent appearance produced in the eye when the sun
pierces through the leaves of trees seems also to belong to the same
class of phenomena.
[Pg 45]
APPENDIX.
101.
We are now sufficiently acquainted with the physiological colours to
distinguish them from the pathological. We know what appearances belong
to the eye in a healthy state, and are necessary to enable the organ to
exert its complete vitality and activity.
102.
Morbid phenomena indicate in like manner the existence of organic
and physical laws: for if a living being deviates from those rules
with reference to which it is constructed, it still seeks to agree
with the general vitality of nature in conformity with general laws,
and throughout its whole course still proves the constancy of those
principles on which the universe has existed, and by which it is held
together.
103.
We will here first advert to a very remarkable state in which the
vision of many persons is found to be. As it presents a deviation
from the ordinary mode of seeing colours, it might be fairly classed
under morbid impressions; but as it is consistent in itself, as it
often occurs,[Pg 46] may extend to several members of a family, and probably
does not admit of cure, we may consider it as bordering only on the
nosological cases, and therefore place it first.
104.
I was acquainted with two individuals not more than twenty years of
age, who were thus affected: both had bluish-grey eyes, an acute sight
for near and distant objects, by day-light and candle-light, and their
mode of seeing colours was in the main quite similar.
105.
They agreed with the rest of the world in denominating white, black,
and grey in the usual manner. Both saw white untinged with any hue. One
saw a somewhat brownish appearance in black, and in grey a somewhat
reddish tinge. In general they appeared to have a very delicate
perception of the gradations of light and dark.
106.
They appeared to see yellow, red-yellow, and yellow-red,[1] like
others: in the last case they said they saw the yellow passing as it
were over the red as if glazed: some thickly-ground carmine, which had
dried in a saucer, they called red.
[Pg 47]
107.
But now a striking difference presented itself. If the carmine was
passed thinly over the white saucer, they would compare the light
colour thus produced to the colour of the sky, and call it blue. If
a rose was shown them beside it, they would, in like manner, call it
blue; and in all the trials which were made, it appeared that they
could not distinguish light blue from rose-colour. They confounded
rose-colour, blue, and violet on all occasions: these colours only
appeared to them to be distinguished from each other by delicate shades
of lighter, darker, intenser, or fainter appearance.
108.
Again they could not distinguish green from dark orange, nor, more
especially, from a red brown.
109.
If any one, accidentally conversing with these individuals, happened
to question them about surrounding objects, their answers occasioned
the greatest perplexity, and the interrogator began to fancy his own
wits were out of order. With some method we may, however, approach to a
nearer knowledge of the law of this deviation from the general law.
[Pg 48]
110.
These persons, as may be gathered from what has been stated, saw fewer
colours than other people: hence arose the confusion of different
colours. They called the sky rose-colour, and the rose blue, or
vice versâ. The question now is: did they see both blue or both
rose-colour? did they see green orange, or orange green?
111.
This singular enigma appears to solve itself, if we assume that they
saw no blue, but, instead of it, a light pure red, a rose-colour.
We can comprehend what would be the result of this by means of the
chromatic diagram.
112.
If we take away blue from the chromatic circle we shall miss violet and
green as well. Pure red occupies the place of blue and violet, and in
again mixing with yellow the red produces orange where green should be.
113.
Professing to be satisfied with this mode of explanation, we have named
this remarkable deviation from ordinary vision "Acyanoblepsia."[2]
We have prepared some coloured figures for[Pg 49] its further elucidation,
and in explaining these we shall add some further details. Among the
examples will be found a landscape, coloured in the mode in which the
individuals alluded to appeared to see nature: the sky rose-colour, and
all that should be green varying from yellow to brown red, nearly as
foliage appears to us in autumn[3].—Note H.
114.
We now proceed to speak of morbid and other extraordinary affections
of the retina, by which the eye may be susceptible of an appearance
of light without external light, reserving for a future occasion the
consideration of galvanic light.
115.
If the eye receives a blow, sparks seem to spread from it. In some
states of body, again, when the blood is heated, and the system much
excited, if the eye is pressed first gently, and then more and more
strongly, a dazzling and intolerable light may be excited.
116.
If those who have been recently couched experience pain and heat in the
eye, they frequently[Pg 50] see fiery flashes and sparks: these symptoms last
sometimes for a week or fortnight, or till the pain and heat diminish.
117.
A person suffering from ear-ache saw sparks and balls of light in the
eye during each attack, as long as the pain lasted.
118.
Persons suffering from worms often experience extraordinary appearances
in the eye, sometimes sparks of fire, sometimes spectres of light,
sometimes frightful figures, which they cannot by an effort of the will
cease to see: sometimes these appearances are double.
119.
Hypochondriacs frequently see dark objects, such as threads, hairs,
spiders, flies, wasps. These appearances also exhibit themselves in the
incipient hard cataract. Many see semi-transparent small tubes, forms
like wings of insects, bubbles of water of various sizes, which fall
slowly down, if the eye is raised: sometimes these congregate together
so as to resemble the spawn of frogs; sometimes they appear as complete
spheres, sometimes in the form of lenses.
120.
As light appeared, in the former instances,[Pg 51] without external light,
so also these images appear without corresponding external objects.
The images are sometimes transient, sometimes they last during
the patient's life. Colour, again, frequently accompanies these
impressions: for hypochondriacs often see yellow-red stripes in the
eye: these are generally more vivid and numerous in the morning, or
when lasting.
121.
We have before seen that the impression of any object may remain for a
time in the eye: this we have found to be a physiological phenomenon
(23): the excessive duration of such an impression, on the other band,
may be considered as morbid.
122.
The weaker the organ the longer the impression of the image lasts.
The retina does not so soon recover itself; and the effect may be
considered as a kind of paralysis (28).
123.
This is not to be wondered at in the case of dazzling lights. If any
one looks at the sun, he may retain the image in his eyes for several
days. Boyle relates an instance of ten years.
124.
The same takes place, in a certain degree, with[Pg 52] regard to objects
that are not dazzling. Büsch relates of himself that the image of an
engraving, complete in all its parts, was impressed on his eye for
seventeen minutes.
125.
A person inclined to fulness of blood retained the image of a bright
red calico, with white spots, many minutes in the eye, and saw it float
before everything like a veil. It only disappeared by rubbing the eye
for some time.
126.
Scherfer observes that the red colour, which is the consequence of a
powerful impression of light, may last for some hours.
127.
As we can produce an appearance of light on the retina by pressure
on the eyeball, so by a gentle pressure a red colour appears, thus
corresponding with the after-image of an impression of light.
128.
Many sick persons, on awaking, see everything in the colour of the
morning sky, as if through a red veil: so, if in the evening they doze
and wake again, the same appearance presents itself. It remains for
some minutes, and[Pg 53] always disappears if the eye is rubbed a little. Red
stars and balls sometimes accompany the impression. This state may last
for a considerable time.
129.
The aëronauts, particularly Zambeccari and his companions, relate
that they saw the moon blood-red at the highest elevation. As they
had ascended above the vapours of the earth, through which we see the
moon and sun naturally of such a colour, it may be suspected that this
appearance may be classed with the pathological colours. The senses,
namely, may be so influenced by an unusual state, that the whole
nervous system, and particularly the retina, may sink into a kind of
inertness and inexcitability. Hence it is not impossible that the moon
might act as a very subdued light, and thus produce the impression of
the red colour. The sun even appeared blood-red to the aëronauts of
Hamburgh.
If those who are at some elevation in a balloon scarcely hear each
other speak, may not this, too, be attributed to the inexcitable state
of the nerves as well as to the thinness of the air?
130.
Objects are often seen by sick persons in variegated colours. Boyle
relates an instance[Pg 54] of a lady, who, after a fall by which an eye was
bruised, saw all objects, but especially white objects, glittering in
colours, even to an intolerable degree.
131.
Physicians give the name of "Chrupsia" to an affection of the sight,
occurring in typhoid maladies. In these cases the patients state that
they see the boundaries of objects coloured where light and dark meet.
A change probably takes place in the humours of the eye, through which
their achromatism is affected.
132.
In cases of milky cataract, a very turbid crystalline lens causes
the patient to see a red light. In a case of this kind, which was
treated by the application of electricity, the red light changed by
degrees to yellow, and at last to white, when the patient again began
to distinguish objects. These changes of themselves warranted the
conclusion that the turbid state of the lens was gradually approaching
the transparent state. We shall be enabled easily to trace this effect
to its source as soon as we become better acquainted with the physical
colours.
133.
If again it may be assumed that a jaundiced[Pg 55] patient sees through
an actually yellow-coloured humour, we are at once referred to the
department of chemical colours, and it is thus evident that we can only
thoroughly investigate the chapter of pathological colours when we
have made ourselves acquainted with the whole range of the remaining
phenomena. What has been adduced may therefore suffice for the present,
till we resume the further consideration of this portion of our subject.
134.
In conclusion we may, however, at once advert to some peculiar states
or dispositions of the organ.
There are painters who, instead of rendering the colours of nature,
diffuse a general tone, a warm or cold hue, over the picture. In some,
again, a predilection for certain colours displays itself; in others a
want of feeling for harmony.
135.
Lastly, it is also worthy of remark, that savage nations, uneducated
people, and children have a great predilection for vivid colours;
that animals are excited to rage by certain colours; that people of
refinement avoid vivid colours in their dress and the objects that are
about them, and seem inclined to banish them altogether from their
presence.—Note I.
PHYSICAL COLOURS.
136.
We give this designation to colours which are produced by certain
material mediums: these mediums, however, have no colour themselves,
and may be either transparent, semi-transparent yet transmitting light,
or altogether opaque. The colours in question are thus produced in the
eye through such external given causes, or are merely reflected to
the eye when by whatever means they are already produced without us.
Although we thus ascribe to them a certain objective character, their
distinctive quality still consists in their being transient, and not to
be arrested.
137.
They are called by former investigators colores apparentes, fluxi,
fugitivi, phantastici, falsi, variantes. They are also called
speciosi and emphatici, on account of their striking splendour.
They are immediately connected with the physiological colours, and
appear to have but little more reality: for, while in the production[Pg 57]
of the physiological colours the eye itself was chiefly efficient, and
we could only perceive the phenomena thus evoked within ourselves,
but not without us, we have now to consider the fact that colours are
produced in the eye by means of colourless objects; that we thus too
have a colourless surface before us which is acted upon as the retina
itself is, and that we can perceive the appearance produced upon it
without us. In such a process, however, every observation will convince
us that we have to do with colours in a progressive and mutable, but
not in a final or complete, state.
138.
Hence, in directing our attention to these physical colours, we find
it quite possible to place an objective phenomenon beside a subjective
one, and often by means of the union of the two successfully to
penetrate farther into the nature of the appearance.
139.
Thus, in the observations by which we become acquainted with the
physical colours, the eye is not to be considered as acting alone; nor
is the light ever to be considered in immediate relation with the eye:
but we direct our attention especially to the various effects produced
by mediums, those mediums being themselves colourless.
[Pg 58]
140.
Light under these circumstances may be affected by three conditions.
First, when it flashes back from the surface of a medium; in
considering which catoptrical experiments invite our attention.
Secondly, when it passes by the edge of a medium: the phenomena
thus produced were formerly called perioptical; we prefer the
term paroptical. Thirdly, when it passes through either a merely
light-transmitting or an actually transparent body; thus constituting
a class of appearances on which dioptrical experiments are founded.
We have called a fourth class of physical colours epoptical, as the
phenomena exhibit themselves on the colourless surface of bodies under
various conditions, without previous or actual dye (βαφή).—Note K.
141.
In examining these categories with reference to our three leading
divisions, according to which we consider the phenomena of colours in a
physiological, physical, or chemical view, we find that the catoptrical
colours are closely connected with the physiological; the paroptical
are already somewhat more distinct and independent; the dioptrical
exhibit themselves as entirely and strictly physical, and as having
a decidedly objective character; the epoptical, although still only
apparent, may be considered as the transition to the chemical colours.
[Pg 59]
142.
If we were desirous of prosecuting our investigation strictly in the
order of nature, we ought to proceed according to the classification
which has just been made; but in didactic treatises it is not of
so much consequence to connect as to duly distinguish the various
divisions of a subject, in order that at last, when every single
class and case has been presented to the mind, the whole may be
embraced in one comprehensive view. We therefore turn our attention
forthwith to the dioptrical class, in order at once to give the reader
the full impression of the physical colours, and to exhibit their
characteristics the more strikingly.
DIOPTRICAL COLOURS.
143.
Colours are called dioptrical when a colourless medium is necessary
to produce them; the medium must be such that light and darkness can
act through it either on the eye or on opposite surfaces. It is thus
required that the medium should be transparent, or at least capable, to
a certain degree, of transmitting light.
[Pg 60]
144.
According to these conditions we divide the dioptrical phenomena into
two classes, placing in the first those which are produced by means of
imperfectly transparent, yet light-transmitting mediums; and in the
second such as are exhibited when the medium is in the highest degree
transparent.
DIOPTRICAL COLOURS OF THE FIRST CLASS.
145.
Space, if we assume it to be empty, would have the quality of absolute
transparency to our vision. If this space is filled so that the eye
cannot perceive that it is so, there exists a more or less material
transparent medium, which may be of the nature of air and gas, may be
fluid or even solid.
146.
The pure and light-transmitting semi-transparent medium is only an
accumulated form of the transparent medium. It may therefore be
presented to us in three modes.
[Pg 61]
147.
The extreme degree of this accumulation is white; the simplest,
brightest, first, opaque occupation of space.
148.
Transparency itself, empirically considered, is already the first
degree of the opposite state. The intermediate degrees from this point
to opaque white are infinite.
149.
At whatever point short of opacity we arrest the thickening medium, it
exhibits simple and remarkable phenomena when placed in relation with
light and darkness.
150.
The highest degree of light, such as that of the sun, of phosphorus
burning in oxygen, is dazzling and colourless: so the light of the
fixed stars is for the most part colourless. This light, however, seen
through a medium but very slightly thickened, appears to us yellow.
If the density of such a medium be increased, or if its volume become
greater, we shall see the light gradually assume a yellow-red hue,
which at last deepens to a ruby-colour.—Note L.
[Pg 62]
151.
If on the other hand darkness is seen through a semi-transparent
medium, which is itself illumined by a light striking on it, a blue
colour appears: this becomes lighter and paler as the density of the
medium is increased, but on the contrary appears darker and deeper the
more transparent the medium becomes: in the least degree of dimness
short of absolute transparence, always supposing a perfectly colourless
medium, this deep blue approaches the most beautiful violet.
152.
If this effect takes place in the eye as here described, and may
thus be pronounced to be subjective, it remains further to convince
ourselves of this by objective phenomena. For a light thus mitigated
and subdued illumines all objects in like manner with a yellow,
yellow-red, or red hue; and, although the effect of darkness through
the non-transparent medium does not exhibit itself so powerfully, yet
the blue sky displays itself in the camera obscura very distinctly on
white paper, as well as every other material colour.
153.
In examining the cases in which this important[Pg 63] leading phenomenon
appears, we naturally mention the atmospheric colours first: most of
these may be here introduced in order.
154.
The sun seen through a certain degree of vapour appears with a yellow
disk; the centre is often dazzlingly yellow when the edges are already
red. The orb seen through a thick yellow mist appears ruby-red (as was
the case in 1794, even in the north); the same appearance is still
more decided, owing to the state of the atmosphere, when the scirocco
prevails in southern climates: the clouds generally surrounding the sun
in the latter case are of the same colour, which is reflected again on
all objects.
The red hues of morning and evening are owing to the same cause. The
sun is announced by a red light, in shining through a greater mass
of vapours. The higher he rises, the yellower and brighter the light
becomes.
155.
If the darkness of infinite space is seen through atmospheric vapours
illumined by the day-light, the blue colour appears. On high mountains
the sky appears by day intensely blue, owing to the few thin vapours
that float before the endless dark space: as soon as we descend in the[Pg 64]
valleys, the blue becomes lighter; till at last, in certain regions,
and in consequence of increasing vapours, it altogether changes to a
very pale blue.
156.
The mountains, in like manner, appear to us blue; for, as we see them
at so great a distance that we no longer distinguish the local tints,
and as no light reflected from their surface acts on our vision, they
are equivalent to mere dark objects, which, owing to the interposed
vapours, appear blue.
157.
So we find the shadowed parts of nearer objects are blue when the air
is charged with thin vapours.
158.
The snow-mountains, on the other hand, at a great distance, still
appear white, or approaching to a yellowish hue, because they act on
our eyes as brightness seen through atmospheric vapour.
159.
The blue appearance at the lower part of the flame of a candle belongs
to the same class of phenomena. If the flame be held before a white
ground, no blue will be seen, but this colour will immediately appear
if the flame is opposed[Pg 65] to a black ground. This phenomenon may be
exhibited most strikingly with a spoonful of lighted spirits of wine.
We may thus consider the lower part of the flame as equivalent to the
vapour which, although infinitely thin, is still apparent before the
dark surface; it is so thin, that one may easily see to read through
it: on the other hand, the point of the flame which conceals objects
from our sight is to be considered as a self-illuminating body.
160.
Lastly, smoke is also to be considered as a semi-transparent medium,
which appears to us yellow or reddish before a light ground, but blue
before a dark one.
161.
If we now turn our attention to fluid mediums, we find that water,
deprived in a very slight degree of its transparency, produces the same
effects.
162.
The infusion of the lignum nephriticum (guilandina Linnæi), which
formerly excited so much attention, is only a semi-transparent liquor,
which in dark wooden cups must appear blue, but held towards the sun in
a transparent glass must exhibit a yellow appearance.
[Pg 66]
163.
A drop of scented water, of spirit varnish, of several metallic
solutions, may be employed to give various degrees of opacity to water
for such experiments. Spirit of soap perhaps answers best.
164.
The bottom of the sea appears to divers of a red colour in bright
sunshine: in this case the water, owing to its depth, acts as a
semi-transparent medium. Under these circumstances, they find the
shadows green, which is the complemental colour.
165.
Among solid mediums the opal attracts our attention first: its colours
are, at least, partly to be explained by the circumstance that it is,
in fact, a semi-transparent medium, through which sometimes light,
sometimes dark, substrata are visible.
166.
For these experiments, however, the opal-glass (vitrum astroides,
girasole) is the most desirable material. It is prepared in various
ways, and its semi-opacity is produced by metallic oxydes. The same
effect is produced also by melting pulverised and calcined bones
together[Pg 67] with the glass, on which account it is also known by the name
of beinglas; but, prepared in this mode, it easily becomes too opaque.
167.
This glass may be adapted for experiments in various ways: it may
either be made in a very slight degree non-transparent, in which case
the light seen through various layers placed one upon the other may
be deepened from the lightest yellow to the deepest red, or, if made
originally more opaque, it may be employed in thinner or thicker
laminæ. The experiments may be successfully made in both ways: in
order, however, to see the bright blue colour, the glass should neither
be too opaque nor too thick. For, as it is quite natural that darkness
must act weakly through the semi-transparent medium, so this medium, if
too thick, soon approaches whiteness.
168.
Panes of glass throw a yellow light on objects through those parts
where they happen to be semi-opaque, and these same parts appear blue
if we look at a dark object through them.
169.
Smoked glass may be also mentioned here, and is, in like manner, to be
considered as a semi-opaque medium. It exhibits the sun more[Pg 68] or less
ruby-coloured; and, although this appearance may be attributed to the
black-brown colour of the soot, we may still convince ourselves that a
semi-transparent medium here acts if we hold such a glass moderately
smoked, and lit by the sun on the unsmoked side, before a dark object,
for we shall then perceive a bluish appearance.
170.
A striking experiment may be made in a dark room with sheets of
parchment. If we fasten a piece of parchment before the opening in the
window-shutter when the sun shines, it will appear nearly white; by
adding a second, a yellowish colour appears, which still increases as
more leaves are added, till at last it changes to red.
171.
A similar effect, owing to the state of the crystalline lens in milky
cataract, has been already adverted to (131).
172.
Having now, in tracing these phenomena, arrived at the effect of a
degree of opacity scarcely capable of transmitting light, we may here
mention a singular appearance which was owing to a momentary state of
this kind.
[Pg 69]
A portrait of a celebrated theologian had been painted some years
before the circumstance to which we allude, by an artist who was known
to have considerable skill in the management of his materials. The
very reverend individual was represented in a rich velvet dress, which
was not a little admired, and which attracted the eye of the spectator
almost more than the face. The picture, however, from the effect of the
smoke of lamps and dust, had lost much of its original vivacity. It
was, therefore, placed in the hands of a painter, who was to clean it,
and give it a fresh coat of varnish. This person began his operations
by carefully washing the picture with a sponge: no sooner, however,
had he gone over the surface once or twice, and wiped away the first
dirt, than to his amazement the black velvet dress changed suddenly to
a light blue plush, which gave the ecclesiastic a very secular, though
somewhat old-fashioned, appearance. The painter did not venture to go
on with his washing: he could not comprehend how a light blue should be
the ground of the deepest black, still less how he could so suddenly
have removed a glazing colour capable of converting the one tint to the
other.
At all events, he was not a little disconcerted at having spoilt the
picture to such an extent. Nothing to characterize the ecclesiastic
remained[Pg 70] but the richly-curled round wig, which made the exchange
of a faded plush for a handsome new velvet dress far from desirable.
Meanwhile, the mischief appeared irreparable, and the good artist,
having turned the picture to the wall, retired to rest with a mind ill
at ease. But what was his joy the next morning, when, on examining the
picture, he beheld the black velvet dress again in its full splendour.
He could not refrain from again wetting a corner, upon which the blue
colour again appeared, and after a time vanished. On hearing of this
phenomenon, I went at once to see the miraculous picture. A wet sponge
was passed over it in my presence, and the change quickly took place. I
saw a somewhat faded, but decidedly light blue plush dress, the folds
under the arm being indicated by some brown strokes.
I explained this appearance to myself by the doctrine of the
semi-opaque medium. The painter, in order to give additional depth
to his black, may have passed some particular varnish over it: on
being washed, this varnish imbibed some moisture, and hence became
semi-opaque, in consequence of which the black underneath immediately
appeared blue. Perhaps those who are practically acquainted with the
effect of varnishes may, through accident or contrivance, arrive at
some means of exhibiting this singular appearance, as an experiment, to
those[Pg 71] who are fond of investigating natural phenomena. Notwithstanding
many attempts, I could not myself succeed in re-producing it.
173.
Having now traced the most splendid instances of atmospheric
appearances, as well as other less striking yet sufficiently remarkable
cases, to the leading examples of semi-transparent mediums, we have no
doubt that attentive observers of nature will carry such researches
further, and accustom themselves to trace and explain the various
appearances which present themselves in every-day experience on the
same principle: we may also hope that such investigators will provide
themselves with an adequate apparatus in order to place remarkable
facts before the eyes of others who may be desirous of information.
174.
We venture, once for all, to call the leading appearance in question,
as generally described in the foregoing pages, a primordial and
elementary phenomenon; and we may here be permitted at once to state
what we understand by the term.
175.
The circumstances which come under our notice in ordinary observation
are, for the most part, insulated cases, which, with some attention,
admit[Pg 72] of being classed under general leading facts. These again range
themselves under theoretical rubrics which are more comprehensive, and
through which we become better acquainted with certain indispensable
conditions of appearances in detail. From henceforth everything is
gradually arranged under higher rules and laws, which, however, are not
to be made intelligible by words and hypotheses to the understanding
merely, but, at the same time, by real phenomena to the senses. We
call these primordial phenomena, because nothing appreciable by the
senses lies beyond them, on the contrary, they are perfectly fit to be
considered as a fixed point to which we first ascended, step by step,
and from which we may, in like manner, descend to the commonest case
of every-day experience. Such an original phenomenon is that which has
lately engaged our attention. We see on the one side light, brightness;
on the other darkness, obscurity: we bring the semi-transparent medium
between the two, and from these contrasts and this medium the colours
develop themselves, contrasted, in like manner, but soon, through a
reciprocal relation, directly tending again to a point of union.[1]
[Pg 73]
176.
With this conviction we look upon the mistake that has been committed
in the investigation of this subject to be a very serious one, inasmuch
as a secondary phenomenon has been thus placed higher in order—the
primordial phenomenon has been degraded to an inferior place; nay, the
secondary phenomenon has been placed at the head, a compound effect has
been treated as simple, a simple appearance as compound: owing to this
contradiction, the most capricious complication and perplexity have
been introduced into physical inquiries, the effects of which are still
apparent.
177.
But when even such a primordial phenomenon is arrived at, the evil
still is that we refuse to recognise it as such, that we still aim at
something beyond, although it would become us to confess that we are
arrived at the limits of experimental knowledge. Let the observer of
nature suffer the primordial phenomenon to remain undisturbed in its
beauty; let the philosopher admit it into his department, and he will
find that important elementary facts are a worthier basis for further
operations than insulated cases, opinions, and hypotheses.—Note M.
[Pg 74]
XI.
DIOPTRICAL COLOURS OF THE SECOND CLASS.—REFRACTION.
178.
Dioptrical colours of both classes are closely connected, as will
presently appear on a little examination. Those of the first class
appeared through semi-transparent mediums, those of the second class
will now appear through transparent mediums. But since every substance,
however transparent, may be already considered to partake of the
opposite quality (as every accumulation of a medium called transparent
proves), so the near affinity of the two classes is sufficiently
manifest.
179.
We will, however, first consider transparent mediums abstractedly as
such, as entirely free from any degree of opacity, and direct our whole
attention to a phenomenon which here presents itself, and which is
known by the name of refraction.
180.
In treating of the physiological colours, we have already had occasion
to vindicate what[Pg 75] were formerly called illusions of sight, as
the active energies of the healthy and duly efficient eye (2), and we
are now again invited to consider similar instances confirming the
constancy of the laws of vision.
181.
Throughout nature, as presented to the senses, everything depends on
the relation which things bear to each other, but especially on the
relation which man, the most important of these, bears to the rest.
Hence the world divides itself into two parts, and the human being
as subject, stands opposed to the object. Thus the practical
man exhausts himself in the accumulation of facts, the thinker in
speculation; each being called upon to sustain a conflict which admits
of no peace and no decision.
182.
But still the main point always is, whether the relations are truly
seen. As our senses, if healthy, are the surest witnesses of external
relations, so we may be convinced that, in all instances where they
appear to contradict reality, they lay the greater and surer stress
on true relations. Thus a distant object appears to us smaller; and
precisely by this means we are aware of distance. We produced coloured
appearances on colourless objects, through colourless mediums, and at
the same moment our[Pg 76] attention was called to the degree of opacity in
the medium.
183.
Thus the different degrees of opacity in so-called transparent mediums,
nay, even other physical and chemical properties belonging to them,
are known to our vision by means of refraction, and invite us to make
further trials in order to penetrate more completely by physical and
chemical means into those secrets which are already opened to our view
on one side.
184.
Objects seen through mediums more or less transparent do not appear
to us in the place which they should occupy according to the laws of
perspective. On this fact the dioptrical colours of the second class
depend.
185.
Those laws of vision which admit of being expressed in mathematical
formulæ are based on the principle that, as light proceeds in straight
lines, it must be possible to draw a straight line from the eye to any
given object in order that it be seen. If, therefore, a case arises in
which the light arrives to us in a bent or broken line, that we see the
object by means of a bent or broken line, we are at once informed that
the[Pg 77] medium between the eye and the object is denser, or that it has
assumed this or that foreign nature.
186.
This deviation from the law of right-lined vision is known by the
general term of refraction; and, although we may take it for granted
that our readers are sufficiently acquainted with its effects, yet we
will here once more briefly exhibit it in its objective and subjective
point of view.
187.
Let the sun shine diagonally into an empty cubical vessel, so that
the opposite side be illumined, but not the bottom: let water be
then poured into this vessel, and the direction of the light will
be immediately altered; for a part of the bottom is shone upon. At
the point where the light enters the thicker medium it deviates from
its rectilinear direction, and appears broken: hence the phenomenon
is called the breaking (brechung) or refraction. Thus much of the
objective experiment.
188.
We arrive at the subjective fact in the following mode:—Let the eye
be substituted for the sun: let the sight be directed in like manner
[Pg 78] diagonally over one side, so that the opposite inner side be
entirely seen, while no part of the bottom is visible. On pouring in
water the eye will perceive a part of the bottom; and this takes place
without our being aware that we do not see in a straight line; for
the bottom appears to us raised, and hence we give the term elevation
(hebung) to the subjective phenomenon. Some points, which are
particularly remarkable with reference to this, will be adverted to
hereafter.
189.
Were we now to express this phenomenon generally, we might here repeat,
in conformity with the view lately taken, that the relation of the
objects is changed or deranged.
190.
But as it is our intention at present to separate the objective from
the subjective appearances, we first express the phenomenon in a
subjective form, and say,—a derangement or displacement of the object
seen, or to be seen, takes place.
191.
But that which is seen without a limiting outline may be thus affected
without our perceiving the change. On the other hand, if what we look
at has a visible termination, we have an evident indication that a
displacement occurs. If, therefore,[Pg 79] we wish to ascertain the
relation or degree of such a displacement, we must chiefly confine
ourselves to the alteration of surfaces with visible boundaries; in
other words, to the displacement of circumscribed objects.
192.
The general effect may take place through parallel mediums, for every
parallel medium displaces the object by bringing it perpendicularly
towards the eye. The apparent change of position is, however, more
observable through mediums that are not parallel.
193.
These latter may be perfectly spherical, or may be employed in the
form of convex or concave lenses. We shall make use of all these as
occasion may require in our experiments. But as they not only displace
the object from its position, but alter it in various ways, we shall,
in most cases, prefer employing mediums with surfaces, not, indeed,
parallel with reference to each other, but still altogether plane,
namely, prisms. These have a triangle for their base, and may, it is
true, be considered as portions of a lens, but they are particularly
available for our experiments, inasmuch as they very perceptibly
displace the object from its position, without producing a remarkable
distortion.
[Pg 80]
194.
And now, in order to conduct our observations with as much exactness
as possible, and to avoid all confusion and ambiguity, we confine
ourselves at first to
SUBJECTIVE EXPERIMENTS,
in which, namely, the object is seen by the observer through a
refracting medium. As soon as we have treated these in due series, the
objective experiments will follow in similar order.
REFRACTION WITHOUT THE APPEARANCE OF COLOUR.
195.
Refraction can visibly take place without our perceiving an appearance
of colour. To whatever extent a colourless or uniformly coloured
surface may be altered as to its position by refraction, no colour
consequent upon refraction appears within it, provided it has no
outline or boundary. We may convince ourselves of this in various ways.
[Pg 81]
196.
Place a glass cube on any larger surface, and look through the glass
perpendicularly or obliquely, the unbroken surface opposite the eye
appears altogether raised, but no colour exhibits itself. If we look at
a pure grey or blue sky or a uniformly white or coloured wall through a
prism, the portion of the surface which the eye thus embraces will be
altogether changed as to its position, without our therefore observing
the smallest appearance of colour.
CONDITIONS OF THE APPEARANCE OF COLOUR.
197.
Although in the foregoing experiments we have found all unbroken
surfaces, large or small, colourless, yet at the outlines or
boundaries, where the surface is relieved upon a darker or lighter
object, we observe a coloured appearance.
198.
Outline, as well as surface, is necessary to constitute a figure or
circumscribed object. We therefore express the leading fact thus:
circumscribed objects must be displaced by refraction in order to the
exhibition of an appearance of colour.
[Pg 82]
199.
We place before us the simplest object, a light disk on a dark ground
(A).[1] A displacement occurs with regard to this object, if we
apparently extend its outline from the centre by magnifying it. This
may be done with any convex glass, and in this case we see a blue edge
(B).
200.
We can, to appearance, contract the circumference of the same light
disk towards the centre by diminishing the object; the edge will then
appear yellow (C). This may be done with a concave glass, which,
however, should not be ground thin like common eye-glasses, but must
have some substance. In order, however, to make this experiment at once
with the convex glass, let a smaller black disk be inserted within
the light disk on a black ground. If we magnify the black disk on a
white ground with a convex glass, the same result takes place as if we
diminished the white disk; for we extend the black outline upon the
white, and we thus perceive the yellow edge together with the blue edge
(D).
201.
These two appearances, the blue and yellow, exhibit themselves in and
upon the white: they[Pg 83] both assume a reddish hue, in proportion as they
mingle with the black.[2]
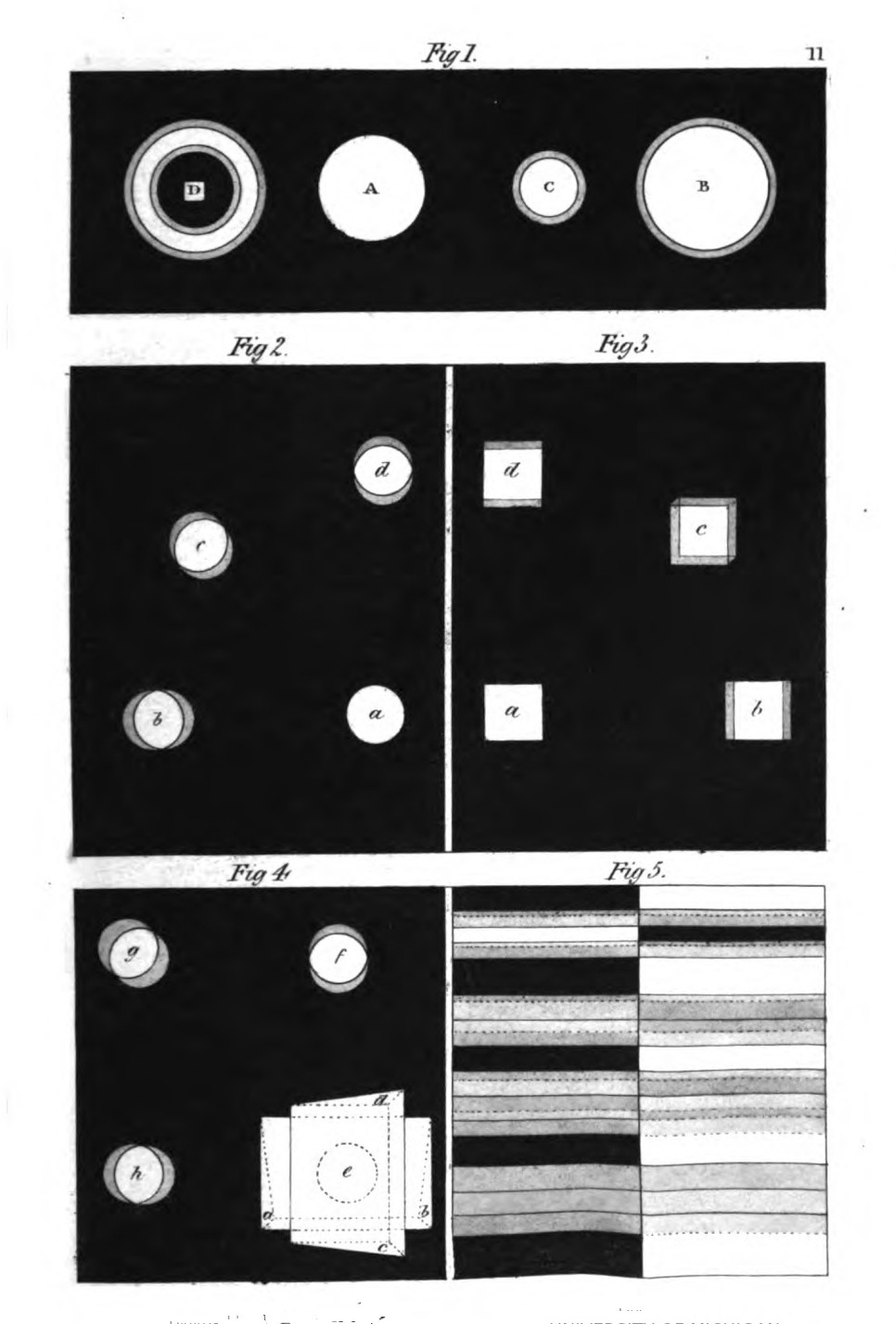
Plate 2.
202.
In this short statement we have described the primordial phenomena of
all appearance of colour occasioned by refraction. These undoubtedly
may be repeated, varied, and rendered more striking; may be combined,
complicated, confused; but, after all, may be still restored to their
original simplicity.
203.
In examining the process of the experiment just given, we find that
in the one case we have, to appearance, extended the white edge upon
the dark surface; in the other we have extended the dark edge upon
the white surface, supplanting one by the other, pushing one over
the other. We will now endeavour, step by step, to analyse these and
similar cases.
204.
If we cause the white disk to move, in appearance, entirely from its
place, which can be done[Pg 84] effectually by prisms, it will be coloured
according to the direction in which it apparently moves, in conformity
with the above laws. If we look at the disk a[3] through a prism,
so that it appear moved to b, the outer edge will appear blue and
blue-red, according to the law of the figure B (fig. 1), the other
edge being yellow, and yellow-red, according to the law of the figure
C (fig. 1). For in the first case the white figure is, as it were,
extended over the dark boundary, and in the other case the dark
boundary is passed over the white figure. The same happens if the disk
is, to appearance, moved from a to c, from a to d, and so
throughout the circle.
205.
As it is with the simple effect, so it is with more complicated
appearances. If we look through a horizontal prism (a b[4]) at a
white disk placed at some distance behind it at e, the disk will
be raised to f, and coloured according to the above law. If we
remove this prism, and look through a vertical one (c d) at the same
disk, it will appear at h, and coloured according to the same law.
If we place the two prisms one upon the other, the disk will appear
displaced diagonally, in conformity with a general law of nature, and
will be coloured as[Pg 85] before; that is, according to its movement in the
direction, e.g.:[5]
206.
If we attentively examine these opposite coloured edges, we find that
they only appear in the direction of the apparent change of place.
A round figure leaves us in some degree uncertain as to this: a
quadrangular figure removes all doubt.
207.
The quadrangular figure a,[6] moved in the direction a b or a d
exhibits no colour on the sides which are parallel with the direction
in which it moves: on the other hand, if moved in the direction a
c, parallel with its diagonal, all the edges of the figure appear
coloured.[7]
208.
Thus, a former position (203) is here confirmed; viz. to produce
colour, an object must be so displaced that the light edges be
apparently carried over a dark surface, the dark edges over a light
surface, the figure over its boundary, the boundary over the figure.
But[Pg 86] if the rectilinear boundaries of a figure could be indefinitely
extended by refraction, so that figure and background might only pursue
their course next, but not over each other, no colour would appear, not
even if they were prolonged to infinity.
CONDITIONS UNDER WHICH THE APPEARANCE OF COLOUR INCREASES.
209.
We have seen in the foregoing experiments that all appearance of colour
occasioned by refraction depends on the condition that the boundary or
edge be moved in upon the object itself, or the object itself over the
ground, that the figure should be, as it were, carried over itself, or
over the ground. And we shall now find that, by increased displacement
of the object, the appearance of colour exhibits itself in a greater
degree. This takes place in subjective experiments, to which, for the
present, we confine ourselves, under the following conditions.
210.
First, if, in looking through parallel mediums, the eye is directed
more obliquely.
Secondly, if the surfaces of the medium are no longer parallel, but
form a more or less acute angle.
[Pg 87]
Thirdly, owing to the increased proportion of the medium, whether
parallel mediums be increased in size, or whether the angle be
increased, provided it does not attain a right angle.
Fourthly, owing to the distance of the eye armed with a refracting
medium from the object to be displaced.
Fifthly, owing to a chemical property that may be communicated to the
glass, and which may be afterwards increased in effect.
211.
The greatest change of place, short of considerable distortion of the
object, is produced by means of prisms, and this is the reason why the
appearance of colour can be exhibited most powerfully through glasses
of this form. Yet we will not, in employing them, suffer ourselves to
be dazzled by the splendid appearances they exhibit, but keep the above
well-established, simple principles calmly in view.
212.
The colour which is outside, or foremost, in the apparent change of an
object by refraction, is always the broader, and we will henceforth
call this a border: the colour that remains next the outline is the
narrower, and this we will call an edge.
[Pg 88]
213.
If we move a dark boundary towards a light surface, the yellow broader
border is foremost, and the narrower yellow-red edge follows close to
the outline. If we move a light boundary towards a dark surface, the
broader violet border is foremost, and the narrower blue edge follows.
214.
If the object is large, its centre remains uncoloured. Its inner
surface is then to be considered as unlimited (195): it is displaced,
but not otherwise altered: but if the object is so narrow, that under
the above conditions the yellow border can reach the blue edge, the
space between the outlines will be entirely covered with colour. If we
make this experiment with a white stripe on a black ground,[1] the two
extremes will presently meet, and thus produce green. We shall then see
the following series of colours:—
Yellow-red.
Yellow.
Green.
Blue.
Blue-red.
215.
If we place a black band, or stripe, on white paper,[2] the violet
border will spread till it meets[Pg 89] the yellow-red edge. In this case the
intermediate black is effaced (as the intermediate white was in the
last experiment), and in its stead a splendid pure red will appear.[3]
The series of colours will now be as follows:—
Blue.
Blue-red.
Red.
Yellow-red.
Yellow.
216.
The yellow and blue, in the first case (214), can by degrees meet so
fully, that the two colours blend entirely in green, and the order will
then be,
Yellow-red.
Green.
Blue-red.
In the second case (215), under similar circumstances, we see only
Blue.
Red.
Yellow.
This appearance is best exhibited by refracting the bars of a window
when they are relieved on a grey sky.[4]
[Pg 90]
217.
In all this we are never to forget that this appearance is not to be
considered as a complete or final state, but always as a progressive,
increasing, and, in many senses, controllable appearance. Thus we
find that, by the negation of the above five conditions, it gradually
decreases, and at last disappears altogether.
EXPLANATION OF THE FOREGOING PHENOMENA.
218.
Before we proceed further, it is incumbent on us to explain the first
tolerably simple phenomenon, and to show its connexion with the
principles first laid down, in order that the observer of nature may
be enabled clearly to comprehend the more complicated appearances that
follow.
219.
In the first place, it is necessary to remember that we have to do
with circumscribed objects. In the act of seeing, generally, it is
the circumscribed visible which chiefly invites our observation; and
in the present instance, in speaking of the appearance of colour, as
occasioned by refraction, the circumscribed visible, the detached
object solely occupies our attention.
[Pg 91]
220.
For our chromatic exhibitions we can, however, divide objects generally
into primary and secondary. The expressions of themselves denote
what we understand by them, but our meaning will be rendered still more
plain by what follows.
221.
Primary objects may be considered firstly as original, as images
which are impressed on the eye by things before it, and which assure
us of their reality. To these the secondary images may be opposed
as derived images, which remain in the organ when the object
itself is taken away; those apparent after-images, which have been
circumstantially treated of in the doctrine of physiological colours.
222.
The primary images, again, may be considered as direct images, which,
like the original impressions, are conveyed immediately from the object
to the eye. In contradistinction to these, the secondary images may
be considered as indirect, being only conveyed to us, as it were,
at second-hand from a reflecting surface. These are the mirrored, or
catoptrical, images, which in certain cases can also become double
images:
223.
When, namely, the reflecting body is transparent,[Pg 92] and has two parallel
surfaces, one behind the other: in such a case, an image may be
reflected to the eye from both surfaces, and thus arise double images,
inasmuch as the upper image does not quite cover the under one: this
may take place in various ways.
Let a playing-card be held before a mirror. We shall at first see the
distinct image of the card, but the edge of the whole card, as well
as that of every spot upon it, will be bounded on one side with a
border, which is the beginning of the second reflection. This effect
varies in different mirrors, according to the different thickness of
the glass, and the accidents of polishing. If a person wearing a white
waistcoat, with the remaining part of his dress dark, stands before
certain mirrors, the border appears very distinctly, and in like manner
the metal buttons on dark cloth exhibit the double reflection very
evidently.
224.
The reader who has made himself acquainted with our former descriptions
of experiments (80) will the more readily follow the present statement.
The window-bars reflected by plates of glass appear double, and
by increased thickness of the glass, and a due adaptation of the
angle of reflection, the two reflections may be entirely separated
from each other. So a vase full of[Pg 93] water, with a plane mirror-like
bottom, reflects any object twice, the two reflections being more or
less separated under the same conditions. In these cases it is to be
observed that, where the two reflections cover each other, the perfect
vivid image is reflected, but where they are separated they exhibit
only weak, transparent, and shadowy images.
225.
If we wish to know which is the under and which the upper image, we
have only to take a coloured medium, for then a light object reflected
from the under surface is of the colour of the medium, while that
reflected from the upper surface presents the complemental colour. With
dark objects it is the reverse; hence black and white surfaces may be
here also conveniently employed. How easily the double images assume
and evoke colours will here again be striking.
226.
Thirdly, the primary images may be considered as principal images,
while the secondary can be, as it were, annexed to these as accessory
images. Such an accessory image produces a sort of double form; except
that it does not separate itself from the principal object, although it
may be said to be always endeavouring to do so. It is[Pg 94] with secondary
images of this last description that we have to do in prismatic
appearances.
227.
A surface without a boundary exhibits no appearance of colour when
refracted (195). Whatever is seen must be circumscribed by an
outline to produce this effect. In other words a figure, an object,
is required; this object undergoes an apparent change of place by
refraction: the change is however not complete, not clean, not sharp;
but incomplete, inasmuch as an accessory image only is produced.
228.
In examining every appearance of nature, but especially in examining
an important and striking one, we should not remain in one spot, we
should not confine ourselves to the insulated fact, nor dwell on it
exclusively, but look round through all nature to see where something
similar, something that has affinity to it, appears: for it is only by
combining analogies that we gradually arrive at a whole which speaks
for itself, and requires no further explanation.
229.
Thus we here call to mind that in certain cases refraction
unquestionably produces double images, as is the case in Iceland spar:
similar[Pg 95] double images are also apparent in cases of refraction through
large rock crystals, and in other instances; phenomena which have not
hitherto been sufficiently observed.[1]
230.
But since in the case under consideration (227) the question relates
not to double but to accessory images, we refer to a phenomenon already
adverted to, but not yet thoroughly investigated. We allude to an
earlier experiment, in which it appeared that a sort of conflict took
place in regard to the retina between a light object and its dark
ground, and between a dark object and its light ground (16). The light
object in this case appeared larger, the dark one smaller.
231.
By a more exact observation of this phenomenon we may remark that the
forms are not sharply distinguished from the ground, but that they
appear with a kind of grey, in some degree, coloured edge; in short,
with an accessory image. If, then, objects seen only with the naked
eye produce such effects, what may not take place when a dense medium
is interposed? It is not that alone which presents itself to us[Pg 96] in
obvious operation which produces and suffers effects, but likewise all
principles that have a mutual relation only of some sort are efficient
accordingly, and indeed often in a very high degree.
232.
Thus when refraction produces its effect on an object there appears an
accessory image next the object itself: the real form thus refracted
seems even to linger behind, as if resisting the change of place; but
the accessory image seems to advance, and extends itself more or less
in the mode already shown (212-216).
233.
We also remarked (224) that in double images the fainter appear only
half substantial, having a kind of transparent, evanescent character,
just as the fainter shades of double shadows must always appear as
half-shadows. These latter assume colours easily, and produce them
readily (69), the former also (80); and the same takes place in the
instance of accessory images, which, it is true, do not altogether
quit the real object, but still advance or extend from it as
half-substantial images, and hence can appear coloured so quickly and
so powerfully.
234.
That the prismatic appearance is in fact an[Pg 97] accessory image we may
convince ourselves in more than one mode. It corresponds exactly with
the form of the object itself. Whether the object be bounded by a
straight line or a curve, indented or waving, the form of the accessory
image corresponds throughout exactly with the form of the object.[2]
235.
Again, not only the form but other qualities of the object are
communicated to the accessory image. If the object is sharply relieved
from its ground, like white on black, the coloured accessory image in
like manner appears in its greatest force. It is vivid, distinct, and
powerful; but it is most especially powerful when a luminous object is
shown on a dark ground, which may be contrived in various ways.
236.
But if the object is but faintly distinguished from the ground, like
grey objects on black or white, or even on each other, the accessory
image is also faint, and, when the original difference of tint or force
is slight, becomes hardly discernible.
[Pg 98]
237.
The appearances which are observable when coloured objects are relieved
on light, dark, or coloured grounds are, moreover, well worthy of
attention. In this case a union takes place between the apparent colour
of the accessory image and the real colour of the object; a compound
colour is the result, which is either assisted and enhanced by the
accordance, or neutralised by the opposition of its ingredients.
238.
But the common and general characteristic both of the double and
accessory image is semi-transparence. The tendency of a transparent
medium to become only half transparent, or merely light-transmitting,
has been before adverted to (147, 148). Let the reader assume that he
sees within or through such a medium a visionary image, and he will at
once pronounce this latter to be a semi-transparent image.
239.
Thus the colours produced by refraction may be fitly explained by the
doctrine of the semi-transparent mediums. For where dark passes over
light, as the border of the semi-transparent accessory image advances,
yellow appears; and, on the other hand, where a light outline passes
over the dark background, blue appears (150, 151).
[Pg 99]
240.
The advancing foremost colour is always the broader. Thus the yellow
spreads over the light with a broad border, but the yellow-red appears
as a narrower stripe and is next the dark, according to the doctrine of
augmentation, as an effect of shade.[3]
241.
On the opposite side the condensed blue is next the edge, while the
advancing border, spreading as a thinner veil over the black, produces
the violet colour, precisely on the principles before explained in
treating of semi-transparent mediums, principles which will hereafter
be found equally efficient in many other cases.
242.
Since an analysis like the present requires to be confirmed by ocular
demonstration, we beg every reader to make himself acquainted with the
experiments hitherto adduced, not in a superficial manner, but fairly
and thoroughly. We have not placed arbitrary signs before him instead
of the appearances themselves; no modes of expression are here proposed
for his[Pg 100] adoption which may be repeated for ever without the exercise
of thought and without leading any one to think; but we invite him to
examine intelligible appearances, which must be present to the eye and
mind, in order to enable him clearly to trace these appearances to
their origin, and to explain them to himself and to others.
DECREASE OF THE APPEARANCE OF COLOUR.
243.
We need only take the five conditions (210) under which the appearance
of colour increases in the contrary order, to produce the contrary or
decreasing state; it may be as well, however, briefly to describe and
review the corresponding modifications which are presented to the eye.
244.
At the highest point of complete junction of the opposite edges, the
colours appear as follows (216):—
| Yellow-red. | Blue. |
| Green. | Red. |
| Blue-red. | Yellow. |
[Pg 101]
245.
Where the junction is less complete, the appearance is as follows (214,
215):—
| Yellow-red. | Blue. |
| Yellow. | Blue-red. |
| Green. | Red. |
| Blue. | Yellow-red. |
| Blue-red. | Yellow. |
Here, therefore, the surface still appears completely coloured, but
neither series is to be considered as an elementary series, always
developing itself in the same manner and in the same degrees; on the
contrary, they can and should be resolved into their elements; and, in
doing this, we become better acquainted with their nature and character.
246.
These elements then are (199, 200, 201)—
| Yellow-red. | Blue. |
| Yellow. | Blue-red. |
| White. | Black. |
| Blue. | Yellow-red. |
| Blue-red. | Yellow. |
Here the surface itself, the original object, which has been hitherto
completely covered, and as it were lost, again appears in the centre of
the colours, asserts its right, and enables us[Pg 102] fully to recognise the
secondary nature of the accessory images which exhibit themselves as
"edges" and "borders."—Note N.
247.
We can make these edges and borders as narrow as we please; nay, we
can still have refraction in reserve after having done away with all
appearance of colour at the boundary of the object.
Having now sufficiently investigated the exhibition of colour in this
phenomenon, we repeat that we cannot admit it to be an elementary
phenomenon. On the contrary, we have traced it to an antecedent and
a simpler one; we have derived it, in connexion with the theory of
secondary images, from the primordial phenomenon of light and darkness,
as affected or acted upon by semi-transparent mediums. Thus prepared,
we proceed to describe the appearances which refraction produces on
grey and coloured objects, and this will complete the section of
subjective phenomena.
[Pg 103]
GREY OBJECTS DISPLACED BY REFRACTION.
248.
Hitherto we have confined our attention to black and white objects
relieved on respectively opposite grounds, as seen through the prism,
because the coloured edges and borders are most clearly displayed in
such cases. We now repeat these experiments with grey objects, and
again find similar results.
249.
As we called black the equivalent of darkness, and white the
representative of light (18), so we now venture to say that grey
represents half-shadow, which partakes more or less of light and
darkness, and thus stands between the two. We invite the reader to call
to mind the following facts as bearing on our present view.
250.
Grey objects appear lighter on a black than on a white ground (33);
they appear as a light on a black ground, and larger; as a dark on the
white ground, and smaller. (16.)
[Pg 104]
251.
The darker the grey the more it appears as a faint light on black, as a
strong dark on white, and vice versâ; hence the accessory images of
dark-grey on black are faint, on white strong: so the accessory images
of light-grey on white are faint, on black strong.
252.
Grey on black, seen through the prism, will exhibit the same
appearances as white on black; the edges are coloured according to the
same law, only the borders appear fainter. If we relieve grey on white,
we have the same edges and borders which would be produced if we saw
black on white through the prism.—Note O.
253.
Various shades of grey placed next each other in gradation will exhibit
at their edges, either blue and violet only, or red and yellow only,
according as the darker grey is placed over or under.
254.
A series of such shades of grey placed horizontally next each other
will be coloured conformably to the same law according as the whole
series is relieved, on a black or white ground above or below.
[Pg 105]
255.
The observer may see the phenomena exhibited by the prism at one
glance, by enlarging the plate intended to illustrate this section.[1]
256.
It is of great importance duly to examine and consider another
experiment in which a grey object is placed partly on a black and
partly on a white surface, so that the line of division passes
vertically through the object.
257.
The colours will appear on this grey object in conformity with the
usual law, but according to the opposite relation of the light to the
dark, and will be contrasted in a line. For as the grey is as a light
to the black, so it exhibits the red and yellow above the blue and
violet below: again, as the grey is as a dark to the white, the blue
and violet appear above the red and yellow below. This experiment will
be found of great importance with reference to the next chapter.
COLOURED OBJECTS DISPLACED BY REFRACTION.
258.
An unlimited coloured surface exhibits no prismatic colour in addition
to its own hue, thus not at all differing from a black, white, or
grey surface. To produce the appearance of colour, light and dark
boundaries must act on it either accidentally or by contrivance. Hence
experiments and observations on coloured surfaces, as seen through the
prism, can only be made when such surfaces are separated by an outline
from another differently tinted surface, in short when circumscribed
objects are coloured.
259.
All colours, whatever they may be, correspond so far with grey, that
they appear darker than white and lighter than black. This shade-like
quality of colour (σκιέρον) has been already alluded to (69), and will
become more and more evident. If then we begin by placing coloured
objects on black and white surfaces, and examine them through the
prism, we shall again have all that we have seen exhibited with grey
surfaces.
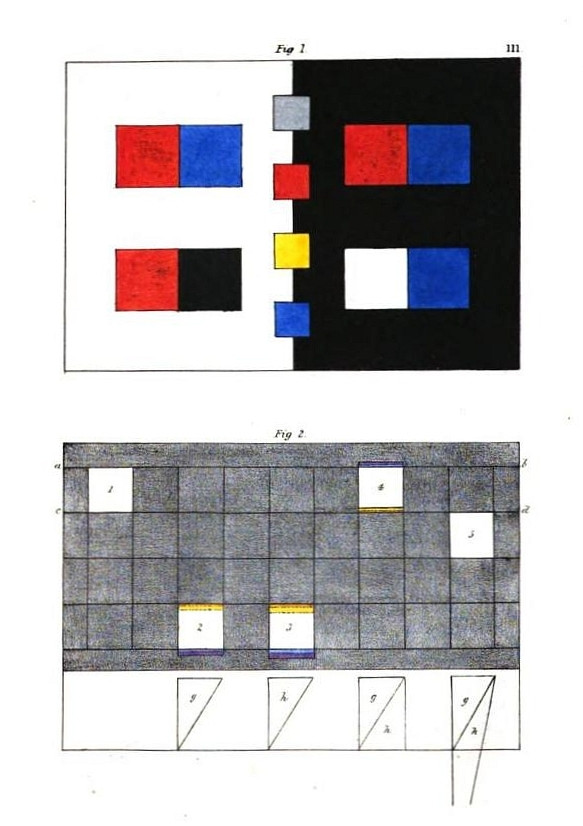
Plate 3.
[Pg 107]
260.
If we displace a coloured object by refraction, there appears, as
in the case of colourless objects and according to the same laws,
an accessory image. This accessory image retains, as far as colour
is concerned, its usual nature, and acts on one side as a blue and
blue-red, on the opposite side as a yellow and yellow-red. Hence the
apparent colour of the edge and border will be either homogeneous
with the real colour of the object, or not so. In the first case the
apparent image identifies itself with the real one, and appears to
increase it, while, in the second case, the real image may be vitiated,
rendered indistinct, and reduced in size by the apparent image. We
proceed to review the cases in which these effects are most strikingly
exhibited.
261.
If we take a coloured drawing enlarged from the plate, which
illustrates this experiment[1], and examine the red and blue squares
placed next each other on a black ground, through the prism as usual,
we shall find that as both colours are lighter than the ground,
similarly coloured edges and borders will appear above and below,[Pg 108] at
the outlines of both, only they will not appear equally distinct to the
eye.
262.
Red is proportionally much lighter on black than blue is. The colours
of the edges will therefore appear stronger on the red than on the
blue, which here acts as a dark-grey, but little different from black.
(251.)
263.
The extreme red edge will identify itself with the vermilion colour
of the square, which will thus appear a little elongated in this
direction; while the yellow border immediately underneath it only gives
the red surface a more brilliant appearance, and is not distinguished
without attentive observation.
264.
On the other hand the red edge and yellow border are heterogeneous
with the blue square; a dull red appears at the edge, and a dull green
mingles with the figure, and thus the blue square seems, at a hasty
glance, to be comparatively diminished on this side.
265.
At the lower outline of the two squares a blue edge and a violet border
will appear, and will[Pg 109] produce the contrary effect; for the blue edge,
which is heterogeneous with the warm red surface, will vitiate it
and produce a neutral colour, so that the red on this side appears
comparatively reduced and driven upwards, and the violet border on the
black is scarcely perceptible.
266.
On the other hand, the blue apparent edge will identify itself with the
blue square, and not only not reduce, but extend it. The blue edge and
even the violet border next it have the apparent effect of increasing
the surface, and elongating it in that direction.
267.
The effect of homogeneous and heterogeneous edges, as I have now
minutely described it, is so powerful and singular that the two squares
at the first glance seem pushed out of their relative horizontal
position and moved in opposite directions, the red upwards, the blue
downwards. But no one who is accustomed to observe experiments in a
certain succession, and respectively to connect and trace them, will
suffer himself to be deceived by such an unreal effect.
268.
A just impression with regard to this important[Pg 110] phenomenon will,
however, much depend on some nice and even troublesome conditions,
which are necessary to produce the illusion in question. Paper should
be tinged with vermilion or the best minium for the red square, and
with deep indigo for the blue square. The blue and red prismatic edges
will then unite imperceptibly with the real surfaces where they are
respectively homogeneous; where they are not, they vitiate the colours
of the squares without producing a very distinct middle tint. The real
red should not incline too much to yellow, otherwise the apparent deep
red edge above will be too distinct; at the same time it should be
somewhat yellow, otherwise the transition to the yellow border will be
too observable. The blue must not be light, otherwise the red edge will
be visible, and the yellow border will produce a too decided green,
while the violet border underneath would not give us the impression of
being part of an elongated light blue square.
269.
All this will be treated more circumstantially hereafter, when we speak
of the apparatus intended to facilitate the experiments connected with
this part of our subject.[2] Every inquirer[Pg 111] should prepare the figures
himself, in order fairly to exhibit this specimen of ocular deception,
and at the same time to convince himself that the coloured edges, even
in this case, cannot escape accurate examination.
270.
Meanwhile various other combinations, as exhibited in the plate, are
fully calculated to remove all doubt on this point in the mind of every
attentive observer.
271.
If, for instance, we look at a white square, next the blue one, on a
black ground, the prismatic hues of the opposite edges of the white,
which here occupies the place of the red in the former experiment, will
exhibit themselves in their utmost force. The red edge extends itself
above the level of the blue almost in a greater degree than was the
case with the red square itself in the former experiment. The lower
blue edge, again, is visible in its full force next the white, while,
on the other hand, it cannot be distinguished next the blue square. The
violet border underneath is also much more apparent on the white than
on the blue.
272.
If the observer now compares these double[Pg 112] squares, carefully prepared
and arranged one above the other, the red with the white, the two blue
squares together, the blue with the red, the blue with the white, he
will clearly perceive the relations of these surfaces to their coloured
edges and borders.
273.
The edges and their relations to the coloured surfaces appear still
more striking if we look at the coloured squares and a black square
on a white ground; for in this case the illusion before mentioned
ceases altogether, and the effect of the edges is as visible as in
any case that has come under our observation. Let the blue and red
squares be first examined through the prism. In both the blue edge now
appears above; this edge, homogeneous with the blue surface, unites
with it, and appears to extend it upwards, only the blue edge, owing
to its lightness, is somewhat too distinct in its upper portion; the
violet border underneath it is also sufficiently evident on the blue.
The apparent blue edge is, on the other hand, heterogeneous with the
red square; it is neutralised by contrast, and is scarcely visible;
meanwhile the violet border, uniting with the real red, produces a hue
resembling that of the peach-blossom.
274.
If thus, owing to the above causes, the upper[Pg 113] outlines of these
squares do not appear level with each other, the correspondence of the
under outlines is the more observable; for since both colours, the red
and the blue, are darks compared with the white (as in the former case
they were light compared with the black), the red edge with its yellow
border appears very distinctly under both. It exhibits itself under the
warm red surface in its full force, and under the dark blue nearly as
it appears under the black: as may be seen if we compare the edges and
borders of the figures placed one above the other on the white ground.
275.
In order to present these experiments with the greatest variety and
perspicuity, squares of various colours are so arranged[3] that the
boundary of the black and white passes through them vertically.
According to the laws now known to us, especially in their application
to coloured objects, we shall find the squares as usual doubly coloured
at each edge; each square will appear to be split in two, and to be
elongated upwards or downwards. We may here call to mind the experiment
with the grey figure seen in like manner on the line of division
between black and white (257).[4]
[Pg 114]
276.
A phenomenon was before exhibited, even to illusion, in the instance of
a red and blue square on a black ground; in the present experiment the
elongation upwards and downwards of two differently coloured figures
is apparent in the two halves of one and the same figure of one and
the same colour. Thus we are still referred to the coloured edges and
borders, and to the effects of their homogeneous and heterogeneous
relations with respect to the real colours of the objects.
277.
I leave it to observers themselves to compare the various gradations
of coloured squares, placed half on black half on white, only inviting
their attention to the apparent alteration which takes place in
contrary directions; for red and yellow appear elongated upwards if
on a black ground, downwards if on a white; blue, downwards if on a
black ground, upwards if on a white. All which, however, is quite in
accordance with the diffusely detailed examples above given.
278.
Let the observer now turn the figures so that the before-mentioned
squares placed on the line of division between black and white may
be in a horizontal series; the black above, the white underneath. On
looking at these squares[Pg 115] through the prism, he will observe that the
red square gains by the addition of two red edges; on more accurate
examination he will observe the yellow border on the red figure, and
the lower yellow border upon the white will be perfectly apparent.
279.
The upper red edge on the blue square is on the other hand hardly
visible; the yellow border next it produces a dull green by mingling
with the figure; the lower red edge and the yellow border are displayed
in lively colours.
280.
After observing that the red figure in these cases appears to gain by
an addition on both sides, while the dark blue, on one side at least,
loses something; we shall see the contrary effect produced by turning
the same figures upside down, so that the white ground be above, the
black below.
281.
For as the homogeneous edges and borders now appear above and below
the blue square, this appears elongated, and a portion of the surface
itself seems even more brilliantly coloured: it is only by attentive
observation that we can distinguish the edges and borders from the
colour of the figure itself.
[Pg 116]
282.
The yellow and red squares, on the other hand, are comparatively
reduced by the heterogeneous edges in this position of the figures,
and their colours are, to a certain extent, vitiated. The blue edge
in both is almost invisible. The violet border appears as a beautiful
peach-blossom hue on the red, as a very pale colour of the same kind on
the yellow; both the lower edges are green; dull on the red, vivid on
the yellow; the violet border is but faintly perceptible under the red,
but is more apparent under the yellow.
283.
Every inquirer should make it a point to be thoroughly acquainted with
all the appearances here adduced, and not consider it irksome to follow
out a single phenomenon through so many modifying circumstances. These
experiments, it is true, may be multiplied to infinity by differently
coloured figures, upon and between differently coloured grounds. Under
all such circumstances, however, it will be evident to every attentive
observer that coloured squares only appear relatively altered, or
elongated, or reduced by the prism, because an addition of homogeneous
or heterogeneous edges produces an illusion. The inquirer will now
be enabled to do away with this illusion if he has the[Pg 117] patience to
go through the experiments one after the other, always comparing the
effects together, and satisfying himself of their correspondence.
Experiments with coloured objects might have been contrived in various
ways: why they have been exhibited precisely in the above mode, and
with so much minuteness, will be seen hereafter. The phenomena,
although formerly not unknown, were much misunderstood; and it was
necessary to investigate them thoroughly to render some portions of our
intended historical view clearer.
284.
In conclusion, we will mention a contrivance by means of which our
scientific readers may be enabled to see these appearances distinctly
at one view, and even in their greatest splendour. Cut in a piece of
pasteboard five perfectly similar square openings of about an inch,
next each other, exactly in a horizontal line: behind these openings
place five coloured glasses in the natural order, orange, yellow,
green, blue, violet. Let the series thus adjusted be fastened in an
opening of the camera obscura, so that the bright sky may be seen
through the squares, or that the sun may shine on them; they will thus
appear very powerfully coloured. Let the spectator now examine them
through the prism, and observe the appearances, already[Pg 118] familiar by
the foregoing experiments, with coloured objects, namely, the partly
assisting, partly neutralising effects of the edges and borders, and
the consequent apparent elongation or reduction of the coloured squares
with reference to the horizontal line. The results witnessed by the
observer in this case, entirely correspond with those in the cases
before analysed; we do not, therefore, go through them again in detail,
especially as we shall find frequent occasions hereafter to return to
the subject.—Note P.
ACHROMATISM AND HYPERCHROMATISM.
285.
Formerly when much that is regular and constant in nature was
considered as mere aberration and accident, the colours arising from
refraction were but little attended to, and were looked upon as an
appearance attributable to particular local circumstances.
286.
But after it had been assumed that this appearance of colour
accompanies refraction at all times, it was natural that it should
be considered as intimately and exclusively connected with that
phenomenon; the belief obtaining that the[Pg 119] measure of the coloured
appearance was in proportion to the measure of the refraction, and that
they must advance pari passu with each other.
287.
If, again, philosophers ascribed the phenomenon of a stronger or weaker
refraction, not indeed wholly, but in some degree, to the different
density of the medium, (as purer atmospheric air, air charged with
vapours, water, glass, according to their increasing density, increase
the so-called refraction, or displacement of the object;) so they
could hardly doubt that the appearance of colour must increase in the
same proportion; and hence took it for granted, in combining different
mediums which were to counteract refraction, that as long as refraction
existed, the appearance of colour must take place, and that as soon as
the colour disappeared, the refraction also must cease.
288.
Afterwards it was, however, discovered that this relation which was
assumed to correspond, was, in fact, dissimilar; that two mediums can
refract an object with equal power, and yet produce very dissimilar
coloured borders.
289.
It was found that, in addition to the physical principle to which
refraction was ascribed, a[Pg 120] chemical one was also to be taken into the
account. We propose to pursue this subject hereafter, in the chemical
division of our inquiry, and we shall have to describe the particulars
of this important discovery in our history of the doctrine of colours.
What follows may suffice for the present.
290.
In mediums of similar or nearly similar refracting power, we find
the remarkable circumstance that a greater and lesser appearance of
colour can be produced by a chemical treatment; the greater effect is
owing, namely, to acids, the lesser to alkalis. If metallic oxydes are
introduced into a common mass of glass, the coloured appearance through
such glasses becomes greatly increased without any perceptible change
of refracting power. That the lesser effect, again, is produced by
alkalis, may be easily supposed.
291.
Those kinds of glass which were first employed after the discovery,
are called flint and crown glass; the first produces the stronger, the
second the fainter appearance of colour.
292.
We shall make use of both these denominations as technical terms in our
present statement,[Pg 121] and assume that the refractive power of both is
the same, but that flint-glass produces the coloured appearance more
strongly by one-third than the crown-glass. The diagram (Plate 3, fig.
2,) may serve in illustration.
293.
A black surface is here divided into compartments for more convenient
demonstration: let the spectator imagine five white squares between the
parallel lines a, b, and c, d. The square No. 1, is presented to
the naked eye unmoved from its place.
294.
But let the square No. 2, seen through a crown-glass prism g, be
supposed to be displaced by refraction three compartments, exhibiting
the coloured borders to a certain extent; again, let the square No. 3,
seen through a flint glass prism h, in like manner be moved downwards
three compartments, when it will exhibit the coloured borders by about
a third wider than No. 2.
295.
Again, let us suppose that the square No. 4, has, like No. 2, been
moved downwards three compartments by a prism of crown-glass, and that
then by an oppositely placed prism h, of[Pg 122] flint-glass, it has been
again raised to its former situation, where it now stands.
296.
Here, it is true, the refraction is done away with by the opposition of
the two; but as the prism h, in displacing the square by refraction
through three compartments, produces coloured borders wider by a
third than those produced by the prism g, so, notwithstanding the
refraction is neutralised, there must be an excess of coloured border
remaining. (The position of this colour, as usual, depends on the
direction of the apparent motion (204) communicated to the square by
the prism h, and, consequently, it is the reverse of the appearance
in the two squares 2 and 3, which have been moved in an opposite
direction.) This excess of colour we have called Hyperchromatism, and
from this the achromatic state may be immediately arrived at.
297.
For assuming that it was the square No. 5 which was removed three
compartments from its first supposed place, like No. 2, by a prism of
crown-glass g, it would only be necessary to reduce the angle of a
prism of flint-glass h, and to connect it, reversed, to the prism
g, in order to raise the square No. 5 two degrees or compartments;
by which means the Hyperchromatism[Pg 123] of the first case would cease, the
figure would not quite return to its first position, and yet be already
colourless. The prolonged lines of the united prisms, under No. 5, show
that a single complete prism remains: again, we have only to suppose
the lines curved, and an object-glass presents itself. Such is the
principle of the achromatic telescopes.
298.
For these experiments, a small prism composed of three different
prisms, as prepared in England, is extremely well adapted. It is to be
hoped our own opticians will in future enable every friend of science
to provide himself with this necessary instrument.
ADVANTAGES OF SUBJECTIVE EXPERIMENTS.—TRANSITION TO THE OBJECTIVE.
299.
We have presented the appearances of colour as exhibited by refraction,
first, by means of subjective experiments; and we have so far arrived
at a definite result, that we have been enabled to deduce the phenomena
in question[Pg 124] from the doctrine of semi-transparent mediums and double
images.
300.
In statements which have reference to nature, everything depends on
ocular inspection, and these experiments are the more satisfactory as
they may be easily and conveniently made. Every amateur can procure
his apparatus without much trouble or cost, and if he is a tolerable
adept in pasteboard contrivances, he may even prepare a great part of
his machinery himself. A few plain surfaces, on which black, white,
grey, and coloured objects may be exhibited alternately on a light and
dark ground, are all that is necessary. The spectator fixes them before
him, examines the appearances at the edge of the figures conveniently,
and as long as he pleases; he retires to a greater distance, again
approaches, and accurately observes the progressive states of the
phenomena.
301.
Besides this, the appearances may be observed with sufficient exactness
through small prisms, which need not be of the purest glass. The other
desirable requisites in these glass instruments will, however, be
pointed out in the section which treats of the apparatus.[1]
[Pg 125]
302.
A great advantage in these experiments, again, is, that they can be
made at any hour of the day in any room, whatever aspect it may have.
We have no need to wait for sunshine, which in general is not very
propitious to northern observers.
303.
The objective experiments, on the contrary, necessarily require the
sun-light which, even when it is to be had, may not always have the
most desirable relation with the apparatus placed opposite to it.
Sometimes the sun is too high, sometimes too low, and withal only a
short time in the meridian of the best situated room. It changes its
direction during the observation, the observer is forced to alter
his own position and that of his apparatus, in consequence of which
the experiments in many cases become uncertain. If the sun shines
through the prism it exhibits all inequalities, lines, and bubbles
in the glass, and thus the appearance is rendered confused, dim, and
discoloured.
304.
Yet both kinds of experiments must be investigated with equal accuracy.
They appear to[Pg 126] be opposed to each other, and yet are always parallel.
What one order of experiments exhibits the other exhibits likewise,
and yet each has its peculiar capabilities, by means of which certain
effects of nature are made known to us in more than one way.
305.
In the next place there are important phenomena which may be exhibited
by the union of subjective and objective experiments. The latter
experiments again have this advantage, that we can in most cases
represent them by diagrams, and present to view the component relations
of the phenomena. In proceeding, therefore, to describe the objective
experiments, we shall so arrange them that they may always correspond
with the analogous subjective examples; for this reason, too, we annex
to the number of each paragraph the number of the former corresponding
one. But we set out by observing generally that the reader must consult
the plates, that the scientific investigator must be familiar with the
apparatus in order that the twin-phenomena in one mode or the other may
be placed before them.
[Pg 127]
REFRACTION WITHOUT THE APPEARANCE OF COLOUR.
306 (195, 196).
That refraction may exhibit its effects without producing an appearance
of colour, is not to be demonstrated so perfectly in objective as
in subjective experiments. We have, it is true, unlimited spaces
which we can look at through the prism, and thus convince ourselves
that no colour appears where there is no boundary; but we have no
unlimited source of light which we can cause to act through the prism.
Our light comes to us from circumscribed bodies; and the sun, which
chiefly produces our prismatic appearances, is itself only a small,
circumscribed, luminous object.
307.
We may, however, consider every larger opening through which the sun
shines, every larger medium through which the sun-light is transmitted
and made to deviate from its course, as so far unlimited that we can
confine our attention to the centre of the surface without considering
its boundaries.
308 (197).
If we place a large water-prism in the sun, a[Pg 128] large bright space is
refracted upwards by it on the plane intended to receive the image, and
the middle of this illumined space will be colourless. The same effect
may be produced if we make the experiment with glass prisms having
angles of few degrees: the appearance may be produced even through
glass prisms, whose refracting angle is sixty degrees, provided we
place the recipient surface near enough.
CONDITIONS OF THE APPEARANCE OF COLOUR.
309 (198).
Although, then, the illumined space before mentioned appears indeed
refracted and moved from its place, but not coloured, yet on the
horizontal edges of this space we observe a coloured appearance.
That here again the colour is solely owing to the displacement of a
circumscribed object may require to be more fully proved.
The luminous body which here acts is circumscribed: the sun, while it
shines and diffuses light, is still an insulated object. However small
the opening in the lid of a camera obscura be made, still the whole
image of the sun will[Pg 129] penetrate it. The light which streams from all
parts of the sun's disk, will cross itself in the smallest opening, and
form the angle which corresponds with the sun's apparent diameter. On
the outside we have a cone narrowing to the orifice; within, this apex
spreads again, producing on an opposite surface a round image, which
still increases in size in proportion to the distance of the recipient
surface from the apex. This image, together with all other objects
of the external landscape, appears reversed on the white surface in
question in a dark room.
310.
How little therefore we have here to do with single sun-rays, bundles
or fasces of rays, cylinders of rays, pencils, or whatever else of the
kind may be imagined, is strikingly evident. For the convenience of
certain diagrams the sun-light may be assumed to arrive in parallel
lines, but it is known that this is only a fiction; a fiction quite
allowable where the difference between the assumption and the true
appearance is unimportant; but we should take care not to suffer such a
postulate to be equivalent to a fact, and proceed to further operations
on such a fictitious basis.
311.
Let the aperture in the window-shutter be now enlarged at pleasure, let
it be made round[Pg 130] or square, nay, let the whole shutter be opened, and
let the sun shine into the room through the whole window; the space
which the sun illumines will always be larger according to the angle
which its diameter makes; and thus even the whole space illumined by
the sun through the largest window is only the image of the sun plus
the size of the opening. We shall hereafter have occasion to return to
this.
312 (199).
If we transmit the image of the sun through convex glasses we contract
it towards the focus. In this case, according to the laws before
explained, a yellow border and a yellow-red edge must appear when the
spectrum is thrown on white paper. But as this experiment is dazzling
and inconvenient, it may be made more agreeably with the image of the
full moon. On contracting this orb by means of a convex glass, the
coloured edge appears in the greatest splendour; for the moon transmits
a mitigated light in the first instance, and can thus the more readily
produce colour which to a certain extent accompanies the subduing of
light: at the same time the eye of the observer is only gently and
agreeably excited.
313 (200).
If we transmit a luminous image through concave[Pg 131] glasses, it is
dilated. Here the image appears edged with blue.
314.
The two opposite appearances may be produced by a convex glass,
simultaneously or in succession; simultaneously by fastening an opaque
disk in the centre of the convex glass, and then transmitting the sun's
image. In this case the luminous image and the black disk within it are
both contracted, and, consequently, the opposite colours must appear.
Again, we can present this contrast in succession by first contracting
the luminous image towards the focus, and then suffering it to expand
again beyond the focus, when it will immediately exhibit a blue edge.
315 (201).
Here too what was observed in the subjective experiments is again to be
remarked, namely, that blue and yellow appear in and upon the white,
and that both assume a reddish appearance in proportion as they mingle
with the black.
316 (202, 203).
These elementary phenomena occur in all subsequent objective
experiments, as they constituted the groundwork of the subjective
ones.[Pg 132] The process too which takes place is the same; a light boundary
is carried over a dark surface, a dark surface is carried over a light
boundary. The edges must advance, and as it were push over each other
in these experiments as in the former ones.
317 (204).
If we admit the sun's image through a larger or smaller opening into
the dark room, if we transmit it through a prism so placed that its
refracting angle, as usual, is underneath; the luminous image, instead
of proceeding in a straight line to the floor, is refracted upwards on
a vertical surface placed to receive it. This is the moment to take
notice of the opposite modes in which the subjective and objective
refractions of the object appear.
318.
If we look through a prism, held with its refracting angle
underneath, at an object above us, the object is moved downwards;
whereas a luminous image refracted through the same prism is moved
upwards. This, which we here merely mention as a matter of fact for
the sake of brevity, is easily explained by the laws of refraction and
elevation.
[Pg 133]
319.
The luminous object being moved from its place in this manner, the
coloured borders appear in the order, and according to the laws before
explained. The violet border is always foremost, and thus in objective
cases proceeds upwards, in subjective cases downwards.
320 (205).
The observer may convince himself in like manner of the mode in which
the appearance of colour takes place in the diagonal direction when the
displacement is effected by means of two prisms, as has been plainly
enough shown in the subjective example; for this experiment, however,
prisms should be procured of few degrees, say about fifteen.
321 (206, 207).
That the colouring of the image takes place here too, according to the
direction in which it moves, will be apparent if we make a square
opening of moderate size in a shutter, and cause the luminous image
to pass through a water-prism; the spectrum being moved first in the
horizontal and vertical directions, then diagonally, the coloured edges
will change their position accordingly.
[Pg 134]
322 (208).
Whence it is again evident that to produce colour the boundaries must
be carried over each other, not merely move side by side.
CONDITIONS OF THE INCREASE OF COLOUR.
323 (209).
Here too an increased displacement of the object produces a greater
appearance of colour.
324 (210).
This increased displacement occurs,
1. By a more oblique direction of the impinging luminous object through
mediums with parallel surfaces.
2. By changing the parallel form for one more or less acute angled.
3. By increased proportion of the medium, whether parallel or acute
angled; partly because the object is by this means more powerfully
displaced, partly because an effect depending on the mere mass
co-operates.
4. By the distance of the recipient surface from the refracting medium
so that the coloured [Pg 135] spectrum emerging from the prism may be said to
have a longer way to travel.
5. When a chemical property produces its effects under all these
circumstances: this we have already entered into more fully under the
head of achromatism and hyperchromatism.
325 (211).
The objective experiments have this advantage that the progressive
states of the phenomenon may be arrested and clearly represented by
diagrams, which is not the case with the subjective experiments.
326.
We can observe the luminous image after it has emerged from the prism,
step by step, and mark its increasing colour by receiving it on a
plane at different distances, thus exhibiting before our eyes various
sections of this cone, with an elliptical base: again, the phenomenon
may at once be rendered beautifully visible throughout its whole course
in the following manner:—Let a cloud of fine white dust be excited
along the line in which the image passes through the dark space; the
cloud is best produced by fine, perfectly dry, hair-powder. The more or
less coloured appearance will now be painted on the white atoms, and
presented in[Pg 136] its whole length and breadth to the eye of the spectator.
327.
By this means we have prepared some diagrams, which will be found among
the plates. In these the appearance is exhibited from its first origin,
and by these the spectator can clearly comprehend why the luminous
image is so much more powerfully coloured through prisms than through
parallel mediums.
328 (212).
At the two opposite outlines of the image an opposite appearance
presents itself, beginning from an acute angle;[1] the appearance
spreads as it proceeds further in space, according to this angle. On
one side, in the direction in which the luminous image is moved, a
violet border advances on the dark, a narrower blue edge remains next
the outline of the image. On the opposite side a yellow border advances
into the light of the image itself, and a yellow-red edge remains at
the outline.
329 (213).
Here, therefore, the movement of the dark against the light, of the
light against the dark, may be clearly observed.
Plate 4.
[Pg 137]
330 (214).
The centre of a large object remains long uncoloured, especially with
mediums of less density and smaller angles; but at last the opposite
borders and edges touch each other, upon which a green appears in the
centre of the luminous image.
331 (215).
Objective experiments have been usually made with the sun's image: an
objective experiment with a dark object has hitherto scarcely been
thought of. We have, however, prepared a convenient contrivance for
this also. Let the large water-prism before alluded to be placed in
the sun, and let a round pasteboard disk be fastened either inside or
outside. The coloured appearance will again take place at the outline,
beginning according to the usual law; the edges will appear, they will
spread in the same proportion, and when they meet, red will appear in
the centre[2]. An intercepting square may be added near the round disk,
and placed in any direction ad libitum, and the spectator can again
convince himself of what has been before so often described.
332 (216).
If we take away these dark objects from the[Pg 138] prism, in which case,
however, the glass is to be carefully cleaned, and hold a rod or a
large pencil before the centre of the horizontal prism, we shall
then accomplish the complete immixture of the violet border and the
yellow-red edge, and see only the three colours, the external blue, and
yellow, and the central red.
333.
If again we cut a long horizontal opening in the middle of a piece of
pasteboard, fastened on the prism, and then cause the sun-light to pass
through it, we shall accomplish the complete union of the yellow border
with the blue edge upon the light, and only see yellow-red, green and
violet. The details of this are further entered into in the description
of the plates.
334 (217).
The prismatic appearance is thus by no means complete and final when
the luminous image emerges from the prism. It is then only that
we perceive its elements in contrast; for as it increases these
contrasting elements unite, and are at last intimately joined. The
section of this phenomenon arrested on a plane surface is different
at every degree of distance from the prism; so that the notion of an
immutable series of colours, or of a pervading similar proportion
between them, cannot be a question for a moment.
EXPLANATION OF THE FOREGOING PHENOMENA.
335 (218).
As we have already entered into this analysis circumstantially while
treating of the subjective experiments, as all that was of force there
is equally valid here, it will require no long details in addition to
show that the phenomena, which are entirely parallel in the two cases,
may also be traced precisely to the same sources.
336 (219).
That in objective experiments also we have to do with circumscribed
images, has been already demonstrated at large. The sun may shine
through the smallest opening, yet the image of the whole disk
penetrates beyond. The largest prism may be placed in the open
sun-light, yet it is still the sun's image that is bounded by the
edges of the refracting surfaces, and produces the accessory images
of this boundary. We may fasten pasteboard, with many openings cut in
it, before the water-prism, yet we still merely see multiplied images
which, after having been moved from their place by refraction, exhibit
coloured edges and borders, and in these mere accessory images.
[Pg 140]
337 (235).
In subjective experiments we have seen that objects strongly relieved
from each other produce a very lively appearance of colour, and this
will be the case in objective experiments in a much more vivid and
splendid degree. The sun's image is the most powerful brightness we
know; hence its accessory image will be energetic in proportion, and
notwithstanding its really secondary dimmed and darkened character,
must be still very brilliant. The colours thrown by the sun-light
through the prism on any object, carry a powerful light with them, for
they have the highest and most intense source of light, as it were, for
their ground.
338.
That we are warranted in calling even these accessory images
semi-transparent, thus deducing the appearances from the doctrine
of the semi-transparent mediums, will be clear to every one who has
followed us thus far, but particularly to those who have supplied
themselves with the necessary apparatus, so as to be enabled at all
times to witness the precision and vivacity with which semi-transparent
mediums act.
[Pg 141]
DECREASE OF THE APPEARANCE OF COLOUR.
339 (243).
If we could afford to be concise in the description of the decreasing
coloured appearance in subjective cases, we may here be permitted
to proceed with still greater brevity while we refer to the former
distinct statement. One circumstance, only on account of its great
importance, may be here recommended to the reader's especial attention
as a leading point of our whole thesis.
340 (244, 247).
The decline of the prismatic appearance must be preceded by its
separation, by its resolution into its elements. At a due distance from
the prism, the image of the sun being entirely coloured, the blue and
yellow at length mix completely, and we see only yellow-red, green, and
blue-red. If we bring the recipient surface nearer to the refracting
medium, yellow and blue appear again, and we see the five colours with
their gradations. At a still shorter distance the yellow and blue
separate from each other entirely, the green vanishes, and the image
itself appears, colourless, between the coloured edges and borders. The
nearer we bring the recipient surface to the prism, the[Pg 142] narrower the
edges and borders become, till at last, when in contact with the prism,
they are reduced to nothing.
GREY OBJECTS.
341 (218).
We have exhibited grey objects as very important to our inquiry in the
subjective experiments. They show, by the faintness of the accessory
images, that these same images are in all cases derived from the
principal object. If we wish here, too, to carry on the objective
experiments parallel with the others, we may conveniently do this by
placing a more or less dull ground glass before the opening through
which the sun's image enters. By this means a subdued image would be
produced, which on being refracted would exhibit much duller colours on
the recipient plane than those immediately derived from the sun's disk;
and thus, even from the intense sun-image, only a faint accessory image
would appear, proportioned to the mitigation of the light by the glass.
This experiment, it is true, will only again and again confirm what is
already sufficiently familiar to us.
[Pg 143]
COLOURED OBJECTS.
342 (260).
There are various modes of producing coloured images in objective
experiments. In the first place, we can fix coloured glass before the
opening, by which means a coloured image is at once produced; secondly,
we can fill the water-prism with coloured fluids; thirdly, we can cause
the colours, already produced in their full vivacity by the prism, to
pass through proportionate small openings in a tin plate, and thus
prepare small circumscribed colours for a second operation. This last
mode is the most difficult; for owing to the continual progress of the
sun, the image cannot be arrested in any direction at will. The second
method has also its inconveniences, since not all coloured liquids can
be prepared perfectly bright and clear. On these accounts the first is
to be preferred, and deserves the more to be adopted because natural
philosophers have hitherto chosen to consider the colours produced
from the sun-light through the prism, those produced through liquids
and glasses, and those which are already fixed on paper or cloth, as
exhibiting effects equally to be depended on, and equally available in
demonstration.
343.
As it is thus merely necessary that the image[Pg 144] should be coloured, so
the large water-prism before alluded to affords us the best means of
effecting this. A pasteboard screen may be contrived to slide before
the large surfaces of the prism, through which, in the first instance,
the light passes uncoloured. In this screen openings of various forms
may be cut, in order to produce different images, and consequently
different accessory images. This being done, we need only fix coloured
glasses before the openings, in order to observe what effect refraction
produces on coloured images in an objective sense.
344.
A series of glasses may be prepared in a mode similar to that before
described (284); these should be accurately contrived to slide in the
grooves of the large water-prism. Let the sun then shine through them,
and the coloured images refracted upwards will appear bordered and
edged, and will vary accordingly: for these borders and edges will be
exhibited quite distinctly on some images, and on others will be mixed
with the specific colour of the glass, which they will either enhance
or neutralize. Every observer will be enabled to convince himself
here again that we have only to do with the same simple phenomenon so
circumstantially described subjectively and objectively.
[Pg 145]
ACHROMATISM AND HYPERCHROMATISM.
345 (285, 290).
It is possible to make the hyperchromatic and achromatic experiments
objectively as well as subjectively. After what has been already
stated, a short description of the method will suffice, especially as
we take it for granted that the compound prism before mentioned is in
the hands of the observer.
346.
Let the sun's image pass through an acute-angled prism of few degrees,
prepared from crown-glass, so that the spectrum be refracted upwards on
an opposite surface; the edges will appear coloured, according to the
constant law, namely, the violet and blue above and outside, the yellow
and yellow-red below and within the image. As the refracting angle of
this prism is undermost, let another proportionate prism of flint-glass
be placed against it, with its refracting angle uppermost. The sun's
image will by this means be again moved to its place, where, owing to
the excess of the colouring power of the prism of flint-glass, it will
still appear a little coloured, and, in consequence of the direction
in which it has been moved, the blue and violet[Pg 146] will now appear
underneath and outside, the yellow and yellow-red above and inside.
347.
If the whole image be now moved a little upwards by a proportionate
prism of crown-glass, the hyperchromatism will disappear, the sun's
image will be moved from its place, and yet will appear colourless.
348.
With an achromatic object-glass composed of three glasses, this
experiment may be made step by step, if we do not mind taking out the
glasses from their setting. The two convex glasses of crown-glass in
contracting the sun's image towards the focus, the concave glass of
flint-glass in dilating the image beyond it, exhibit at the edges the
usual colours. A convex glass united with a concave one exhibits the
colours according to the law of the latter. If all three glasses are
placed together, whether we contract the sun's image towards the focus,
or suffer it to dilate beyond the focus, coloured edges never appear,
and the achromatic effect intended by the optician is, in this case,
again attained.
349.
But as the crown-glass has always a greenish tint, and as a tendency
to this hue may be more[Pg 147] decided in large and strong object-glasses,
and under certain circumstances produce the compensatory red,
(which, however, in repeated experiments with several instruments of
this kind did not occur to us,) philosophers have resorted to the
most extraordinary modes of explaining such a result; and having
been compelled, in support of their system, theoretically to prove
the impossibility of achromatic telescopes, have felt a kind of
satisfaction in having some apparent ground for denying so great an
improvement. Of this, however, we can only treat circumstantially in
our historical account of these discoveries.
COMBINATION OF SUBJECTIVE AND OBJECTIVE EXPERIMENTS.
350.
Having shown above (318) that refraction, considered objectively and
subjectively, must act in opposite directions, it will follow that if
we combine the experiments, the effects will reciprocally destroy each
other.
351.
Let the sun's image be thrown upwards on a[Pg 148] vertical plane, through
a horizontally-placed prism. If the prism is long enough to admit of
the spectator also looking through it, he will see the image elevated
by the objective refraction again depressed, and in the same place in
which it appeared without refraction.
352.
Here a remarkable case presents itself, but at the same time a natural
result of a general law. For since, as often before stated, the
objective sun's image thrown on the vertical plane is not an ultimate
or unchangeable state of the phenomenon, so in the above operation the
image is not only depressed when seen through the prism, but its edges
and borders are entirely robbed of their hues, and the spectrum is
reduced to a colourless circular form.
353.
By employing two perfectly similar prisms placed next each other, for
this experiment, we can transmit the sun's image through one, and look
through the other.
354.
If the spectator advances nearer with the prism through which he looks,
the image is again elevated, and by degrees becomes coloured according
to the law of the first prism. If he[Pg 149] again retires till he has brought
the image to the neutralized point, and then retires still farther
away, the image, which had become round and colourless, moves still
more downwards and becomes coloured in the opposite sense, so that
if we look through the prism and upon the refracted spectrum at the
same time, we see the same image coloured according to subjective and
objective laws.
355.
The modes in which this experiment may be varied are obvious. If the
refracting angle of the prism, through which the sun's image was
objectively elevated, is greater than that of the prism through which
the observer looks, he must retire to a much greater distance, in order
to depress the coloured image so low on the vertical plane that it
shall appear colourless, and vice versâ.
356.
It will be easily seen that we may exhibit achromatic and
hyperchromatic effects in a similar manner, and we leave it to the
amateur to follow out such researches more fully. Other complicated
experiments in which prisms and lenses are employed together, others
again, in which objective and subjective experiments are variously
intermixed, we reserve for a future[Pg 150] occasion, when it will be our
object to trace such effects to the simple phenomena with which we are
now sufficiently familiar.
TRANSITION.
357.
In looking back on the description and analysis of dioptrical colours,
we do not repent either that we have treated them so circumstantially,
or that we have taken them into consideration before the other physical
colours, out of the order we ourselves laid down. Yet, before we quit
this branch of our inquiry, it may be as well to state the reasons that
have weighed with us.
358.
If some apology is necessary for having treated the theory of the
dioptrical colours, particularly those of the second class, so
diffusely, we should observe, that the exposition of any branch of
knowledge is to be considered partly with reference to the intrinsic
importance of the subject, and partly with reference to the particular
necessities of the time in which the[Pg 151] inquiry is undertaken. In our
own case we were forced to keep both these considerations constantly
in view. In the first place we had to state a mass of experiments with
our consequent convictions; next, it was our especial aim to exhibit
certain phenomena (known, it is true, but misunderstood, and above
all, exhibited in false connection,) in that natural and progressive
development which is strictly and truly conformable to observation; in
order that hereafter, in our polemical or historical investigations,
we might be enabled to bring a complete preparatory analysis to bear
on, and elucidate, our general view. The details we have entered into
were on this account unavoidable; they may be considered as a reluctant
consequence of the occasion. Hereafter, when philosophers will look
upon a simple principle as simple, a combined effect as combined; when
they will acknowledge the first elementary, and the second complicated
states, for what they are; then, indeed, all this statement may be
abridged to a narrower form; a labour which, should we ourselves
not be able to accomplish it, we bequeath to the active interest of
contemporaries and posterity.
359.
With respect to the order of the chapters, it should be remembered
that natural phenomena,[Pg 152] which are even allied to each other, are
not connected in any particular sequence or constant series; their
efficient causes act in a narrow circle, so that it is in some sort
indifferent what phenomenon is first or last considered; the main point
is, that all should be as far as possible present to us, in order that
we may embrace them at last from one point of view, partly according to
their nature, partly according to generally received methods.
360.
Yet, in the present particular instance, it may be asserted that the
dioptrical colours are justly placed at the head of the physical
colours; not only on account of their striking splendour and their
importance in other respects, but because, in tracing these to their
source, much was necessarily entered into which will assist our
subsequent enquiries.
361.
For, hitherto, light has been considered as a kind of abstract
principle, existing and acting independently; to a certain extent
self-modified, and on the slightest cause, producing colours out of
itself. To divert the votaries of physical science from this mode
of viewing the subject; to make them attentive to the fact, that in
prismatic and other appearances we have not to do[Pg 153] with light as an
uncircumscribed and modifying principle, but as circumscribed and
modified; that we have to do with a luminous image; with images or
circumscribed objects generally, whether light or dark: this was the
purpose we had in view, and such is the problem to be solved.
362.
All that takes place in dioptrical cases,—especially those of the
second class which are connected with the phenomena of refraction,—is
now sufficiently familiar to us, and will serve as an introduction to
what follows.
363.
Catoptrical appearances remind us of the physiological phenomena, but
as we ascribe a more objective character to the former, we thought
ourselves justified in classing them with the physical examples. It is
of importance, however, to remember that here again it is not light, in
an abstract sense, but a luminous image that we have to consider.
364.
In proceeding onwards to the paroptrical class, the reader, if duly
acquainted with the foregoing facts, will be pleased to find himself
once more in the region of circumscribed forms. The shadows of bodies,
especially, as secondary[Pg 154] images, so exactly accompanying the object,
will serve greatly to elucidate analogous appearances.
365.
We will not, however, anticipate these statements, but proceed as
heretofore in what we consider the regular course.
CATOPTRICAL COLOURS.
366.
Catoptrical colours are such as appear in consequence of a mirror-like
reflection. We assume, in the first place, that the light itself
as well as the surface from which it is reflected, is perfectly
colourless. In this sense the appearances in question come under the
head of physical colours. They arise in consequence of reflection, as
we found the dioptrical colours of the second class appear by means of
refraction. Without further general definitions, we turn our attention
at once to particular cases, and to the conditions which are essential
to the exhibition of these phenomena.
[Pg 155]
367.
If we unroll a coil of bright steel-wire, and after suffering it to
spring confusedly together again, place it at a window in the light,
we shall see the prominent parts of the circles and convolutions
illumined, but neither resplendent nor iridescent. But if the sun
shines on the wire, this light will be condensed into a point, and we
perceive a small resplendent image of the sun, which, when seen near,
exhibits no colour. On retiring a little, however, and fixing the eyes
on this refulgent appearance, we discern several small mirrored suns,
coloured in the most varied manner; and although the impression is that
green and red predominate, yet, on a more accurate inspection, we find
that the other colours are also present.
368.
If we take an eye-glass, and examine the appearance through it, we
find the colours have vanished, as well as the radiating splendour in
which they were seen, and we perceive only the small luminous points,
the repeated images of the sun. We thus find that the impression is
subjective in its nature, and that the appearance is allied to those
which we have adverted to under the name of radiating halos (100).
[Pg 156]
369.
We can, however, exhibit this phenomenon objectively. Let a piece
of white paper be fastened beneath a small aperture in the lid of a
camera-obscura, and when the sun shines through this aperture, let
the confusedly-rolled steel-wire be held in the light, so that it be
opposite to the paper. The sun-light will impinge on and in the circles
of the wire, and will not, as in the concentrating lens of the eye,
display itself in a point; but, as the paper can receive the reflection
of the light in every part of its surface will be seen in hair-like
lines, which are also iridescent.
370.
This experiment is purely catoptrical; for as we cannot imagine that
the light penetrates the surface of the steel, and thus undergoes a
change, we are soon convinced that we have here a mere reflection
which, in its subjective character, is connected with the theory of
faintly acting lights, and the after-image of dazzling lights, and as
far as it can be considered objective, announces even in the minutest
appearances, a real effect, independent of the action and reaction of
the eye.
371.
We have seen that to produce these effects[Pg 157] not merely light but a
powerful light is necessary; that this powerful light again is not an
abstract and general quality, but a circumscribed light, a luminous
image. We can convince ourselves still further of this by analogous
cases.
372.
A polished surface of silver placed in the sun reflects a dazzling
light, but in this case no colour is seen. If, however, we slightly
scratch the surface, an iridescent appearance, in which green and red
are conspicuous, will be exhibited at a certain angle. In chased and
carved metals the effect is striking: yet it may be remarked throughout
that, in order to its appearance, some form, some alternation of light
and dark must co-operate with the reflection; thus a window-bar,
the stem of a tree, an accidentally or purposely interposed object
produces a perceptible effect. This appearance, too, may be exhibited
objectively in the camera-obscura.
373.
If we cause a polished plated surface to be so acted on by aqua fortis
that the copper within is touched, and the surface itself thus rendered
rough, and if the sun's image be then reflected from it, the splendour
will be reverberated from every minutest prominence, and the surface
will appear iridescent. So, if we hold a sheet of[Pg 158] black unglazed paper
in the sun, and look at it attentively, it will be seen to glisten in
its minutest points with the most vivid colours.
374.
All these examples are referable to the same conditions. In the first
case the luminous image is reflected from a thin line; in the second
probably from sharp edges; in the third from very small points. In all
a very powerful and circumscribed light is requisite. For all these
appearances of colour again it is necessary that the eye should be at a
due distance from the reflecting points.
375.
If these observations are made with the microscope, the appearance
will be greatly increased in force and splendour, for we then see the
smallest portion of the surfaces, lit by the sun, glittering in these
colours of reflection, which, allied to the hues of refraction, now
attain their highest degree of brilliancy. In such cases we may observe
a vermiform iridescence on the surface of organic bodies, the further
description of which will be given hereafter.
376.
Lastly, the colours which are chiefly exhibited[Pg 159] in reflection are red
and green, whence we may infer that the linear appearance especially
consists of a thin line of red, bounded by blue on one side and yellow
on the other. If these triple lines approach very near together, the
intermediate space must appear green; a phenomenon which will often
occur to us as we proceed.
377.
We frequently meet with these colours in nature. The colours of the
spider's web might be considered exactly of the same class with those
reflected from the steel wire, except that the non-translucent quality
of the former is not so certain as in the case of steel; on which
account some have been inclined to class the colours of the spider's
web with the phenomena of refraction.
378.
In mother-of-pearl we perceive infinitely fine organic fibres and
lamellæ in juxta-position, from which, as from the scratched silver
before alluded to, varied colours, but especially red and green, may
arise.
379.
The changing colours of the plumage of birds may also be mentioned
here, although in all organic[Pg 160] instances a chemical principle
and an adaptation of the colour to the structure may be assumed;
considerations to which we shall return in treating of chemical colours.
380.
That the appearances of objective halos also approximate catoptrical
phenomena will be readily admitted, while we again do not deny that
refraction as well may here come into the account. For the present
we restrict ourselves to one or two observations; hereafter we may
be enabled to make a fuller application of general principles to
particular examples.
381.
We first call to mind the yellow and red circles produced on a white or
grey wall by a light placed near it (88). Light when reflected appears
subdued, and a subdued light excites the impression of yellow, and
subsequently of red.
382.
Let the wall be illumined by a candle placed quite close to it. The
farther the light is diffused the fainter it becomes; but it is still
the effect of the flame, the continuation of its action, the dilated
effect of its image. We might, therefore, very fairly call these
circles[Pg 161] reiterated images, because they constitute the successive
boundaries of the action of the light, and yet at the same time only
present an extended image of the flame.
383.
If the sky is white and luminous round the sun owing to the atmosphere
being filled with light vapours; if mists or clouds pass before the
moon, the reflection of the disk mirrors itself in them; the halos we
then perceive are single or double, smaller or greater, sometimes very
large, often colourless, sometimes coloured.
384.
I witnessed a very beautiful halo round the moon the 15th of November,
1799, when the barometer stood high; the sky was cloudy and vapoury.
The halo was completely coloured, and the circles were concentric round
the light as in subjective halos. That this halo was objective I was
presently convinced by covering the moon's disk, when the same circles
were nevertheless perfectly visible.
385.
The different extent of the halos appears to have a relation with the
proximity or distance of the vapour from the eye of the observer.
[Pg 162]
386.
As window-panes lightly breathed upon increase the brilliancy of
subjective halos, and in some degree give them an objective character,
so, perhaps, with a simple contrivance in winter, during a quickly
freezing temperature, a more exact definition of this might be arrived
at.
387.
How much reason we have in considering these circles to insist on the
image and its effects, is apparent in the phenomenon of the so-called
double suns. Similar double images always occur in certain points
of halos and circles, and only present in a circumscribed form what
takes place in a more general way in the whole circle. All this will
be more conveniently treated in connexion with the appearance of the
rainbow.—Note Q.
388.
In conclusion it is only necessary to point out the affinity between
the catoptrical and paroptical colours.
We call those paroptical colours which appear when the light passes
by the edge of an opaque colourless body. How nearly these are allied
to the dioptrical colours of the second class will be easily seen by
those who are convinced with us that the colours of refraction[Pg 163]
take place only at the edges of objects. The affinity again between the
catoptrical and paroptical colours will be evident in the following
chapter.
PAROPTICAL COLOURS.
389.
The paroptical colours have been hitherto called peri-optical, because
a peculiar effect of light was supposed to take place as it were round
the object, and was ascribed to a certain flexibility of the light to
and from the object.
390.
These colours again may be divided into subjective and objective,
because they appear partly without us, as it were, painted on surfaces,
and partly within us, immediately on the retina. In this chapter we
shall find it more to our purpose to take the objective cases first,
since the subjective are so closely connected with other appearances
already known to us, that it is hardly possible to separate them.
391.
The paroptical colours then are so called because[Pg 164] the light must pass
by an outline or edge to produce them. They do not, however, always
appear in this case; to produce the effect very particular conditions
are necessary besides.
392.
It is also to be observed that in this instance again light does not
act as an abstract diffusion (361), the sun shines towards an edge.
The volume of light poured from the sun-image passes by the edge of
a substance, and occasions shadows. Within these shadows we shall
presently find colours appear.
393.
But, above all, we should make the experiments and observations that
bear upon our present inquiry in the fullest light. We, therefore,
place the observer in the open air before we conduct him to the limits
of a dark room.
394.
A person walking in sun-shine in a garden, or on any level path, may
observe that his shadow only appears sharply defined next the foot on
which he rests; farther from this point, especially round the head, it
melts away into the bright ground. For as the sun-light proceeds not
only from the middle of the sun, but also acts cross-wise from the two
extremes of every[Pg 165] diameter, an objective parallax takes place which
produces a half-shadow on both sides of the object.
395.
If the person walking raises and spreads his hand, he distinctly sees
in the shadow of each finger the diverging separation of the two
half-shadows outwards, and the diminution of the principal shadow
inwards, both being effects of the cross action of the light.
396.
This experiment may be repeated and varied before a smooth wall,
with rods of different thicknesses, and again with balls; we shall
always find that the farther the object is removed from the surface of
the wall, the more the weak double shadow spreads, and the more the
forcible main shadow diminishes, till at last the main shadow appears
quite effaced, and even the double shadows become so faint, that they
almost disappear; at a still greater distance they are, in fact,
imperceptible.
397.
That this is caused by the cross-action of the light we may easily
convince ourselves; for the shadow of a pointed object plainly exhibits
two points. We must thus never lose sight of the[Pg 166] fact that in this
case the whole sun-image acts, produces shadows, changes them to double
shadows, and finally obliterates them.
398.
Instead of solid bodies let us now take openings cut of various given
sizes next each other, and let the sun shine through them on a plane
surface at some little distance; we shall find that the bright image
produced by the sun on the surface, is larger than the opening; this
is because one edge of the sun shines towards the opposite edge of the
opening, while the other edge of the disk is excluded on that side.
Hence the bright image is more weakly lighted towards the edges.
399.
If we take square openings of any size we please, we shall find that
the bright image on a surface nine feet from the opening, is on every
side about an inch larger than the opening; thus nearly corresponding
with the angle of the apparent diameter of the sun.
400.
That the brightness should gradually diminish towards the edges of the
image is quite natural, for at last only a minimum of the light can
act cross-wise from the sun's circumference through the edge of the
aperture.
[Pg 167]
401.
Thus we here again see how much reason we have in actual observation to
guard against the assumption of parallel rays, bundles and fasces of
rays, and the like hypothetical notions.
402.
We might rather consider the splendour of the sun, or of any light,
as an infinite specular multiplication of the circumscribed luminous
image, whence it may be explained that all square openings through
which the sun shines, at certain distances, according as the apertures
are greater or smaller, must give a round image of light.
403.
The above experiments may be repeated through openings of various
shapes and sizes, and the same effect will always take place at
proportionate distances. In all these cases, however, we may still
observe that in a full light and while the sun merely shines past an
edge, no colour is apparent.
404.
We therefore proceed to experiments with a subdued light, which is
essential to the appearance of colour. Let a small opening be made in
the window-shutter of a dark room; let the[Pg 168] crossing sun-light which
enters, be received on a surface of white paper, and we shall find that
the smaller the opening is, the dimmer the light image will be. This is
quite obvious, because the paper does not receive light from the whole
sun, but partially from single points of its disk.
405.
If we look attentively at this dim image of the sun, we find it still
dimmer towards the outlines where a yellow border is perceptible. The
colour is still more apparent if a vapour or a transparent cloud passes
before the sun, thus subduing and dimming its brightness. The halo on
the wall, the effect of the decreasing brightness of a light placed
near it, is here forced on our recollection. (88.)
406.
If we examine the image more accurately, we perceive that this yellow
border is not the only appearance of colour; we can see, besides, a
bluish circle, if not even a halo-like repetition of the coloured
border. If the room is quite dark, we discern that the sky next the
sun also has its effect: we see the blue sky, nay, even the whole
landscape, on the paper, and are thus again convinced that as far as
regards the sun, we have here only to do with a luminous image.
[Pg 169]
407.
If we take a somewhat larger square opening, so large that the image
of the sun shining through it does not immediately become round, we
may distinctly observe the half-shadows of every edge or side, the
junction of these in the corners, and their colours; just as in the
above-mentioned appearance with the round opening.
408.
We have now subdued a parallactic light by causing it to shine through
small apertures, but we have not taken from it its parallactic
character; so that it can produce double shadows of bodies, although
with diminished power. These double shadows which we have hitherto
been describing, follow each other in light and dark, coloured and
colourless circles, and produce repeated, nay, almost innumerable
halos. These effects have been often represented in drawings and
engravings. By placing needles, hairs, and other small bodies, in the
subdued light, the numerous halo-like double shadows may be increased;
thus observed, they have been ascribed to an alternating flexile action
of the light, and the same assumption has been employed to explain the
obliteration of the central shadow, and the appearance of a light in
the place of the dark.
[Pg 170]
409.
For ourselves, we maintain that these again are parallactic double
shadows, which appear edged with coloured borders and halos.
410.
After having seen and investigated the foregoing phenomena, we
can proceed to the experiments with knife-blades,[1] exhibiting
effects which may be referred to the contact and parallactic mutual
intersection of the half-shadows and halos already familiar to us.
411.
Lastly, the observer may follow out the experiments with hairs,
needles, and wires, in the half-light produced as before described by
the sun, as well as in that derived from the blue sky, and indicated on
the white paper. He will thus make himself still better acquainted with
the true nature of this phenomenon.
412.
But since in these experiments everything depends on our being
persuaded of the parallactic action of the light, we can make this more
evident by means of two sources of light, the two shadows from which
intersect each other, and may be altogether separated. By day this may
be contrived with two small[Pg 171] openings in a window-shutter; by night,
with two candles. There are even accidental effects in interiors, on
opening and closing shutters, by means of which we can better observe
these appearances than with the most careful apparatus. But still,
all and each of these may be reduced to experiment by preparing a box
which the observer can look into from above, and gradually diminishing
the openings after having caused a double light to shine in. In this
case, as might be expected, the coloured shadow, considered under the
physiological colours, appears very easily.
413.
It is necessary to remember, generally, what has been before stated
with regard to the nature of double shadows, half-lights, and the like.
Experiments also should especially be made with different shades of
grey placed next each other, where every stripe will appear light by a
darker, and dark by a lighter stripe next it. If at night, with three
or more lights, we produce shadows which cross each other successively,
we can observe this phenomenon very distinctly, and we shall be
convinced that the physiological case before more fully treated, here
comes into the account (38).
414.
To what extent the appearances that accompany[Pg 172] the paroptical colours,
may be derived from the doctrine of subdued lights, from half-shadows,
and from the physiological disposition of the retina, or whether we
shall be forced to take refuge in certain intrinsic qualities of light,
as has hitherto been done, time may teach. Suffice it here to have
pointed out the conditions under which the paroptical colours appear,
and we may hope that our allusion to their connexion with the facts
before adduced by us will not remain unnoticed by the observers of
nature.
415.
The affinity of the paroptical colours with the dioptrical of the
second class will also be readily seen and followed up by every
reflecting investigator. Here, as in those instances, we have to do
with edges or boundaries; here, as in those instances, with a light,
which appears at the outline. How natural, therefore, it is to conclude
that the paroptical effects may be heightened, strengthened, and
enriched by the dioptrical. Since, however, the luminous image actually
shines through the medium, we can here only have to do with objective
cases of refraction: it is these which are strictly allied to the
paroptical cases. The subjective cases of refraction, where we see
objects through the medium, are quite distinct from the paroptical.[Pg 173]
We have already recommended them on account of their clearness and
simplicity.
416.
The connexion between the paroptical colours and the catoptrical may
be already inferred from what has been said: for as the catoptrical
colours only appear on scratches, points, steel-wire, and delicate
threads, so it is nearly the same case as if the light shone past an
edge. The light must always be reflected from an edge in order to
produce colour. Here again, as before pointed out, the partial action
of the luminous image and the subduing of the light are both to be
taken into the account.
417.
We add but few observations on the subjective paroptical colours,
because these may be classed partly with the physiological colours,
partly with the dioptrical of the second order. The greater part hardly
seem to belong here, but, when attentively considered, they still
diffuse a satisfactory light over the whole doctrine, and establish its
connexion.
418.
If we hold a ruler before the eyes so that the flame of a light just
appears above it, we see the ruler as it were indented and notched
at the[Pg 174] place where the light appears. This seems deducible from the
expansive power of light acting on the retina (18).
419.
The same phenomenon on a large scale is exhibited at sun-rise; for when
the orb appears distinctly, but not too powerfully, so that we can
still look at it, it always makes a sharp indentation in the horizon.
420.
If, when the sky is grey, we approach a window, so that the dark cross
of the window-bars be relieved on the sky; if after fixing the eyes on
the horizontal bar we bend the head a little forward; on half closing
the eyes as we look up, we shall presently perceive a bright yellow-red
border under the bar, and a bright light-blue one above it. The duller
and more monotonous the grey of the sky, the more dusky the room, and,
consequently, the more previously unexcited the eye, the livelier the
appearance will be; but it may be seen by an attentive observer even in
bright daylight.
421.
If we move the head backwards while half closing the eyes, so that the
horizontal bar be seen below, the phenomenon will appear reversed.[Pg 175] The
upper edge will appear yellow, the under edge blue.
422.
Such observations are best made in a dark room. If white paper is
spread before the opening where the solar microscope is commonly
fastened, the lower edge of the circle will appear blue, the upper
yellow, even while the eyes are quite open, or only by half-closing
them so far that a halo no longer appears round the white. If the head
is moved backwards the colours are reversed.
423.
These phenomena seem to prove that the humours of the eye are in fact
only really achromatic in the centre where vision takes place, but that
towards the circumference, and in unusual motions of the eyes, as in
looking horizontally when the head is bent backwards or forwards, a
chromatic tendency remains, especially when distinctly relieved objects
are thus looked at. Hence such phenomena may be considered as allied to
the dioptrical colours of the second class.
424.
Similar colours appear if we look on black and white objects, through a
pin-hole in a card.[Pg 176] Instead of a white object we may take the minute
light aperture in the tin plate of a camera obscura, as prepared for
paroptical experiments.
425.
If we look through a tube, the farther end of which is contracted or
variously indented, the same colours appear.
426.
The following phenomena appear to me to be more nearly allied to the
paroptical appearances. If we hold up a needle near the eye, the point
appears double. A particularly remarkable effect again is produced if
we look towards a grey sky through the blades of knives prepared for
paroptical experiments. We seem to look through a gauze; a multitude of
threads appear to the eye; these are in fact only the reiterated images
of the sharp edges, each of which is successively modified by the next,
or perhaps modified in a parallactic sense by the oppositely acting
one, the whole mass being thus changed to a thread-like appearance.
427.
Lastly, it is to be remarked that if we look through the blades towards
a minute light in[Pg 177] the window-shutter, coloured stripes and halos
appear on the retina as on the paper.
428.
The present chapter may be here terminated, the less reluctantly,
as a friend has undertaken to investigate this subject by further
experiments. In our recapitulation, in the description of the
plates and apparatus, we hope hereafter to give an account of his
observations.[2]
EPOPTICAL COLOURS.
429.
We have hitherto had to do with colours which appear with vivacity, but
which immediately vanish again when certain conditions cease. We have
now to become acquainted with others, which it is true are still to be
considered as transient, but which, under certain circumstances, become
so fixed that, even after the conditions which first occasioned their
appearance cease, they still remain, and thus constitute[Pg 178] the link
between the physical and the chemical colours.
430.
They appear from various causes on the surface of a colourless body,
originally, without communication, die or immersion (βαφή); and we now
proceed to trace them, from their faintest indication to their most
permanent state, through the different conditions of their appearance,
which for easier survey we here at once summarily state.
431.
First condition.—The contact of two smooth surfaces of hard
transparent bodies.
First case: if masses or plates of glass, or if lenses are pressed
against each other.
Second case: if a crack takes place in a solid mass of glass, chrystal,
or ice.
Third case: if lamellæ of transparent stones become separated.
Second condition.—If a surface of glass or a polished stone is
breathed upon.
Third condition.—The combination of the two last; first, breathing on
the glass, then placing another plate of glass upon it, thus exciting
the colours by pressure; then removing the upper glass, upon which the
colours begin to fade and vanish with the breath.
[Pg 179]
Fourth condition.—Bubbles of various liquids, soap, chocolate, beer,
wine, fine glass bubbles.
Fifth condition.—Very fine pellicles and lamellæ, produced by the
decomposition of minerals and metals. The pellicles of lime, the
surface of stagnant water, especially if impregnated with iron, and
again pellicles of oil on water, especially of varnish on aqua fortis.
Sixth condition.—If metals are heated; the operation of imparting
tints to steel and other metals.
Seventh condition.—If the surface of glass is beginning to decompose.
432.
First condition, first case. If two convex glasses, or a convex and
plane glass, or, best of all, a convex and concave glass come in
contact, concentric coloured circles appear. The phenomenon exhibits
itself immediately on the slightest pressure, and may then be gradually
carried through various successive states. We will describe the
complete appearance at once, as we shall then be better enabled to
follow the different states through which it passes.
433.
The centre is colourless; where the glasses are, so to speak, united
in one by the strongest pressure, a dark grey point appears with a
silver[Pg 180] white space round it: then follow, in decreasing distances,
various insulated rings, all consisting of three colours, which are
in immediate contact with each other. Each of these rings, of which
perhaps three or four might be counted, is yellow on the inner side,
blue on the outer, and red in the centre. Between two rings there
appears a silver white interval. The rings which are farthest from the
centre are always nearer together: they are composed of red and green
without a perceptible white space between them.
434.
We will now observe the appearances in their gradual formation,
beginning from the slightest pressure.
435.
On the slightest pressure the centre itself appears of a green colour.
Then follow as far as the concentric circles extend, red and green
rings. They are wide, accordingly, and no trace of a silver white
space is to be seen between them. The green is produced by the blue of
an imperfectly developed circle, mixing with the yellow of the first
circle. All the remaining circles are, in this slight contact, broad;
their yellow and blue edges mix together, thus producing a beautiful
green. The red, however, of[Pg 181] each circle, remains pure and untouched;
hence the whole series is composed of these two colours.
436.
A somewhat stronger pressure separates the first circle by a slight
interval from the imperfectly developed one: it is thus detached, and
may be said to appear in a complete state. The centre is now a blue
point; for the yellow of the first circle is now separated from this
central point by a silver white space. From the centre of the blue a
red appears, which is thus, in all cases, bounded on the outside by
its blue edge. The second and third rings from the centre are quite
detached. Where deviations from this order present themselves, the
observer will be enabled to account for them, from what has been or
remains to be stated.
437.
On a stronger pressure the centre becomes yellow; this yellow is
surrounded by a red and blue edge: at last, the yellow also retires
from the centre; the innermost circle is formed and is bounded with
yellow. The whole centre itself now appears silver white, till at last,
on the strongest pressure, the dark point appears, and the phenomenon,
as described at first, is complete.
[Pg 182]
438.
The relative size of the concentric circles and their intervals depends
on the form of the glasses which are pressed together.
439.
We remarked above, that the coloured centre is, in fact, an undeveloped
circle. It is, however, often found, on the slightest pressure, that
several undeveloped circles exist there, as it were, in the germ; these
can be successively developed before the eye of the observer.
440.
The regularity of these rings is owing to the form of the convex
glasses, and the diameter of the coloured appearance depends on the
greater or lesser section of a circle on which a lens is polished. We
easily conclude from this, that by pressing plane glasses together,
irregular appearances only will be produced; the colours, in fact,
undulate like watered silks, and spread from the point of pressure in
all directions. Yet, the phenomenon as thus exhibited is much more
splendid than in the former instance, and cannot fail to strike every
spectator. If we make the experiment in this mode, we shall distinctly
see, as in the other case, that, on a slight pressure, the green and
red waves appear; on a stronger, stripes of blue, red, and yellow,
become detached.[Pg 183] At first, the outer sides of these stripes touch; on
increased pressure they are separated by a silver white space.
441.
Before we proceed to a further description of this phenomenon, we may
point out the most convenient mode of exhibiting it. Place a large
convex glass on a table near the window; upon this glass lay a plate
of well-polished mirror-glass, about the size of a playing-card, and
the mere weight of the plate will press sufficiently to produce one
or other of the phenomena above described. So, also, by the different
weight of plates of glass, by other accidental circumstances, for
instance, by slipping the plate on the side of the convex glass where
the pressure cannot be so strong as in the centre, all the gradations
above described can be produced in succession.
442.
In order to observe the phenomenon it is necessary to look obliquely
on the surface where it appears. But, above all, it is to be remarked
that by stooping still more, and looking at the appearance under a more
acute angle, the circles not only grow larger but other circles are
developed from the centre, of which no trace is to be discovered when
we look perpendicularly, even through the strongest magnifiers.
[Pg 184]
443.
In order to exhibit the phenomenon in its greatest beauty, the utmost
attention should be paid to the cleanness of the glasses. If the
experiment is made with plate-glass adapted for mirrors, the glass
should be handled with gloves. The inner surfaces, which must come in
contact with the utmost nicety, may be most conveniently cleaned before
the experiment, and the outer surfaces should be kept clean while the
pressure is increased.
444.
From what has been said it will be seen that an exact contact of two
smooth surfaces is necessary. Polished glasses are best adapted for the
purpose. Plates of glass exhibit the most brilliant colours when they
fit closely together, and for this reason the phenomenon will increase
in beauty if exhibited under an air-pump, by exhausting the air.
445.
The appearance of the coloured rings may be produced in the greatest
perfection by placing a convex and concave glass together which have
been ground on similar segments of circles. I have never seen the
effect more brilliant than with the object-glass of an achromatic
telescope,[Pg 185] in which the crown-glass and flint-glass were necessarily
in the closest contact.
446.
A remarkable appearance takes place when dissimilar surfaces are
pressed together; for example, a polished crystal and a plate of
glass. The appearance does not at all exhibit itself in large flowing
waves, as in the combination of glass with glass, but it is small and
angular, and, as it were, disjointed: thus it appears that the surface
of the polished crystal, which consists of infinitely small sections of
lamellæ, does not come so uninterruptedly in contact with the glass as
another glass-plate would.
447.
The appearance of colour vanishes on the strongest pressure, which so
intimately unites the two surfaces that they appear to make but one
substance. It is this which occasions the dark centre, because the
pressed lens no longer reflects any light from this point, for the
very same point, when seen against the light, is perfectly clear and
transparent. On relaxing the pressure, the colours, in like manner,
gradually diminish, and disappear entirely when the surfaces are
separated.
[Pg 186]
448.
These same appearances occur in two similar cases. If entirely
transparent masses become partially separated, the surfaces of their
parts being still sufficiently in contact, we see the same circles and
waves more or less. They may be produced in great beauty by plunging a
hot mass of glass in water; the different fissures and cracks enabling
us to observe the colours in various forms. Nature often exhibits the
same phenomena in split rock crystals.
449.
This appearance, again, frequently displays itself in the mineral world
in those kinds of stone which by nature have a tendency to exfoliate.
These original lamellæ are, it is true, so intimately united, that
stones of this kind appear altogether transparent and colourless, yet,
the internal layers become separated, from various accidental causes,
without altogether destroying the contact: thus the appearance, which
is now familiar to us by the foregoing description, often occurs in
nature, particularly in calcareous spars; the specularis, adularia, and
other minerals of similar structure. Hence it shows an ignorance of the
proximate causes of an appearance so often accidentally produced, to
consider it so important in mineralogy, and to attach especial value to
the specimens exhibiting it.
[Pg 187]
450.
We have yet to speak of the very remarkable inversion of this
appearance, as related by men of science. If, namely, instead of
looking at the colours by a reflected light, we examine them by a
transmitted light, the opposite colours are said to appear, and in
a mode corresponding with that which we have before described as
physiological; the colours evoking each other. Instead of blue, we
should thus see red-yellow; instead of red, green, &c., and vice
versâ. We reserve experiments in detail, the rather as we have
ourselves still some doubts on this point.
451.
If we were now called upon to give some general explanation of these
epoptical colours, as they appear under the first condition, and to
show their connexion with the previously detailed physical phenomena,
we might proceed to do so as follows:—
452.
The glasses employed for the experiments are to be regarded as the
utmost possible practical approach to transparence. By the intimate
contact, however, occasioned by the pressure applied to them, their
surfaces, we are persuaded, immediately become in a very slight
degree dimmed. Within this semi-transparence[Pg 188] the colours immediately
appear, and every circle comprehends the whole scale; for when the two
opposites, yellow and blue, are united by their red extremities, pure
red appears: the green, on the other hand, as in prismatic experiments,
when yellow and blue touch.
453.
We have already repeatedly found that where colour exists at all, the
whole scale is soon called into existence; a similar principle may be
said to lurk in the nature of every physical phenomenon; it already
follows, from the idea of polar opposition, from which an elementary
unity or completeness results.
454.
The fact that a colour exhibited by transmitted light is different
from that displayed by reflected light, reminds us of those dioptrical
colours of the first class which we found were produced precisely in
the same way through semi-opacity. That here, too, a diminution of
transparency exists there can scarcely be a doubt; for the adhesion
of the perfectly smooth plates of glass (an adhesion so strong that
they remain hanging to each other) produces a degree of union which
deprives each of the two surfaces, in some degree, of its smoothness
and transparence. The fullest proof may, however,[Pg 189] be found in the
fact that in the centre, where the lens is most strongly pressed on
the other glass, and where a perfect union is accomplished, a complete
transparence takes place, in which we no longer perceive any colour.
All this may be hereafter confirmed in a recapitulation of the whole.
455.
Second condition.—If after breathing on a plate of glass, the breath
is merely wiped away with the finger, and if we then again immediately
breathe on the glass, we see very vivid colours gliding through each
other; these, as the moisture evaporates, change their place, and at
last vanish altogether. If this operation is repeated, the colours are
more vivid and beautiful, and remain longer than they did the first
time.
456.
Quickly as this appearance passes, and confused as it appears to be, I
have yet remarked the following effects:—At first all the principal
colours appear with their combinations; on breathing more strongly, the
appearance may be perceived in some order. In this succession it may be
remarked, that when the breath in evaporating becomes contracted from
all sides[Pg 190] towards the centre, the blue colour vanishes last.
457.
The phenomenon appears most readily between the minute lines, which the
action of passing the fingers leaves on the clear surface; a somewhat
rough state of the surface of the glass is otherwise requisite. On
some glass the appearance may be produced by merely breathing; in
other cases the wiping with the fingers is necessary: I have even met
with polished mirror-glasses, one side of which immediately showed the
colours vividly; the other not. To judge from some remaining pieces,
the former was originally the front of the glass, the latter the side
which was covered with quicksilver.
458.
These experiments may be best made in cold weather, because the glass
may be more quickly and distinctly breathed upon, and the breath
evaporates more suddenly. In severe frost the phenomenon may be
observed on a large scale while travelling in a carriage; the glasses
being well cleaned, and all closed. The breath of the persons within is
very gently diffused over the glass, and immediately produces the most
vivid play of colours. How far they may present a regular succession I
have not been able to remark;[Pg 191] but they appear particularly vivid when
they have a dark object as a background. This alternation of colours
does not, however, last long; for as soon as the breath gathers in
drops, or freezes to points of ice, the appearance is at once at an end.
459.
Third condition.—The two foregoing experiments of the pressure and
breathing may be united; namely, by breathing on a plate of glass, and
immediately after pressing the other upon it. The colours then appear
as in the case of two glasses unbreathed upon, with this difference,
that the moisture occasions here and there an interruption of the
undulations. On pushing one glass away from the other the moisture
appears iridescent as it evaporates.
460.
It might, however, be asserted that this combined experiment exhibits
no more than each single experiment; for it appears the colours excited
by pressure disappear in proportion as the glasses are less in contact,
and the moisture then evaporates with its own colours.
461.
Fourth condition.—Iridescent appearances are observable in almost all
bubbles; soap-bubbles[Pg 192] are the most commonly known, and the effect in
question is thus exhibited in the easiest mode; but it may be observed
in wine, beer, in pure spirit, and again, especially, in the froth of
chocolate.
462.
As in the above cases we required an infinitely narrow space between
two surfaces which are in contact, so we can consider the pellicle
of the soap-bubble as an infinitely thin lamina between two elastic
bodies; for the appearance in fact takes place between the air within,
which distends the bubble, and the atmospheric air.
463.
The bubble when first produced is colourless; then coloured stripes,
like those in marble paper, begin to appear: these at length spread
over the whole surface, or rather are driven round it as it is
distended.
464.
In a single bubble, suffered to hang from the straw or tube, the
appearance of colour is difficult to observe, for the quick rotation
prevents any accurate observation, and all the colours seem to mix
together; yet we can perceive that the colours begin at the orifice of
the tube. The solution itself may, however, be blown into carefully,[Pg 193]
so that only one bubble shall appear. This remains white (colourless)
if not much agitated; but if the solution is not too watery, circles
appear round the perpendicular axis of the bubble; these being near
each other, are commonly composed alternately of green and red. Lastly,
several bubbles may be produced together by the same means; in this
case the colours appear on the sides where two bubbles have pressed
each other flat.
465.
The bubbles of chocolate-froth may perhaps be even more conveniently
observed than those of soap; though smaller, they remain longer. In
these, owing to the heat, an impulse, a movement, is produced and
sustained, which appears necessary to the development and succession of
the appearances.
466.
If the bubble is small, or shut in between others, coloured lines
chase each other over the surface, resembling marbled paper; all the
colours of the scale are seen to pass through each other; the pure, the
augmented, the combined, all distinctly clear and beautiful. In small
bubbles the appearance lasts for a considerable time.
[Pg 194]
467.
If the bubble is larger, or if it becomes by degrees detached, owing
to the bursting of others near, we perceive that this impulsion and
attraction of the colours has, as it were, an end in view; for on
the highest point of the bubble we see a small circle appear, which
is yellow in the centre; the other remaining coloured lines move
constantly round this with a vermicular action.
468.
In a short time the circle enlarges and sinks downwards on all sides;
in the centre the yellow remains; below and on the outside it becomes
red, and soon blue; below this again appears a new circle of the
same series of colours: if they approximate sufficiently, a green is
produced by the union of the border-colours.
469.
When I could count three such leading circles, the centre was
colourless, and this space became by degrees larger as the circles sank
lower, till at last the bubble burst.
470.
Fifth condition.—Very delicate pellicles may be formed in various
ways: on these films we discover a very lively play of colours, either
in the usual order, or more confusedly passing through each other. The
water in which lime[Pg 195] has been slaked soon skims over with a coloured
pellicle: the same happens on the surface of stagnant water, especially
if impregnated with iron. The lamellæ of the fine tartar which adheres
to bottles, especially in red French wine, exhibit the most brilliant
colours, on being exposed to the light, if carefully detached. Drops of
oil on water, brandy, and other fluids, produce also similar circles
and brilliant effects: but the most beautiful experiment that can be
made is the following:—Let aqua fortis, not too strong, be poured into
a flat saucer, and then with a brush drop on it some of the varnish
used by engravers to cover certain portions during the process of
biting their plates. After quick commotion there presently appears a
film which spreads itself out in circles, and immediately produces the
most vivid appearances of colour.
471.
Sixth condition.—When metals are heated, colours rapidly succeeding
each other appear on the surface: these colours can, however, be
arrested at will.
472.
If a piece of polished steel is heated, it will, at a certain degree
of warmth, be overspread with yellow. If taken suddenly away from the
fire, this yellow remains.
[Pg 196]
473.
As the steel becomes hotter, the yellow appears darker, intenser, and
presently passes into red. This is difficult to arrest, for it hastens
very quickly to bright blue.
474.
This beautiful blue is to be arrested if the steel is suddenly taken
out of the heat and buried in ashes. The blue steel works are produced
in this way. If, again, the steel is held longer over the fire, it soon
becomes a light blue, and so it remains.
475.
These colours pass like a breath over the plate of steel; each seems
to fly before the other, but, in reality, each successive hue is
constantly developed from the preceding one.
476.
If we hold a penknife in the flame of a light, a coloured stripe will
appear across the blade. The portion of the stripe which was nearest to
the flame is light blue; this melts into blue-red; the red is in the
centre; then follow yellow-red and yellow.
477.
This phenomenon is deducible from the preceding[Pg 197] ones; for the portion
of the blade next the handle is less heated than the end which is in
the flame, and thus all the colours which in other cases exhibited
themselves in succession, must here appear at once, and may thus be
permanently preserved.
478.
Robert Boyle gives this succession of colours as follows:—"A florido
flavo ad flavum saturum et rubescentem (quem artifices sanguineum
vocant) inde ad languidum, postea ad saturiorem cyaneum." This would be
quite correct if the words "languidus" and "saturior" were to change
places. How far the observation is correct, that the different colours
have a relation to the degree of temper which the metal afterwards
acquires, we leave to others to decide. The colours are here only
indications of the different degrees of heat.—Note R.
479.
When lead is calcined, the surface is first greyish. This greyish
powder, with greater heat, becomes yellow, and then orange. Silver,
too, exhibits colours when heated; the fracture of silver in the
process of refining belongs to the same class of examples. When
metallic glasses melt, colours in like manner appear on the surface.
[Pg 198]
480.
Seventh condition.—When the surface of glass becomes decomposed. The
accidental opacity (blindwerden) of glass has been already noticed: the
term (blindwerden) is employed to denote that the surface of the glass
is so affected as to appear dim to us.
481.
White glass becomes "blind" soonest; cast, and afterwards polished
glass is also liable to be so affected; the bluish less, the green
least.
482.
Of the two sides of a plate of glass one is called the mirror side;
it is that which in the oven lies uppermost, on which one may observe
roundish elevations: it is smoother than the other, which is undermost
in the oven, and on which scratches may be sometimes observed. On this
account the mirror side is placed facing the interior of rooms, because
it is less affected by the moisture adhering to it from within, than
the other would be, and the glass is thus less liable to become "blind."
483.
This half-opacity or dimness of the glass assumes by degrees an
appearance of colour which may become very vivid, and in which[Pg 199] perhaps
a certain succession, or otherwise regular order, might be discovered.
484.
Having thus traced the physical colours from their simplest effects to
the present instances, where these fleeting appearances are found to
be fixed in bodies, we are, in fact, arrived at the point where the
chemical colours begin; nay, we have in some sort already passed those
limits; a circumstance which may excite a favourable prejudice for the
consistency of our statement. By way of conclusion to this part of our
inquiry, we subjoin a general observation, which may not be without its
bearing on the common connecting principle of the phenomena that have
been adduced.
485.
The colouring of steel and the appearances analogous to it, might
perhaps be easily deduced from the doctrine of the semi-opaque mediums.
Polished steel reflects light powerfully: we may consider the colour
produced by the heat as a slight degree of dimness: hence a bright
yellow must immediately appear; this, as the dimness increases, must
still appear deeper, more condensed, and redder, and at last pure and
ruby-red. The colour has now reached the extreme point of depth, and
if we suppose the same degree[Pg 200] of semi-opacity still to continue, the
dimness would now spread itself over a dark ground, first producing a
violet, then a dark-blue, and at last a light-blue, and thus complete
the series of the appearances.
We will not assert that this mode of explanation will suffice in
all cases; our object is rather to point out the road by which the
all-comprehensive formula, the very key of the enigma, may be at last
discovered.—Note S.
[Pg 201]
CHEMICAL COLOURS.
486.
We give this denomination to colours which we can produce, and more
or less fix, in certain bodies; which we can render more intense,
which we can again take away and communicate to other bodies, and to
which, therefore, we ascribe a certain permanency: duration is their
prevailing characteristic.
487.
In this view the chemical colours were formerly distinguished with
various epithets; they were called colores proprii, corporei,
materiales, veri, permanentes, fixi.
488.
In the preceding chapter we observed how the fluctuating and transient
nature of the physical colours becomes gradually fixed, thus forming
the natural transition to our present subject.
489.
Colour becomes fixed in bodies more or less permanently; superficially,
or thoroughly.
490.
All bodies are susceptible of colour; it can[Pg 202] either be excited,
rendered intense, and gradually fixed in them, or at least communicated
to them.
CHEMICAL CONTRAST.
491.
In the examination of coloured appearances we had occasion everywhere
to take notice of a principle of contrast: so again, in approaching the
precincts of chemistry, we find a chemical contrast of a remarkable
nature. We speak here, with reference to our present purpose, only of
that which is comprehended under the general names of acid and alkali.
492.
We characterised the chromatic contrast, in conformity with all other
physical contrasts as a more and less; ascribing the plus to
the yellow side, the minus to the blue; and we now find that these
two divisions correspond with the chemical contrasts. The yellow and
yellow-red affect the acids, the blue and blue-red the alkalis; thus
the phenomena of chemical colours, although still necessarily mixed
up with[Pg 203] other considerations, admit of being traced with sufficient
simplicity.
493.
The principal phenomena in chemical colours are produced by the
oxydation of metals, and it will be seen how important this
consideration is at the outset. Other facts which come into the
account, and which are worthy of attention, will be examined under
separate heads; in doing this we, however, expressly state that we only
propose to offer some preparatory suggestions to the chemist in a very
general way, without entering into the nicer chemical problems and
questions, or presuming to decide on them. Our object is only to give a
sketch of the mode in which, according to our conviction, the chemical
theory of colours may be connected with general physics.
WHITE.
494.
In treating of the dioptrical colours of the first class (155) we
have already in some degree anticipated this subject. Transparent
substances[Pg 204] may be said to be in the highest class of inorganic matter.
With these, colourless semi-transparence is closely connected, and
white may be considered the last opaque degree of this.
495.
Pure water crystallised to snow appears white, for the transparence of
the separate parts makes no transparent whole. Various crystallised
salts, when deprived to a certain extent of moisture, appear as a white
powder. The accidentally opaque state of a pure transparent substance
might be called white; thus pounded glass appears as a white powder.
The cessation of a combining power, and the exhibition of the atomic
quality of the substance might at the same time be taken into the
account.
496.
The known undecomposed earths are, in their pure state, all white.
They pass to a state of transparence by natural crystallization. Silex
becomes rock-crystal; argile, mica; magnesia, talc; calcareous earth
and barytes appear transparent in various spars.—Note T.
497.
As in the colouring of mineral bodies the[Pg 205] metallic oxydes will often
invite our attention, we observe, in conclusion, that metals, when
slightly oxydated, at first appear white, as lead is converted to white
lead by vegetable acid.
BLACK.
498.
Black is not exhibited in so elementary a state as white. We meet
with it in the vegetable kingdom in semi-combustion; and charcoal, a
substance especially worthy of attention on other accounts, exhibits
a black colour. Again, if woods—for example, boards, owing to the
action of light, air, and moisture, are deprived in part of their
combustibility, there appears first the grey then the black colour. So
again, we can convert even portions of animal substance to charcoal by
semi-combustion.
499.
In the same manner we often find that a sub-oxydation takes place
in metals when the black colour is to be produced. Various metals,
particularly iron, become black by slight oxydation,[Pg 206] by vinegar, by
mild acid fermentations; for example, a decoction of rice, &c.
500.
Again, it may be inferred that a de-oxydation may produce black. This
occurs in the preparation of ink, which becomes yellow by the solution
of iron in strong sulphuric acid, but when partly de-oxydised by the
infusion of gall-nuts, appears black.
FIRST EXCITATION OF COLOUR.
501.
In the division of physical colours, where semi-transparent mediums
were considered, we saw colours antecedently to white and black. In the
present case we assume a white and black already produced and fixed;
and the question is, how colour can be excited in them?
502.
Here, too, we can say, white that becomes darkened or dimmed inclines
to yellow; black, as it becomes lighter, inclines to blue.—Note U.
[Pg 207]
503.
Yellow appears on the active (plus) side, immediately in the light, the
bright, the white. All white surfaces easily assume a yellow tinge;
paper, linen, wool, silk, wax: transparent fluids again, which have
a tendency to combustion, easily become yellow; in other words they
easily pass into a very slight state of semi-transparence.
504.
So again the excitement on the passive side, the tendency to obscure,
dark, black, is immediately accompanied with blue, or rather with a
reddish-blue. Iron dissolved in sulphuric acid, and much diluted with
water, if held to the light in a glass, exhibits a beautiful violet
colour as soon as a few drops only of the infusion of gall-nuts are
added. This colour presents the peculiar hues of the dark topaz, the
orphninon of a burnt-red, as the ancients expressed it.
505.
Whether any colour can be excited in the pure earths by the chemical
operations of nature and art, without the admixture of metallic oxydes,
is an important question, generally, indeed, answered in the negative.
It is perhaps connected with the question—to what extent[Pg 208] changes may
be produced in the earths through oxydation?
506.
Undoubtedly the negation of the above question is confirmed by the
circumstance that wherever mineral colours are found, some trace of
metal, especially of iron, shows itself; we are thus naturally led
to consider how easily iron becomes oxydised, how easily the oxyde
of iron assumes different colours, how infinitely divisible it is,
and how quickly it communicates its colour. It were to be wished,
notwithstanding, that new experiments could be made in regard to the
above point, so as either to confirm or remove any doubt.
507.
However this may be, the susceptibility of the earths with regard
to colours already existing is very great; aluminous earth is thus
particularly distinguished.
508.
In proceeding to consider the metals, which in the inorganic world
have the almost exclusive prerogative of appearing coloured, we find
that, in their pure, independent, natural state, they are already
distinguished from the[Pg 209] pure earths by a tendency to some one colour or
other.
509.
While silver approximates most to pure white,—nay, really represents
pure white, heightened by metallic splendour,—steel, tin, lead, and so
forth, incline towards pale blue-grey; gold, on the other hand, deepens
to pure yellow, copper approaches a red hue, which, under certain
circumstances, increases almost to bright red, but which again returns
to a yellow golden colour when combined with zinc.
510.
But if metals in their pure state have so specific a determination
towards this or that exhibition of colour, they are, through the effect
of oxydation, in some degree reduced to a common character; for the
elementary colours now come forth in their purity, and although this
or that metal appears to have a particular tendency to this or that
colour, we find some that can go through the whole circle of hues,
others, that are capable of exhibiting more than one colour; tin,
however, is distinguished by its comparative inaptitude to become
coloured. We propose to give a table hereafter, showing how far the
different metals can be more or less made to exhibit the different
colours.
[Pg 210]
511.
When the clean, smooth surface of a pure metal, on being heated,
becomes overspread with a mantling colour, which passes through a
series of appearances as the heat increases, this, we are persuaded,
indicates the aptitude of the metal to pass through the whole range of
colours. We find this phenomenon most beautifully exhibited in polished
steel; but silver, copper, brass, lead, and tin, easily present similar
appearances. A superficial oxydation is probably here taking place,
as may be inferred from the effects of the operation when continued,
especially in the more easily oxydizable metals.
512.
The same conclusion may be drawn from the fact that iron is more
easily oxydizable by acid liquids when it is red hot, for in this
case the two effects concur with each other. We observe, again, that
steel, accordingly as it is hardened in different stages of its
colorification, may exhibit a difference of elasticity: this is quite
natural, for the various appearances of colour indicate various degrees
of heat.[1]
513.
If we look beyond this superficial mantling,[Pg 211] this pellicle of colour,
we observe that as metals are oxydized throughout their masses, white
or black appears with the first degree of heat, as may be seen in white
lead, iron, and quicksilver.
514.
If we examine further, and look for the actual exhibition of colour,
we find it most frequently on the plus side. The mantling, so often
mentioned, of smooth metallic surfaces begins with yellow. Iron
passes presently into yellow ochre, lead from white lead to massicot,
quicksilver from æthiops to yellow turbith. The solutions of gold and
platinum in acids are yellow.
515.
The exhibitions on the minus side are less frequent. Copper slightly
oxydized appears blue. In the preparation of Prussian-blue, alkalis are
employed.
516.
Generally, however, these appearances of colour are of so mutable a
nature that chemists look upon them as deceptive tests, at least in the
nicer gradations. For ourselves, as we can only treat of these matters
in a general way, we merely observe that the appearances of colour in
metals may be classed according to their[Pg 212] origin, manifold appearance,
and cessation, as various results of oxydation, hyper-oxydation,
ab-oxydation, and de-oxydation.[2]
AUGMENTATION OF COLOUR.[1]
517.
The augmentation of colour exhibits itself as a condensation, a
fulness, a darkening of the hue. We have before seen, in treating of
colourless mediums, that by increasing the degree of opacity in the
medium, we can deepen a bright object from the lightest yellow to the
intensest ruby-red. Blue, on the other hand, increases to the most
beautiful violet, if we rarefy and diminish a semi-opaque medium,
itself lighted, but through which we see darkness (150, 151).
518.
If the colour is positive, a similar colour appears in the intenser
state. Thus if we fill a white porcelain cup with a pure yellow
liquor, the fluid will appear to become gradually redder[Pg 213] towards the
bottom, and at last appears orange. If we pour a pure blue solution
into another cup, the upper portion will exhibit a sky-blue, that
towards the bottom, a beautiful violet. If the cup is placed in the
sun, the shadowed side, even of the upper portion, is already violet.
If we throw a shadow with the hand, or any other substance, over the
illumined portion, the shadow in like manner appears reddish.
519.
This is one of the most important appearances connected with the
doctrine of colours, for we here manifestly find that a difference of
quantity produces a corresponding qualified impression on our senses.
In speaking of the last class of epoptical colours (452, 485), we
stated our conjecture that the colouring of steel might perhaps be
traced to the doctrine of the semi-transparent mediums, and we would
here again recall this to the reader's recollection.
520.
All chemical augmentation of colour, again, is the immediate
consequence of continued excitation. The augmentation advances
constantly and unremittingly, and it is to be observed that the
increase of intenseness is most common on the plus side. Yellow iron
ochre increases, as well by fire as by other operations, to a very[Pg 214]
strong red: massicot is increased to red lead, turbith to vermilion,
which last attains a very high degree of the yellow-red. An intimate
saturation of the metal by the acid, and its separation to infinity,
take place together with the above effects.
521.
The augmentation on the minus side is less frequent; but we observe
that the more pure and condensed the Prussian-blue or cobalt glass is
prepared, the more readily it assumes a reddish hue and inclines to the
violet.
522.
The French have a happy expression for the less perceptible tendency of
yellow and blue towards red: they say the colour has "un œil de rouge,"
which we might perhaps express by a reddish glance (einen röthlichen
blick).
CULMINATION[1]
523.
This is the consequence of still progressing augmentation. Red, in
which neither yellow nor[Pg 215] blue is to be detected, here constitutes the
acme.
524.
If we wish to select a striking example of a culmination on the plus
side, we again find it in the coloured steel, which attains the bright
red acme, and can be arrested at this point.
525.
Were we here to employ the terminology before proposed, we should
say that the first oxydation produces yellow, the hyper-oxydation
yellow-red; that here a kind of maximum exists, and that then an
ab-oxydation, and lastly a de-oxydation takes place.
526.
High degrees of oxydation produce a bright red. Gold in solution,
precipitated by a solution of tin, appears bright red: oxyde of
arsenic, in combination, with sulphur, produces a ruby colour.
527.
How far, however, a kind of sub-oxydation may co-operate in some
culminations, is matter for inquiry; for an influence of alkalis on[Pg 216]
yellow-red also appears to produce the culmination; the colour reaching
the acme by being forced towards the minus side.
528.
The Dutch prepare a colour known by the name of vermilion, from the
best Hungarian cinnabar, which exhibits the brightest yellow-red. This
vermilion is still only a cinnabar, which, however, approximates the
pure red, and it may be conjectured that alkalis are used to bring it
nearer to the culminating point.
529.
Vegetable juices, treated in this way, offer very striking examples of
the above effects. The colouring-matter of turmeric, annotto, dyer's
saffron,[2] and other vegetables, being extracted with spirits of wine,
exhibits tints of yellow, yellow-red, and hyacinth-red; these, by the
admixture of alkalis, pass to the culminating point, and even beyond it
to blue-red.
530.
No instance of a culmination on the minus side has come to my
knowledge in the mineral and vegetable kingdoms. In the animal
kingdom the juice of the murex is remarkable; of its augmentation and
culmination on the minus side, we shall hereafter have occasion to
speak.
FLUCTUATION.
531.
The mutability of colour is so great, that even those pigments, which
may have been considered to be defined and arrested, still admit of
slight variations on one side or the other. This mutability is most
remarkable near the culminating point, and is effected in a very
striking manner by the alternate employment of acids and alkalis.
532.
To express this appearance in dyeing, the French make use of the word
"virer," to turn from one side to the other; they thus very adroitly
convey an idea which others attempt to express by terms indicating the
component hues.
533.
The effect produced with litmus is one of the most known and striking
of this kind. This colouring substance is tendered red-blue by means of
alkalis. The red-blue is very readily changed to red-yellow by means
of acids, and again returns to its first state by again employing
alkalis. The question whether a culminating point is to be discovered
and arrested by[Pg 218] nice experiments, is left to those who are practised
in these operations. Dyeing, especially scarlet-dyeing, might afford a
variety of examples of this fluctuation.
PASSAGE THROUGH THE WHOLE SCALE.
534.
The first excitation and gradual increase of colour take place more on
the plus than on the minus side. So, also, in passing through the
whole scale, colour exhibits itself most on the plus side.
535.
A passage of this kind, regular and evident to the senses, from yellow
through red to blue, is apparent in the colouring of steel.
536.
The metals may be arrested at various points of the colorific circle by
various degrees and kinds of oxydation.
537.
As they also appear green, a question arises whether chemists know any
instance in the[Pg 219] mineral kingdom of a constant transition from yellow,
through green, to blue, and vice versâ. Oxyde of iron, melted with
glass, produces first a green, and with a more powerful heat, a blue
colour.
538.
We may here observe of green generally, that it appears, especially
in an atomic sense, and certainly in a pure state, when we mix blue
and yellow: but, again, an impure and dirty yellow soon gives us the
impression of green; yellow and black already produce green; this,
however, is owing to the affinity between black and blue. An imperfect
yellow, such as that of sulphur, gives us the impression of a greenish
hue: thus, again, an imperfect blue appears green. The green of wine
bottles arises, it appears, from an imperfect union of the oxyde of
iron with the glass. If we produce a more complete union by greater
heat, a beautiful blue-glass is the result.
539.
From all this it appears that a certain chasm exists in nature between
yellow and blue, the opposite characters of which, it is true, may be
done away atomically by due immixture, and, thus combined, to green;
but the true reconciliation between yellow and blue, it seems, only
takes place by means of red.
[Pg 220]
540.
The process, however, which appears unattainable in inorganic
substances, we shall find to be possible when we turn our attention to
organic productions; for in these, the passage through the whole circle
from yellow, through green and blue, to red, really takes place.
INVERSION.
541.
Again, an immediate inversion or change to the totally opposite hue, is
a very remarkable appearance which sometimes occurs; at present, we are
merely enabled to adduce what follows.
542.
The mineral chameleon, a name which has been given to an oxyde of
manganese, may be considered, in its perfectly dry state, as a green
powder. If we strew it in water, the green colour displays itself very
beautifully in the first moment of solution, but it changes presently
to the bright red opposite to green, without any apparent intermediate
state.
[Pg 221]
543.
The same occurs with the sympathetic ink, which may be considered a
reddish liquid, but which, when dried by warmth, appears as a green
colour on paper.
544.
In fact, this phenomenon appears to be owing to the conflict between
a dry and moist state, as has been already observed, if we are not
mistaken, by the chemists. We may look to the improvements of time to
point out what may further be deduced from these phenomena, and to show
what other facts they may be connected with.
FIXATION.
545.
Mutable as we have hitherto found colour to be, even as a substance,
yet under certain circumstances it may at last be fixed.
546.
There are bodies capable of being entirely converted into colouring
matter: here it may be said that the colour fixes itself in its own
substance,[Pg 222] stops at a certain point, and is there defined. Such
colouring substances are found throughout nature; the vegetable world
affords a great quantity of examples, among which some are particularly
distinguished, and may be considered as the representatives of the
rest; such as, on the active side, madder, on the passive side, indigo.
547.
In order to make these materials available in use, it is necessary
that the colouring quality in them should be intimately condensed, and
the tinging substance refined, practically speaking, to an infinite
divisibility. This is accomplished in various ways, and particularly by
the well-known means of fermentation and decomposition.
548.
These colouring substances now attach themselves again to other bodies.
Thus, in the mineral kingdom they adhere to earths and metallic oxydes;
they unite in melting with glasses; and in this case, as the light is
transmitted through them, they appear in the greatest beauty, while an
eternal duration may be ascribed to them.
549.
They fasten on vegetable and animal bodies with more or less power, and
remain more or less[Pg 223] permanently; partly owing to their nature,—as
yellow, for instance, is more evanescent than blue,—or owing to
the nature of the substance on which they appear. They last less in
vegetable than in animal substances, and even within this latter
kingdom there are again varieties. Hemp or cotton threads, silk or
wool, exhibit very different relations to colouring substances.
550.
Here comes into the account the important operation of employing
mordants, which may be considered as the intermediate agents between
the colour and the recipient substance; various works on dyeing speak
of this circumstantially. Suffice it to have alluded to processes by
means of which the colour retains a permanency only to be destroyed
with the substance, and which may even increase in brightness and
beauty by use.
INTERMIXTURE, REAL.
551.
Every intermixture pre-supposes a specific state of colour; and thus
when we speak of intermixture, we here understand it in an atomic[Pg 224]
sense. We must first have before us certain bodies arrested at any
given point of the colorific circle, before we can produce gradations
by their union.
552.
Yellow, blue, and red, may be assumed as pure elementary colours,
already existing; from these, violet, orange, and green, are the
simplest combined results.
553.
Some persons have taken much pains to define these intermixtures more
accurately, by relations of number, measure, and weight, but nothing
very profitable has been thus accomplished.
554.
Painting consists, strictly speaking, in the intermixture of
such specific colouring bodies and their infinite possible
combinations—combinations which can only be appreciated by the nicest,
most practised eye, and only accomplished under its influence.
555.
The intimate combination of these ingredients is effected, in the first
instance, through the most perfect comminution of the material by means
of grinding, washing, &c., as well as by vehicles[Pg 225] or liquid mediums
which hold together the pulverized substance, and combine organically,
as it were, the unorganic; such are the oils, resins, &c.—Note V.
556.
If all the colours are mixed together they retain their general
character as σκιερόν, and as they are no longer seen next each other,
no completeness, no harmony, is experienced; the result is grey, which,
like apparent colour, always appears somewhat darker than white, and
somewhat lighter than black.
557.
This grey may be produced in various ways. By mixing yellow and blue to
an emerald green, and then adding pure red, till all three neutralize
each other; or, by placing the primitive and intermediate colours next
each other in a certain proportion, and afterwards mixing them.
558.
That all the colours mixed together produce white, is an absurdity
which people have credulously been accustomed to repeat for a century,
in opposition to the evidence of their senses.
559.
Colours when mixed together retain their[Pg 226] original darkness. The darker
the colours, the darker will be the grey resulting from their union,
till at last this grey approaches black. The lighter the colours the
lighter will be the grey, which at last approaches white.
INTERMIXTURE, APPARENT.
560.
The intermixture, which is only apparent, naturally invites our
attention in connexion with the foregoing; it is in many respects
important, and, indeed, the intermixture which we have distinguished as
real, might be considered as merely apparent. For the elements of which
the combined colour consists are only too small to be considered as
distinct parts. Yellow and blue powders mingled together appear green
to the naked eye, but through a magnifying glass we can still perceive
yellow and blue distinct from each other. Thus yellow and blue stripes
seen at a distance, present a green mass; the same observation is
applicable with regard to the intermixture of other specific colours.
561.
In the description of our apparatus we shall[Pg 227] have occasion to mention
the wheel by means of which the apparent intermixture is produced by
rapid movement. Various colours are arranged near each other round
the edge of a disk, which is made to revolve with velocity, and thus
by having several such disks ready, every possible intermixture can
be presented to the eye, as well as the mixture of all colours to
grey, darker or lighter, according to the depth of the tints as above
explained.
562.
Physiological colours admit, in like manner, of being mixed with
others. If, for example, we produce the blue shadow (65) on a light
yellow paper, the surface will appear green. The same happens with
regard to the other colours if the necessary preparations are attended
to.
563.
If, when the eye is impressed with visionary images that last for a
while, we look on coloured surfaces, an intermixture also takes place;
the spectrum is determined to a new colour which is composed of the two.
564.
Physical colours also admit of combination. Here might be adduced the
experiments in[Pg 228] which many-coloured images are seen through the prism,
as we have before shown in detail (258, 284).
565.
Those who have prosecuted these inquiries have, however, paid most
attention to the appearances which take place when the prismatic
colours are thrown on coloured surfaces.
566.
What is seen under these circumstances is quite simple. In the first
place it must be remembered that the prismatic colours are much more
vivid than the colours of the surface on which they are thrown.
Secondly, we have to consider that the prismatic colours may be either
homogeneous or heterogeneous, with the recipient surface. In the former
case the surface deepens and enhances them, and is itself enhanced in
return, as a coloured stone is displayed by a similarly coloured foil.
In the opposite case each vitiates, disturbs, and destroys the other.
567.
These experiments may be repeated with coloured glasses, by causing the
sun-light to shine through them on coloured surfaces. In every instance
similar results will appear.
[Pg 229]
568.
The same effect takes place when we look on coloured objects through
coloured glasses; the colours being thus according to the same
conditions enhanced, subdued, or neutralized.
569.
If the prismatic colours are suffered to pass through coloured glasses,
the appearances that take place are perfectly analogous; in these cases
more or less force, more or less light and dark, the clearness and
cleanness of the glass are all to be allowed for, as they produce many
delicate varieties of effect: these will not escape the notice of every
accurate observer who takes sufficient interest in the inquiry to go
through the experiments.
570.
It is scarcely necessary to mention that several coloured glasses, as
well as oiled or transparent papers, placed over each other, may be
made to produce and exhibit every kind of intermixture at pleasure.
571.
Lastly, the operation of glazing in painting belongs to this kind of
intermixture; by this means a much more refined union may be produced
than that arising from the mechanical, atomic mixture which is commonly
employed.
[Pg 230]
COMMUNICATION, ACTUAL.
572.
Having now provided the colouring materials, as before shown, a further
question arises how to communicate these to colourless substances:
the answer is of the greatest importance from the connexion of the
object with the ordinary wants of men, with useful purposes, and with
commercial and technical interests.
573.
Here, again, the dark quality of every colour again comes into the
account. From a yellow, that is very near to white, through orange,
and the hue of minium to pure red and carmine, through all gradations
of violet to the deepest blue which is almost identified with black,
colour still increases in darkness. Blue once defined, admits of
being diluted, made light, united with yellow, and then, as green,
it approaches the light side of the scale: but this is by no means
according to its own nature.
574.
In the physiological colours we have already seen that they are less
than the light, inasmuch[Pg 231] as they are a repetition of an impression
of light, nay, at last they leave this impression quite as a dark. In
physical experiments the employment of semi-transparent mediums, the
effect of semi-transparent accessory images, taught us that in such
cases we have to do with a subdued light, with a transition to darkness.
575.
In treating of the chemical origin of pigments we found that the same
effect was produced on the very first excitement. The yellow tinge
which mantles over the steel, already darkens the shining surface. In
changing white lead to massicot it is evident that the yellow is darker
than white.
576.
This process is in the highest degree delicate; the growing
intenseness, as it still increases, tinges the substance more and more
intimately and powerfully, and thus indicates the extreme fineness, and
the infinite divisibility of the coloured atoms.
577.
The colours which approach the dark side, and consequently, blue in
particular, can be made to approximate to black; in fact, a very
perfect Prussian blue, or an indigo acted on by vitriolic acid appears
almost as a black.
[Pg 232]
578.
A remarkable appearance may be here adverted to; pigments, in their
deepest and most condensed state, especially those produced from
the vegetable kingdom, such as the indigo just mentioned, or madder
carried to its intensest hue, no longer show their own colour; on the
contrary, a decided metallic shine is seen on their surface, in which
the physiological compensatory colour appears.
579.
All good indigo exhibits a copper-colour in its fracture, a
circumstance attended to, as a known characteristic, in trade. Again,
the indigo which has been acted on by sulphuric acid, if thickly laid
on, or suffered to dry so that neither white paper nor the porcelain
can appear through, exhibits a colour approaching to orange.
580.
The bright red Spanish rouge, probably prepared from madder, exhibits
on its surface a perfectly green, metallic shine. If this colour, or
the blue before mentioned, is washed with a pencil on porcelain or
paper, it is seen in its real state owing to the bright ground shining
through.
581.
Coloured liquids appear black when no light[Pg 233] is transmitted through
them, as we may easily see in cubic tin vessels with glass bottoms.
In these every transparent-coloured infusion will appear black and
colourless if we place a black surface under them.
582.
If we contrive that the image of a flame be reflected from the bottom,
the image will appear coloured. If we lift up the vessel and suffer the
transmitted light to fall on white paper under it, the colour of the
liquid appears on the paper. Every light ground seen through such a
coloured medium exhibits the colour of the medium.
583.
Thus every colour, in order to be seen, must have a light within or
behind it. Hence the lighter and brighter the grounds are, the more
brilliant the colours appear. If we pass lac-varnish over a shining
white metal surface, as the so-called foils are prepared, the splendour
of the colour is displayed by this internally reflected light as
powerfully as in any prismatic experiment; nay, the force of the
physical colours is owing principally to the circumstance that light is
always acting with and behind them.
584.
Lichtenberg, who of necessity followed the[Pg 234] received theory, owing
to the time and circumstances in which he lived, was yet too good an
observer, and too acute not to explain and classify, after his fashion,
what was evident to his senses. He says, in the preface to Delaval,
"It appears to me also, on other grounds, probable, that our organ, in
order to be impressed by a colour, must at the same time be impressed
by all light (white)."
585.
To procure white as a ground is the chief business of the dyer. Every
colour may be easily communicated to colourless earths, especially
to alum: but the dyer has especially to do with animal and vegetable
products as the ground of his operations.
586.
Everything living tends to colour—to local, specific colour, to
effect, to opacity—pervading the minutest atoms. Everything in which
life is extinct approximates to white (494), to the abstract, the
general state, to clearness[1], to transparence.
587.
How this is put in practice in technical operations remains to be
adverted to in the chapter on the privation of colour. With regard
to the[Pg 235] communication of colour, we have especially to bear in mind
that animals and vegetables, in a living state, produce colours, and
hence their substances, if deprived of colours, can the more readily
re-assume them.
COMMUNICATION, APPARENT.
588.
The communication of colours, real as well as apparent, corresponds, as
may easily be seen, with their intermixture: we need not, therefore,
repeat what has been already sufficiently entered into.
589.
Yet we may here point out more circumstantially the importance of an
apparent communication which takes place by means of reflection. This
phenomenon is well known, but still it is pregnant with inferences, and
is of the greatest importance both to the investigator of nature and to
the painter.
590.
Let a surface coloured with any one of the positive colours be placed
in the sun, and let its[Pg 236] reflection be thrown on other colourless
objects. This reflection is a kind of subdued light, a half-light,
a half-shadow, which, in a subdued state, reflects the colours in
question.
591.
If this reflection acts on light surfaces, it is so far overpowered
that we can scarcely perceive the colour which accompanies it; but if
it acts on shadowed portions, a sort of magical union takes place with
the σκιερῷ. Shadow is the proper element of colour, and in this case
a subdued colour approaches it, lighting up, tinging, and enlivening
it. And thus arises an appearance, as powerful as agreeable, which may
render the most pleasing service to the painter who knows how to make
use of it. These are the types of the so-called reflexes, which were
only noticed late in the history of art, and which have been too seldom
employed in their full variety.
592.
The schoolmen called these colours colores notionales and
intentionales, and the history of the doctrine of colours will
generally show that the old inquirers already observed the phenomena
well enough, and knew how to distinguish them properly, although the
whole method of treating such subjects is very different from ours.
[Pg 237]
EXTRACTION.
593.
Colour may be extracted from substances, whether they possess it
naturally or by communication, in various ways. We have thus the power
to remove it intentionally for a useful purpose, but, on the other
hand, it often flies contrary to our wish.
594.
Not only are the elementary earths in their natural state white, but
vegetable and animal substances can be reduced to a white state without
disturbing their texture. A pure white is very desirable for various
uses, as in the instance of our preferring to use linen and cotton
stuffs uncoloured. In like manner some silk stuffs, paper, and other
substances, are the more agreeable the whiter they can be. Again,
the chief basis of all dyeing consists in white grounds. For these
reasons manufacturers, aided by accident and contrivance, have devoted
themselves assiduously to discover means of extracting colour: infinite
experiments have been made in connexion with this object, and many
important facts have been arrived at.
[Pg 238]
595.
It is in accomplishing this entire extraction of colour that the
operation of bleaching consists, which is very generally practised
empirically or methodically. We will here shortly state the leading
principles.
596.
Light is considered as one of the first means of extracting colour
from substances, and not only the sun-light, but the mere powerless
day-light: for as both lights—the direct light of the sun, as well as
the derived light of the sky—kindle Bologna phosphorus, so both act on
coloured surfaces. Whether the light attacks the colour allied to it,
and, as it were, kindles and consumes it, thus reducing the definite
quality to a general state, or whether some other operation, unknown
to us, takes place, it is clear that light exercises a great power on
coloured surfaces, and bleaches them more or less. Here, however, the
different colours exhibit a different degree of durability; yellow,
especially if prepared from certain materials, is, in this case, the
first to fly.
597.
Not only light, but air, and especially water, act strongly in
destroying colour. It has been even asserted that thread, well soaked
and[Pg 239] spread on the grass at night, bleaches better than that which is
exposed, after soaking, to the sun-light. Thus, in this case, water
proves to be a solving and conducting agent, removing the accidental
quality, and restoring the substance to a general or colourless state.
598.
The extraction of colour is also effected by re-agents. Spirits of wine
has a peculiar tendency to attract the juice which tinges plants, and
becomes coloured with it often in a very permanent manner. Sulphuric
acid is very efficient in removing colour, especially from wool and
silk, and every one is acquainted with the use of sulphur vapours in
bleaching.
599.
The strongest acids have been recommended more recently as more
expeditious agents in bleaching.
600.
The alkaline re-agents produce the same effects by contrary
means—lixiviums alone, oils and fat combined with lixiviums to soap,
and so forth.
601.
Before we dismiss this subject, we observe [Pg 240] that it may be
well worth while to make certain delicate experiments as to how far
light and air exhibit their action in the removal of colour. It might
be possible to expose coloured substances to the light under glass
bells, without air, or filled with common or particular kinds of air.
The colours might be those of known fugacity, and it might be observed
whether any of the volatilized colour attached itself to the glass or
was otherwise perceptible as a deposit or precipitate; whether, again,
in such a case, this appearance would be perfectly like that which had
gradually ceased to be visible, or whether it had suffered any change.
Skilful experimentalists might devise various contrivances with a view
to such researches.
602.
Having thus first considered the operations of nature as subservient to
our proposes, we add a few observations on the modes in which they act
against us.
603.
The art of painting is so circumstanced that the most beautiful results
of mind and labour are altered and destroyed in various ways by time.
Hence great pains have been always taken to find durable pigments, and
so to unite them with each other and with their ground, that their[Pg 241]
permanency might be further insured. The technical history of the
schools of painting affords sufficient information on this point.
604.
We may here, too, mention a minor art, to which, in relation to
dyeing, we are much indebted, namely, the weaving of tapestry. As the
manufacturers were enabled to imitate the most delicate shades of
pictures, and hence often brought the most variously coloured materials
together, it was soon observed that the colours were not all equally
durable, but that some faded from the tapestry more quickly than
others. Hence the most diligent efforts were made to ensure an equal
permanency to all the colours and their gradations. This object was
especially promoted in France, under Colbert, whose regulations to this
effect constitute an epoch in the history of dyeing. The gay dye which
only aimed at a transient beauty, was practised by a particular guild.
On the other hand, great pains were taken to define the technical
processes which promised durability.
And thus, after considering the artificial extraction, the evanescence,
and the perishable nature of brilliant appearances of colour, we are
again returned to the desideratum of permanency.
[Pg 242]
NOMENCLATURE.
605.
After what has been adduced respecting the origin, the increase,
and the affinity of colours, we may be better enabled to judge what
nomenclature would be desirable in future, and what might be retained
of that hitherto in use.
606.
The nomenclature of colours, like all other modes of designation,
but especially those employed to distinguish the objects of sense,
proceeded in the first instance from particular to general, and from
general back again to particular terms. The name of the species became
a generic name to which the individual was again referred.
607.
This method might have been followed in consequence of the mutability
and uncertainty of ancient modes of expression, especially since, in
the early ages, more reliance may be supposed to have been placed on
the vivid impressions of sense. The qualities of objects were described
indistinctly, because they were impressed clearly on every imagination.
[Pg 243]
608.
The pure chromatic circle was limited, it is true; but, specific as it
was, it appears to have been applied to innumerable objects, while it
was circumscribed by qualifying characteristics. If we take a glance
at the copiousness of the Greek and Roman terms, we shall perceive how
mutable the words were, and how easily each was adapted to almost every
point in the colorific circle.—Note W.
609.
In modern ages terms for many new gradations were introduced in
consequence of the various operations of dyeing. Even the colours
of fashion and their designations, represented an endless series of
specific hues. We shall, on occasion, employ the chromatic terminology
of modern languages, whence it will appear that the aim has gradually
been to introduce more exact definitions, and to individualise and
arrest a fixed and specific state by language equally distinct.
610.
With regard to the German terminology, it has the advantage of
possessing four monosyllabic names no longer to be traced to their
origin, viz., yellow (Gelb), blue, red, green. They represent the most
general idea of colour to the imagination, without reference to any
very specific modification.
[Pg 244]
611.
If we were to add two other qualifying terms to each of these four, as
thus—red-yellow, and yellow-red, red-blue and blue-red, yellow-green
and green-yellow, blue-green and green-blue,[1] we should express the
gradations of the chromatic circle with sufficient distinctness; and if
we were to add the designations of light and dark, and again define, in
some measure, the degree of purity or its opposite by the monosyllables
black, white, grey, brown, we should have a tolerably sufficient range
of expressions to describe the ordinary appearances presented to us,
without troubling ourselves whether they were produced dynamically or
atomically.
612.
The specific and proper terms in use might, however, still be
conveniently employed, and we have thus made use of the words orange
and violet. We have in like manner employed the word "purpur" to
designate a pure central red, because the secretion of the murex or
"purpura" is to be carried to the highest point of culmination by the
action of the sun-light on fine linen saturated with the juice.
MINERALS.
613.
The colours of minerals are all of a chemical nature, and thus the
modes in which they are produced may be explained in a general way by
what has been said on the subject of chemical colours.
614.
Among the external characteristics of minerals, the description of
their colours occupies the first place; and great pains have been
taken, in the spirit of modern times, to define and arrest every
such appearance exactly: by this means, however, new difficulties,
it appears to us, have been created, which occasion no little
inconvenience in practice.
615.
It is true, this precision, when we reflect how it arose, carries with
it its own excuse. The painter has at all times been privileged in
the use of colours. The few specific hues, in themselves, admitted of
no change; but from these, innumerable gradations were artificially
produced which imitated the surface of natural objects. It was,
therefore, not to be wondered[Pg 246] at that these gradations should also be
adopted as criterions, and that the artist should be invited to produce
tinted patterns with which the objects of nature might be compared, and
according to which they were to receive their designations.
616.
But, after all, the terminology of colours which has been introduced in
mineralogy, is open to many objections. The terms, for instance, have
not been borrowed from the mineral kingdom, as was possible enough in
most cases, but from all kinds of visible objects. Too many specific
terms have been adopted; and in seeking to establish new definitions
by combining these, the nomenclators have not reflected that they thus
altogether efface the image from the imagination, and the idea from
the understanding. Lastly, these individual designations of colours,
employed to a certain extent as elementary definitions, are not
arranged in the best manner as regards their respective derivation from
each other: hence, the scholar must learn every single designation,
and impress an almost lifeless but positive language on his memory.
The further consideration of this would be too foreign to our present
subject.[1]
PLANTS.
617.
The colours of organic bodies in general may be considered as a higher
kind of chemical operation, for which reason the ancients employed the
word concoction, πέψις, to designate the process. All the elementary
colours, as well as the combined and secondary hues, appear on the
surface of organic productions, while on the other hand, the interior,
if not colourless, appears, strictly speaking, negative when brought to
the light. As we propose to communicate our views respecting organic
nature, to a certain extent, in another place, we only insert here
what has been before connected with the doctrine of colours, while it
may serve as an introduction to the further consideration of the views
alluded to: and first, of plants.
618.
Seeds, bulbs, roots, and what is generally shut out from the light, or
immediately surrounded by the earth, appear, for the most part, white.
619.
Plants reared from seed, in darkness, are white, or approaching to
yellow. Light, on the[Pg 248] other hand, in acting on their colours, acts at
the same time on their form.
620.
Plants which grow in darkness make, it is true, long shoots from joint
to joint: but the stems between two joints are thus longer than they
should be; no side stems are produced, and the metamorphosis of the
plant does not take place.
621.
Light, on the other hand, places it at once in an active state; the
plant appears green, and the course of the metamorphosis proceeds
uninterruptedly to the period of reproduction.
622.
We know that the leaves of the stem are only preparations and
pre-significations of the instruments of florification and
fructification, and accordingly we can already see colours in the
leaves of the stem which, as it were, announce the flower from afar, as
is the case in the amaranthus.
623.
There are white flowers whose petals have wrought or refined themselves
to the greatest purity; there are coloured ones, in which the[Pg 249]
elementary hues may be said to fluctuate to and fro. There are some
which, in tending to the higher state, have only partially emancipated
themselves from the green of the plant.
624.
Flowers of the same genus, and even of the same kind, are found of all
colours. Roses, and particularly mallows, for example, vary through
a great portion of the colorific circle from white to yellow, then
through red-yellow to bright red, and from thence to the darkest hue it
can exhibit as it approaches blue.
625.
Others already begin from a higher degree in the scale, as, for
example, the poppy, which is yellow-red in the first instance, and
which afterwards approaches a violet hue.
626.
Yet the same colours in species, varieties, and even in families and
classes, if not constant, are still predominant, especially the yellow
colour: blue is throughout rarer.
627.
A process somewhat similar takes place in the juicy capsule of
the fruit, for it increases in colour from the green, through the
yellowish[Pg 250] and yellow, up to the highest red, the colour of the rind
thus indicating the degree of ripeness. Some are coloured all round,
some only on the sunny side, in which last case the augmentation of the
yellow into red,—the gradations crowding in and upon each other,—may
be very well observed.
628.
Many fruits, too, are coloured internally; pure red juices, especially,
are common.
629.
The colour which is found superficially in the flower and penetratingly
in the fruit, spreads itself through all the remaining parts, colouring
the roots and the juices of the stem, and this with a very rich and
powerful hue.
630.
So, again, the colour of the wood passes from yellow through the
different degrees of red up to pure red and on to brown. Blue woods are
unknown to me; and thus in this degree of organisation the active side
exhibits itself powerfully, although both principles appear balanced in
the general green of the plant.
631.
We have seen above that the germ pushing[Pg 251] from the earth is generally
white and yellowish, but that by means of the action of light and air
it acquires a green colour. The same happens with young leaves of
trees, as may be seen, for example, in the birch, the young leaves of
which are yellowish, and if boiled, yield a beautiful yellow juice:
afterwards they become greener, while the leaves of other trees become
gradually blue-green.
632.
Thus a yellow ingredient appears to belong more essentially to leaves
than a blue one; for this last vanishes in the autumn, and the yellow
of the leaf appears changed to a brown colour. Still more remarkable,
however, are the particular cases where leaves in autumn again become
pure yellow, and others increase to the brightest red.
633.
Other plants, again, may, by artificial treatment be entirely converted
to a colouring matter, which is as fine, active, and infinitely
divisible as any other. Indigo and madder, with which so much is
effected, are examples: lichens are also used for dyes.
634.
To this fact another stands immediately opposed;[Pg 252] we can, namely,
extract the colouring part of plants, and, as it were, exhibit it
apart, while the organisation does not on this account appear to suffer
at all. The colours of flowers may be extracted by spirits of wine, and
tinge it; the petals meanwhile becoming white.
635.
There are various modes of acting on flowers and their juices by
re-agents. This has been done by Boyle in many experiments. Roses are
bleached by sulphur, and may be restored to their first state by other
acids; roses are turned green by the smoke of tobacco.
WORMS, INSECTS, FISHES.
636.
With regard to creatures belonging to the lower degrees of
organisation, we may first observe that worms, which live in the earth
and remain in darkness and cold moisture, are imperfectly negatively
coloured; worms bred in warm moisture and darkness are colourless;
light seems expressly necessary to the definite exhibition of colour.
[Pg 253]
637.
Creatures which live in water, which, although a very dense medium,
suffers sufficient light to pass through it, appear more or less
coloured. Zoophytes, which appear to animate the purest calcareous
earth, are mostly white; yet we find corals deepened into the most
beautiful yellow-red: in other cells of worms this colour increases
nearly to bright red.
638.
The shells of the crustaceous tribe are beautifully designed and
coloured, yet it is to be remarked that neither land-snails nor the
shells of crustacea of fresh water, are adorned with such bright
colours as those of the sea.
639.
In examining shells, particularly such as are spiral, we find that
a series of animal organs, similar to each other, must have moved
increasingly forward, and in turning on an axis produced the shell in
a series of chambers, divisions, tubes, and prominences, according to
a plan for ever growing larger. We remark, however, that a tinging
juice must have accompanied the development of these organs, a juice
which marked the surface of the shell, probably through the immediate
co-operation of the sea-water, with coloured lines, points, spots, and
shadings:[Pg 254] this must have taken place at regular intervals, and thus
left the indications of increasing growth lastingly on the exterior;
meanwhile the interior is generally found white or only faintly
coloured.
640.
That such a juice is to be found in shell-fish is, besides,
sufficiently proved by experience; for the creatures furnish it in its
liquid and colouring state: the juice of the ink-fish is an example.
But a much stronger is exhibited in the red juice found in many
shell-fish, which was so famous in ancient times, and has been employed
with advantage by the moderns. There is, it appears, in the entrails of
many of the crustaceous tribe a certain vessel which is filled with a
red juice; this contains a very strong and durable colouring substance,
so much so that the entire creature may be crushed and boiled, and
yet out of this broth a sufficiently strong tinging liquid may be
extracted. But the little vessel filled with colour may be separated
from the animal, by which means of course a concentrated juice is
gained.
641.
This juice has the property that when exposed to light and air it
appears first yellowish, then greenish; it then passes to blue, then to
a[Pg 255] violet, gradually growing redder; and lastly, by the action of the
sun, and especially if transferred to cambric, it assumes a pure bright
red colour.
642.
Thus we should here have an augmentation, even to culmination, on the
minus side, which we cannot easily meet with in inorganic cases;
indeed, we might almost call this example a passage through the
whole scale, and we are persuaded that by due experiments the entire
revolution of the circle might really be effected, for there is no
doubt that by acids duly employed, the pure red may be pushed beyond
the culminating point towards scarlet.
643.
This juice appears on the one hand to be connected with the phenomena
of reproduction, eggs being found, the embryos of future shell-fish,
which contain a similar colouring principle. On the other hand, in
animals ranking higher in the scale of being, the secretion appears to
bear some relation to the development of the blood. The blood exhibits
similar properties in regard to colour; in its thinnest state it
appears yellow; thickened, as it is found in the veins, it appears red;
while the arterial blood exhibits a brighter red, probably owing to the
oxydation[Pg 256] which takes place by means of breathing. The venous blood
approaches more to violet, and by this mutability denotes the tendency
to that augmentation and progression which are now familiar to us.
644.
Before we quit the element whence we derived the foregoing examples,
we may add a few observations on fishes, whose scaly surface is
coloured either altogether in stripes, or in spots, and still oftener
exhibits a certain iridescent appearance, indicating the affinity of
the scales with the coats of shell-fish, mother-of-pearl, and even
the pearl itself. At the same time it should not be forgotten that
warmer climates, the influence of which extends to the watery regions,
produce, embellish, and enhance these colours in fishes in a still
greater degree.
645.
In Otaheite, Forster observed fishes with beautifully iridescent
surfaces, and this effect was especially apparent at the moment when
the fish died. We may here call to mind the hues of the chameleon,
and other similar appearances; for when similar facts are presented
together, we are better enabled to trace them.
646.
Lastly, although not strictly in the same[Pg 257] class, the iridescent
appearance of certain molluscæ may be mentioned, as well as the
phosphorescence which, in some marine creatures, it is said becomes
iridescent just before it vanishes.
647.
We now turn our attention to those creatures which belong to light,
air and dry warmth, and it is here that we first find ourselves in
the living region of colours. Here, in exquisitely organised parts,
the elementary colours present themselves in their greatest purity
and beauty. They indicate, however, that the creatures they adorn,
are still low in the scale of organisation, precisely because these
colours can thus appear, as it were, unwrought. Here, too, heat seems
to contribute much to their development.
648.
We find insects which may be considered altogether as concentrated
colouring matter; among these, the cochineals especially are
celebrated; with regard to these we observe that their mode of settling
on vegetables, and even nestling in them, at the same time produces
those excrescences which are so useful as mordants in fixing colours.
[Pg 258]
649.
But the power of colour, accompanied by regular organisation, exhibits
itself in the most striking manner in those insects which require a
perfect metamorphosis for their development—in scarabæ, and especially
in butterflies.
650.
These last, which might be called true productions of light and air,
often exhibit the most beautiful colours, even in their chrysalis
state, indicating the future colours of the butterfly; a consideration
which, if pursued further hereafter, must undoubtedly afford a
satisfactory insight into many a secret of organised being.
651.
If, again, we examine the wings of the butterfly more accurately, and
in its net-like web discover the rudiments of an arm, and observe
further the mode in which this, as it were, flattened arm is covered
with tender plumage and constituted an organ of flying; we believe
we recognise a law according to which the great variety of tints is
regulated. This will be a subject for further investigation hereafter.
652.
That, again, heat generally has an influence[Pg 259] on the size of the
creature, on the accomplishment of the form, and on the greater beauty
of the colours, hardly needs to be remarked.
BIRDS.
653.
The more we approach the higher organisations, the more it becomes
necessary to limit ourselves to a few passing observations; for all the
natural conditions of such organised beings are the result of so many
premises, that, without having at least hinted at these, our remarks
would only appear daring, and at the same time insufficient.
654.
We find in plants, that the consummate flower and fruit are, as it
were, rooted in the stem, and that they are nourished by more perfect
juices than the original roots first afforded; we remark, too,
that parasitical plants which derive their support from organised
structures, exhibit themselves especially endowed as to their energies
and qualities. We might in some sense compare the feathers of birds
with plants of this description; the feathers spring up as a last
structural result from the surface of a body[Pg 260] which has yet much in
reserve for the completion of the external economy, and thus are very
richly endowed organs.
655.
The quills not only grow proportionally to a considerable size, but are
throughout branched, by which means they properly become feathers, and
many of these feathered branches are again subdivided; thus, again,
recalling the structure of plants.
656.
The feathers are very different in shape and size, but each still
remains the same organ, forming and transforming itself according to
the constitution of the part of the body from which it springs.
657.
With the form, the colour also becomes changed, and a certain law
regulates the general order of hues as well as that particular
distribution by which a single feather becomes party coloured, It
is from this that all combination of variegated plumage arises, and
whence, at last, the eyes in the peacock's tail are produced. It is
a result similar to that which we have already unfolded in treating
of the metamorphosis of plants, and which we shall take an early
opportunity to prove.
[Pg 261]
658.
Although time and circumstances compel us here to pass by this organic
law, yet we are bound to refer to the chemical operations which
commonly exhibit themselves in the tinting of feathers in a mode now
sufficiently known to us.
659.
Plumage is of all colours, yet, on the whole, yellow deepening to red
is commoner than blue.
660.
The operation of light on the feathers and their colours, is to be
remarked in all cases. Thus, for example, the feathers on the breast of
certain parrots, are strictly yellow; the scale-like anterior portion,
which is acted on by the light, is deepened from yellow to red. The
breast of such a bird appears bright-red, but if we blow into the
feathers the yellow appears.
661.
The exposed portion of the feathers is in all cases very different
from that which, in a quiet state, is covered; it is only the exposed
portion, for instance, in ravens, which exhibits the iridescent
appearance; the covered portion does not: from which indication, the
feathers of the tail when ruffled together, may be at once placed in
the natural order again.
[Pg 262]
MAMMALIA AND HUMAN BEINGS.
662.
Here the elementary colours begin to leave us altogether. We are
arrived at the highest degree of the scale, and shall not dwell on its
characteristics long.
663.
An animal of this class is distinguished among the examples of
organised being. Every thing that exhibits itself about him is living.
Of the internal structure we do not speak, but confine ourselves
briefly to the surface. The hairs are already distinguished from
feathers, inasmuch as they belong more to the skin, inasmuch as they
are simple, thread-like, not branched. They are however, like feathers,
shorter, longer, softer, and firmer, colourless or coloured, and all
this in conformity to laws which might be defined.
664.
White and black, yellow, yellow-red and brown, alternate in various
modifications, but they never appear in such a state as to remind us
of the elementary hues. On the contrary,[Pg 263] they are all broken colours
subdued by organic concoction, and thus denote, more or less, the
perfection of life in the being they belong to.
665.
One of the most important considerations connected with morphology,
so far as it relates to surfaces, is this, that even in quadrupeds
the spots of the skin have a relation with the parts underneath
them. Capriciously as nature here appears, on a hasty examination,
to operate, she nevertheless consistently observes a secret law. The
development and application of this, it is true, are reserved only for
accurate and careful investigation and sincere co-operation.
666.
If in some animals portions appear variegated with positive colours,
this of itself shows how far such creatures are removed from a perfect
organisation; for, it may be said, the nobler a creature is, the more
all the mere material of which he is composed, is disguised by being
wrought together; the more essentially his surface corresponds with the
internal organisation, the less can it exhibit the elementary colours.
Where all tends to make up a perfect whole, any detached specific
developments cannot take place.
667.
Of man we have little to say, for he is entirely[Pg 264] distinct from the
general physiological results of which we now treat. So much in this
case is in affinity with the internal structure, that the surface can
only be sparingly endowed.
668.
When we consider that brutes are rather encumbered than advantageously
provided with intercutaneous muscles; when we see that much that is
superfluous tends to the surface, as, for instance, large ears and
tails, as well as hair, manes, tufts; we see that nature, in such
cases, had much to give away and to lavish.
669.
On the contrary, the general surface of the human form is smooth and
clean, and thus in the most perfect examples, the beautiful forms are
apparent; for it may be remarked in passing, that a superfluity of
hair on the chest, arms, and lower limbs, rather indicates weakness
than strength. Poets only have sometimes been induced, probably by the
example of the ferine nature, so strong in other respects, to extol
similar attributes in their rough heroes.
670.
But we have here chiefly to speak of colour, and observe that the
colour of the human skin, in all its varieties, is never an elementary
colour,[Pg 265] but presents, by means of organic concoction, a highly
complicated result.—Note X.
671.
That the colour of the skin and hair has relation with the differences
of character, is beyond question; and we are led to conjecture that the
circumstance of one or other organic system predominating, produces
the varieties we see. A similar hypothesis may be applied to nations,
in which case it might perhaps be observed, that certain colours
correspond with certain confirmations, which has always been observed
of the negro physiognomy.
672.
Lastly, we might here consider the problematical question, whether all
human forms and hues are not equally beautiful, and whether custom
and self-conceit are not the causes why one is preferred to another?
We venture, however, after what has been adduced, to assert that the
white man, that is, he whose surface varies from white to reddish,
yellowish, brownish, in short, whose surface appears most neutral in
hue and least inclines to any particular or positive colour, is the
most beautiful. On the same principle a similar point of perfection in
human conformation may be defined hereafter, when the question relates
to form. We do not[Pg 266] imagine that this long-disputed question is to be
thus, once for all, settled, for there are persons enough who have
reason to leave this significancy of the exterior in doubt; but we thus
express a conclusion, derived from observation and reflection, such
as might suggest itself to a mind aiming at a satisfactory decision.
We subjoin a few observations connected with the elementary chemical
doctrine of colours.—Note Y.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL EFFECTS OF THE TRANSMISSION OF LIGHT THROUGH
COLOURED MEDIUMS.
673.
The physical and chemical effects of colourless light are known, so
that it is unnecessary here to describe them at length. Colourless
light exhibits itself under various conditions as exciting warmth, as
imparting a luminous quality to certain bodies, as promoting oxydation
and de-oxydation. In the modes and degrees of these effects many
varieties take place, but no difference is found indicating a principle
of contrast such as we find in the transmission of coloured light. We
proceed briefly to advert to this.
[Pg 267]
674.
Let the temperature of a dark room be observed by means of a very
sensible air-thermometer; if the bulb is then brought to the direct sun
light as it shines into the room, nothing is more natural than that the
fluid should indicate a much higher degree of warmth. If upon this we
interpose coloured glasses, it follows again quite naturally that the
degree of warmth must be lowered; first, because the operation of the
direct light is already somewhat impeded by the glass, and again, more
especially, because a coloured glass, as a dark medium, admits less
light through it.
675.
But here a difference in the excitation of warmth exhibits itself to
the attentive observer, according to the colour of the glass. The
yellow and the yellow-red glasses produce a higher temperature than the
blue and blue-red, the difference being considerable.
676.
This experiment may be made with the prismatic spectrum. The
temperature of the room being first remarked on the thermometer, the
blue coloured light is made to fall on the bulb, when a somewhat higher
degree of warmth is exhibited, which still increases as the other
colours[Pg 268] are gradually brought to act on the mercury. If the experiment
is made with the water-prism, so that the white light can be retained
in the centre, this, refracted indeed, but not yet coloured light, is
the warmest; the other colours, stand in relation to each other as
before.
677.
As we here merely describe, without undertaking to deduce or explain
this phenomenon, we only remark in passing, that the pure light is by
no means abruptly and entirely at an end with the red division in the
spectrum, but that a refracted light is still to be observed deviating
from its course and, as it were, insinuating itself beyond the
prismatic image, so that on closer examination it will hardly be found
necessary to take refuge in invisible rays and their refraction.
678.
The communication of light by means of coloured mediums exhibits the
same difference. The light communicates itself to Bologna phosphorus
through blue and violet glasses, but by no means through yellow and
yellow-red glasses. It has been even remarked that the phosphori which
have been rendered luminous under violet and blue glasses, become
sooner extinguished when afterwards placed under yellow and yellow-red
glasses than those which have been[Pg 269] suffered to remain in a dark room
without any further influence.
679.
These experiments, like the foregoing, may also be made by means of the
prismatic spectrum, when the same results take place.
680.
To ascertain the effect of coloured light on oxydation and
de-oxydation, the following means may be employed:—Let moist,
perfectly white muriate of silver[1] be spread on a strip of paper;
place it in the light, so that it may become to a certain degree grey,
and then cut it in three portions. Of these, one may be preserved
in a book, as a specimen of this state; let another be placed under
a yellow-red, and the third under a blue-red glass. The last will
become a darker grey, and exhibit a de-oxydation; the other, under the
yellow-red glass, will, on the contrary, become a lighter grey, and
thus approach nearer to the original state of more perfect oxydation.
The change in both may be ascertained by a comparison with the
unaltered specimen.
681.
An excellent apparatus has been contrived to[Pg 270] perform these experiments
with the prismatic image. The results are analogous to those already
mentioned, and we shall hereafter give the particulars, making use
of the labours of an accurate observer, who has been for some time
carefully prosecuting these experiments.[2]
CHEMICAL EFFECT IN DIOPTRICAL ACHROMATISM.
682.
We first invite our readers to turn to what has been before observed on
this subject (285, 298), to avoid unnecessary repetition here.
683.
We can thus give a glass the property of producing much wider coloured
edges without refracting more strongly than before, that is, without
displacing the object much more perceptibly.
684.
This property is communicated to the glass by means of metallic oxydes.
Minium, melted and thoroughly united with a pure glass, produces[Pg 271] this
effect, and thus flint-glass (291) is prepared with oxyde of lead.
Experiments of this kind have been carried farther, and the so-called
butter of antimony, which, according to a new preparation, may be
exhibited as a pure fluid, has been made use of in hollow lenses and
prisms, producing a very strong appearance of colour with a very
moderate refraction, and presenting the effect which we have called
hyperchromatism in a very vivid manner.
685.
In common glass, the alkaline nature obviously preponderates, since
it is chiefly composed of sand and alkaline salts; hence a series of
experiments, exhibiting the relation of perfectly alkaline fluids to
perfect acids, might lead to useful results.
686.
For, could the maximum and minimum be found, it would be a question
whether a refracting medium could not be discovered, in which the
increasing and diminishing appearance of colour, (an effect almost
independent of refraction,) could not be done away with altogether,
while the displacement of the object would be unaltered.
687.
How desirable, therefore, it would be with[Pg 272] regard to this last point,
as well as for the elucidation of the whole of this third division of
our work, and, indeed, for the elucidation of the doctrine of colours
generally, that those who are occupied in chemical researches, with new
views ever opening to them, should take this subject in hand, pursuing
into more delicate combinations what we have only roughly hinted at,
and prosecuting their inquiries with reference to science as a whole.
[Pg 273]
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS.
688.
We have hitherto, in a manner forcibly, kept phenomena asunder,
which, partly from their nature, partly in accordance with our mental
habits, have, as it were, constantly sought to be reunited. We have
exhibited them in three divisions. We have considered colours, first,
as transient, the result of an action and re-action in the eye
itself; next, as passing effects of colourless, light-transmitting,
transparent, or opaque mediums on light; especially on the luminous
image; lastly, we arrived at the point where we could securely
pronounce them as permanent, and actually inherent in bodies.
689.
In following this order we have as far as possible endeavoured to
define, to separate, and to class the appearances. But now that we
need no longer be apprehensive of mixing or confounding them, we may
proceed, first, to state the general nature of these appearances
considered abstractedly, as an independent circle of facts, and, in the
next place, to show how this particular circle is connected with other
classes of analogous phenomena in nature.
[Pg 274]
THE FACILITY WITH WHICH COLOUR APPEARS.
690.
We have observed that colour under many conditions appears very easily.
The susceptibility of the eye with regard to light, the constant
re-action of the retina against it, produce instantaneously a slight
iridescence. Every subdued light may be considered as coloured, nay, we
ought to call any light coloured, inasmuch as it is seen. Colourless
light, colourless surfaces, are, in some sort, abstract ideas; in
actual experience we can hardly be said to be aware of them.—Note Z.
691.
If light impinges on a colourless body, is reflected from it or passes
through it, colour immediately appears; but it is necessary here to
remember what has been so often urged by us, namely, that the leading
conditions of refraction, reflection, &c., are not of themselves
sufficient to produce the appearance. Sometimes, it is true, light acts
with these merely as light, but oftener as a defined, circumscribed
appearance, as a luminous image. The semi-opacity of the medium is
often a necessary condition; while half, and double shadows, are
required for many coloured appearances. In all cases, however, colour
appears instantaneously. We find, again, that by means of pressure,
breathing heat (432, 471), by various kinds of motion and[Pg 275] alteration
on smooth clean surfaces (461), as well as on colourless fluids (470),
colour is immediately produced.
692.
The slightest change has only to take place in the component parts
of bodies, whether by immixture with other particles or other such
effects, and colour either makes its appearance or becomes changed.
THE FORCE OF COLOUR.
693.
The physical colours, and especially those of the prism, were formerly
called "colores emphatici," on account of their extraordinary beauty
and force. Strictly speaking, however, a high degree of effect may be
ascribed to all appearances of colour, assuming that they are exhibited
under the purest and most perfect conditions.
694.
The dark nature of colour, its full rich quality, is what produces
the grave, and at the same time fascinating impression we sometimes
experience, and as colour is to be considered a condition of light,
so it cannot dispense with light as the co-operating cause of its
appearance, as its basis or ground; as a power thus displaying and
manifesting colour.
[Pg 276]
THE DEFINITE NATURE OF COLOUR.
695.
The existence and the relatively definite character of colour are one
and the same thing. Light displays itself and the face of nature, as
it were, with a general indifference, informing us as to surrounding
objects perhaps devoid of interest or importance; but colour is at all
times specific, characteristic, significant.
696.
Considered in a general point of view, colour is determined towards one
of two sides. It thus presents a contrast which we call a polarity, and
which we may fitly designate by the expressions plus and minus.
| Plus. | Minus. |
|---|
| Yellow. | Blue. |
| Action. | Negation.[1] |
| Light. | Shadow. |
| Brightness. | Darkness. |
| Force. | Weakness. |
| Warmth. | Coldness. |
| Proximity. | Distance. |
| Repulsion | Attraction. |
| Affinity with acids. | Affinity with alkalis. |
[Pg 277]
COMBINATION OF THE TWO PRINCIPLES.
697.
If these specific, contrasted principles are combined, the respective
qualities do not therefore destroy each other: for if in this
intermixture the ingredients are so perfectly balanced that neither
is to be distinctly recognised, the union again acquires a specific
character; it appears as a quality by itself in which we no longer
think of combination. This union we call green.
698.
Thus, if two opposite phenomena springing from the same source do not
destroy each other when combined, but in their union present a third
appreciable and pleasing appearance, this result at once indicates
their harmonious relation. The more perfect result yet remains to be
adverted to.
AUGMENTATION TO RED.
699.
Blue and yellow do not admit of increased intensity without presently
exhibiting a new appearance in addition to their own. Each colour, in
its lightest state, is a dark; if condensed it must become darker, but
this effect no sooner takes place than the hue assumes an appearance
which we designate by the word reddish.
[Pg 278]
700.
This appearance still increases, so that when the highest degree of
intensity is attained it predominates over the original hue. A powerful
impression of light leaves the sensation of red on the retina. In the
prismatic yellow-red which springs directly from the yellow, we hardly
recognise the yellow.
701.
This deepening takes place again by means of colourless
semi-transparent mediums, and here we see the effect in its utmost
purity and extent. Transparent fluids, coloured with any given hues, in
a series of glass-vessels, exhibit it very strikingly. The augmentation
is unremittingly rapid and constant; it is universal, and obtains in
physiological as well as in physical and chemical colours.
JUNCTION OF THE TWO AUGMENTED EXTREMES.
702.
As the extremes of the simple contrast produce a beautiful and
agreeable appearance by their union, so the deepened extremes on being
united, will present a still more fascinating colour; indeed, it might
naturally be expected that we should here find the acme of the whole
phenomenon.
[Pg 279]
COMPLETENESS THE RESULT OF VARIETY.
703.
And such is the fact, for pure red appears; a colour to which, from its
excellence, we have appropriated the term "purpur."[2]
704.
There are various modes in which pure red may appear. By bringing
together the violet edge and yellow-red border in prismatic
experiments, by continued augmentation in chemical operations, and by
the organic contrast in physiological effects.
705.
As a pigment it cannot be produced by intermixture or union, but
only by arresting the hue in substances chemically acted on, at the
high culminating point. Hence the painter is justified in assuming
that there are three primitive colours from which he combines all
the others. The natural philosopher, on the other hand, assumes only
two elementary colours, from which he, in like manner, developes and
combines the rest.
COMPLETENESS THE RESULT OF VARIETY IN COLOUR.
706.
The various appearances of colour arrested in[Pg 280] their different degrees,
and seen in juxtaposition, produce a whole. This totality is harmony to
the eye.
707.
The chromatic circle has been gradually presented to us; the
various relations of its progression are apparent to us. Two pure
original principles in contrast, are the foundation of the whole;
an augmentation manifests itself by means of which both approach a
third state; hence there exists on both sides a lowest and highest,
a simplest and most qualified state. Again, two combinations present
themselves; first that of the simple primitive contrasts, then that of
the deepened contrasts.
HARMONY OF THE COMPLETE STATE.
708.
The whole ingredients of the chromatic scale, seen in juxtaposition,
produce an harmonious impression on the eye. The difference between the
physical contrast and harmonious opposition in all its extent should
not be overlooked. The first resides in the pure restricted original
dualism, considered in its antagonizing elements; the other results
from the fully developed effects of the complete state.
709.
Every single opposition in order to be harmonious must comprehend the
whole. The[Pg 281] physiological experiments are sufficiently convincing
on this point. A development of all the possible contrasts of the
chromatic scale will be shortly given.[3]
FACILITY WITH WHICH COLOUR MAY BE MADE TO TEND EITHER TO THE PLUS OR
MINUS SIDE.
710.
We have already had occasion to take notice of the mutability of colour
in considering its so-called augmentation and progressive variations
round the whole circle; but the hues even pass and repass from one side
to the other, rapidly and of necessity.
711.
Physiological colours are different in appearance as they happen
to fall on a dark or on a light ground. In physical colours the
combination of the objective and subjective experiments is very
remarkable. The epoptical colours, it appears, are contrasted according
as the light shines through or upon them. To what extent the chemical
colours may be changed by fire and alkalis, has been sufficiently shown
in its proper place.
EVANESCENCE OF COLOUR.
712.
All that has been adverted to as subsequent[Pg 282] to the rapid excitation
and definition of colour, immixture, augmentation, combination,
separation, not forgetting the law of compensatory harmony, all takes
place with the greatest rapidity and facility; but with equal quickness
colour again altogether disappears.
713.
The physiological appearances are in no wise to be arrested; the
physical last only as long as the external condition lasts; even the
chemical colours have great mutability, they may be made to pass and
repass from one side to the other by means of opposite re-agents, and
may even be annihilated altogether.
PERMANENCE OF COLOUR.
714.
The chemical colours afford evidence of very great duration. Colours
fixed in glass by fusion, and by nature in gems, defy all time and
re-action.
715.
The art of dyeing again fixes colour very powerfully. The hues of
pigments which might otherwise be easily rendered mutable by re-agents,
may be communicated to substances in the greatest permanency by means
of mordants.
RELATION TO OTHER PURSUITS—RELATION TO PHILOSOPHY.
716.
The investigator of nature cannot be required to be a philosopher,
but it is expected that he should so far have attained the habit of
philosophizing, as to distinguish himself essentially from the world,
in order to associate himself with it again in a higher sense. He
should form to himself a method in accordance with observation, but
he should take heed not to reduce observation to mere notion, to
substitute words for this notion, and to use and deal with these words
as if they were things. He should be acquainted with the labours of
philosophers, in order to follow up the phenomena which have been the
subject of his observation, into the philosophic region.
717.
It cannot be required that the philosopher should be a naturalist, and
yet his co-operation in physical researches is as necessary as it is
desirable. He needs not an acquaintance with details for this, but only
a clear view of those conclusions where insulated facts meet.
[Pg 284]
718.
We have before (175) alluded to this important consideration, and
repeat it here where it is in its place. The worst that can happen
to physical science as well as to many other kinds of knowledge is,
that men should treat a secondary phenomenon as a primordial one, and
(since it is impossible to derive the original fact from the secondary
state), seek to explain what is in reality the cause by an effect made
to usurp its place. Hence arises an endless confusion, a mere verbiage,
a constant endeavour to seek and to find subterfuges whenever truth
presents itself and threatens to be overpowering.
719.
While the observer, the investigator of nature, is thus dissatisfied
in finding that the appearances he sees still contradict a received
theory, the philosopher can calmly continue to operate in his abstract
department on a false result, for no result is so false but that it can
be made to appear valid, as form without substance, by some means or
other.
720.
If, on the other hand, the investigator of nature can attain to the
knowledge of that which we have called a primordial phenomenon, he is
safe; and the philosopher with him. The investigator[Pg 285] of nature is
safe, since he is persuaded that he has here arrived at the limits
of his science, that he finds himself at the height of experimental
research; a height whence he can look back upon the details of
observation in all its steps, and forwards into, if he cannot enter,
the regions of theory. The philosopher is safe, for he receives
from the experimentalist an ultimate fact, which, in his hands, now
becomes an elementary one. He now justly pays little attention to
appearances which are understood to be secondary, whether he already
finds them scientifically arranged, or whether they present themselves
to his casual observation scattered and confused. Should he even be
inclined to go over this experimental ground himself, and not be
averse to examination in detail, he does this conveniently, instead of
lingering too long in the consideration of secondary and intermediate
circumstances, or hastily passing them over without becoming accurately
acquainted with them.
721.
To place the doctrine of colours nearer, in this sense, within the
philosopher's reach, was the author's wish; and although the execution
of his purpose, from various causes, does not correspond with his
intention, he will still keep this object in view in an intended
recapitulation,[Pg 286] as well as in the polemical and historical portions of
his work; for he will have to return to the consideration of this point
hereafter, on an occasion where it will be necessary to speak with less
reserve.
RELATION TO MATHEMATICS.
722.
It may be expected that the investigator of nature, who proposes to
treat the science of natural philosophy in its entire range, should be
a mathematician. In the middle ages, mathematics was the chief organ by
means of which men hoped to master the secrets of nature, and even now,
geometry in certain departments of physics, is justly considered of
first importance.
723.
The author can boast of no attainments of this kind, and on this
account confines himself to departments of science which are
independent of geometry; departments which in modern times have been
opened up far and wide.
724.
It will be universally allowed that mathematics, one of the noblest
auxiliaries which can be employed by man, has, in one point of view,
been of the greatest use to the physical sciences; but that, by a
false application of its methods,[Pg 287] it has, in many respects, been
prejudicial to them, is also not to be denied; we find it here and
there reluctantly admitted.
725.
The theory of colours, in particular, has suffered much, and its
progress has been incalculably retarded by having been mixed up with
optics generally, a science which cannot dispense with mathematics;
whereas the theory of colours, in strictness, may be investigated quite
independently of optics.
726.
But besides this there was an additional evil. A great mathematician
was possessed with an entirely false notion on the physical origin of
colours; yet, owing to his great authority as a geometer, the mistakes
which he committed as an experimentalist long became sanctioned in the
eyes of a world ever fettered in prejudices.
727.
The author of the present inquiry has endeavoured throughout to keep
the theory of colours distinct from the mathematics, although there
are evidently certain points where the assistance of geometry would be
desirable. Had not the unprejudiced mathematicians, with whom he has
had, or still has, the good fortune to be acquainted,[Pg 288] been prevented
by other occupations from making common cause with him, his work would
not have wanted some merit in this respect. But this very want may be
in the end advantageous, since it may now become the object of the
enlightened mathematician to ascertain where the doctrine of colours is
in need of his aid, and how he can contribute the means at his command
with a view to the complete elucidation of this branch of physics.
728.
In general it were to be wished that the Germans, who render such
good service to science, while they adopt all that is good from other
nations, could by degrees accustom themselves to work in concert. We
live, it must be confessed, in an age, the habits of which are directly
opposed to such a wish. Every one seeks, not only to be original in
his views, but to be independent of the labours of others, or at least
to persuade himself that he is so, even in the course of his life
and occupation. It is very often remarked that men who undoubtedly
have accomplished much, quote themselves only, their own writings,
journals, and compendiums; whereas it would be far more advantageous
for the individual, and for the world, if many were devoted to a common
pursuit. The conduct of our neighbours the French is, in this respect,
worthy[Pg 289] of imitation; we have a pleasing instance in Cuvier's preface
to his "Tableau Élémentaire de l'Histoire Naturelle des Animaux."
729.
He who has observed science and its progress with an unprejudiced eye,
might even ask whether it is desirable that so many occupations and
aims, though allied to each other, should be united in one person, and
whether it would not be more suitable for the limited powers of the
human mind to distinguish, for example, the investigator and inventor,
from him who employs and applies the result of experiment? Astronomers,
who devote themselves to the observation of the heavens and the
discovery or enumeration of stars, have in modern times formed, to a
certain extent, a distinct class from those who calculate the orbits,
consider the universe in its connexion, and more accurately define its
laws. The history of the doctrine of colours will often lead us back to
these considerations.
RELATION TO THE TECHNICAL OPERATIONS OF THE DYER.
730.
If in our labours we have gone out of the province of the
mathematician, we have, on the other hand, endeavoured to meet the
practical[Pg 290] views of the dyer; and although the chapter which treats
of colour in a chemical point of view is not the most complete and
circumstantial, yet in that portion, as well as in our general
observations respecting colour, the dyer will find his views assisted
far more than by the theory hitherto in vogue, which failed to afford
him any assistance.
731.
It is curious, in this view, to take a glance at the works containing
directions on the art of dyeing. As the Catholic, on entering his
temple, sprinkles himself with holy water, and after bending the knee,
proceeds perhaps to converse with his friends on his affairs, without
any especial devotion; so all the treatises on dyeing begin with a
respectful allusion to the accredited theory, without afterwards
exhibiting a single trace of any principle deduced from this theory,
or showing that it has thrown light on any part of the art, or that it
offers any useful hints in furtherance of practical methods.
732.
On the other hand, there are men who, after having become thoroughly
and experimentally acquainted with the nature of dyes, have not been
able to reconcile their observations with the received theory; who
have, in short, discovered[Pg 291] its weak points, and sought for a general
view more consonant to nature and experience. When we come to the names
of Castel and Gülich, in our historical review, we shall have occasion
to enter into this more fully, and an opportunity will then present
itself to show that an assiduous experience in taking advantage of
every accident may, in fact, be said almost to exhaust the knowledge
of the province to which it is confined. The high and complete result
is then submitted to the theorist, who, if he examines facts with
accuracy, and reasons with candour, will find such materials eminently
useful as a basis for his conclusions.—Note AA.
RELATION TO PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY.
733.
If the phenomena adduced in the chapter where colours were considered
in a physiological and pathological view are for the most part
generally known, still some new views, mixed up with them, will not be
unacceptable to the physiologist. We especially hope to have given him
cause to be satisfied by classing certain phenomena which stood alone,
under analogous facts, and thus, in some measure, to have prepared the
way for his further investigations.
734.
The appendix on pathological colours, again,[Pg 292] is admitted to be scanty
and unconnected. We reflect, however, that Germany can boast of men who
are not only highly experienced in this department, but are likewise so
distinguished for general cultivation, that it can cost them but little
to revise this portion, to complete what has been sketched, and at the
same time to connect it with the higher facts of organisation.
RELATION TO NATURAL HISTORY.
735.
If we may at all hope that natural history will gradually be modified
by the principle of deducing the ordinary appearances of nature from
higher phenomena, the author believes he may have given some hints
and introductory views bearing on this object also. As colour, in its
infinite variety, exhibits itself on the surface of living beings, it
becomes an important part of the outward indications, by means of which
we can discover what passes underneath.
736.
In one point of view it is certainly not to be too much relied on, on
account of its indefinite and mutable nature; yet even this mutability,
inasmuch as it exhibits itself as a constant quality, again becomes
a criterion of a mutable vitality; and the author wishes nothing
more[Pg 293] than that time may be granted him to develop the results of his
observations on this subject more fully; here they would not be in
their place.
RELATION TO GENERAL PHYSICS.
737.
The state in which general physics now is, appears, again, particularly
favourable to our labours; for natural philosophy, owing to
indefatigable and variously directed research, has gradually attained
such eminence, that it appears not impossible to refer a boundless
empiricism to one centre.
738.
Without referring to subjects which are too far removed from our own
province, we observe that the formulæ under which the elementary
appearances of nature are expressed, altogether tend in this direction;
and it is easy to see that through this correspondence of expression, a
correspondence in meaning will necessarily be soon arrived at.
739.
True observers of nature, however they may differ in opinion in other
respects, will agree that all which presents itself as appearance, all
that we meet with as phenomenon, must either[Pg 294] indicate an original
division which is capable of union, or an original unity which admits
of division, and that the phenomenon will present itself accordingly.
To divide the united, to unite the divided, is the life of nature;
this is the eternal systole and diastole, the eternal collapsion and
expansion, the inspiration and expiration of the world in which we live
and move.
740.
It is hardly necessary to observe that what we here express as number
and restrict to dualism is to be understood in a higher sense; the
appearance of a third, a fourth order of facts progressively developing
themselves is to be similarly understood; but actual observation
should, above all, be the basis of all these expressions.
741.
Iron is known to us as a peculiar substance, different from other
substances: in its ordinary state we look upon it as a mere material
remarkable only on account of its fitness for various uses and
applications. How little, however, is necessary to do away with the
comparative insignificancy of this substance. A two-fold power is
called forth,[1] which, while it tends again to a[Pg 295] state of union, and,
as it were, seeks itself, acquires a kind of magical relation with
its like, and propagates this double property, which is in fact but a
principle of reunion, throughout all bodies of the same kind. We here
first observe the mere substance, iron; we see the division that takes
place in it propagate itself and disappear, and again easily become
re-excited. This, according to our mode of thinking, is a primordial
phenomenon in immediate relation with its idea, and which acknowledges
nothing earthly beyond it.
742.
Electricity is again peculiarly characterised. As a mere quality we are
unacquainted with it; for us it is a nothing, a zero, a mere point,
which, however, dwells in all apparent existences, and at the same time
is the point of origin whence, on the slightest stimulus, a double
appearance presents itself, an appearance which only manifests itself
to vanish. The conditions under which this manifestation is excited
are infinitely varied, according to the nature of particular bodies.
From the rudest mechanical friction of very different substances with
one another, to the mere contiguity of two entirely similar bodies,
the phenomenon is present and stirring, nay, striking and powerful,
and so decided and specific, that when we employ the terms or formulæ[Pg 296]
polarity, plus and minus, for north and south, for glass and resin, we
do so justifiably and in conformity with nature.
743.
This phenomenon, although it especially affects the surface, is yet by
no means superficial. It influences the tendency or determination of
material qualities, and connects itself in immediate co-operation with
the important double phenomenon which takes place so universally in
chemistry,—oxydation, and de-oxydation.
744.
To introduce and include the appearances of colour in this series,
this circle of phenomena was the object of our labours. What we have
not succeeded in others will accomplish. We found a primordial vast
contrast between light and darkness, which may be more generally
expressed by light and its absence. We looked for the intermediate
state, and sought by means of it to compose the visible world of light,
shade, and colour. In the prosecution of this we employed various terms
applicable to the development of the phenomena, terms which we adopted
from the theories of magnetism, of electricity, and of chemistry. It
was necessary, however, to extend this terminology, since we found
ourselves in an abstract region, and had to express more complicated
relations.
[Pg 297]
745.
If electricity and galvanism, in their general character, are
distinguished as superior to the more limited exhibition of magnetic
phenomena, it may be said that colour, although coming under similar
laws, is still superior; for since it addresses itself to the noble
sense of vision, its perfections are more generally displayed. Compare
the varied effects which result from the augmentation of yellow and
blue to red, from the combination of these two higher extremes to pure
red, and the union of the two inferior extremes to green. What a far
more varied scheme is apparent here than that in which magnetism and
electricity are comprehended. These last phenomena may be said to be
inferior again on another account; for though they penetrate and give
life to the universe, they cannot address themselves to man in a higher
sense in order to his employing them æsthetically. The general, simple,
physical law must first be elevated and diversified itself in order to
be available for elevated uses.
746.
If the reader, in this spirit, recalls what has been stated by us
throughout, generally and in detail, with regard to colour, he will
himself pursue and unfold what has been here only lightly hinted at.
He will augur well for[Pg 298] science, technical processes, and art, if it
should prove possible to rescue the attractive subject of the doctrine
of colours from the atomic restriction and isolation in which it has
been banished, in order to restore it to the general dynamic flow of
life and action which the present age loves to recognise in nature.
These considerations will press upon us more strongly when, in the
historical portion, we shall have to speak of many an enterprising
and intelligent man who failed to possess his contemporaries with his
convictions.
RELATION TO THE THEORY OF MUSIC.
747.
Before we proceed to the moral associations of colour, and the æsthetic
influences arising from them, we have here to say a few words on its
relation to melody. That a certain relation exists between the two,
has been always felt; this is proved by the frequent comparisons we
meet with, sometimes as passing allusions, sometimes as circumstantial
parallels. The error which writers have fallen into in trying to
establish this analogy we would thus define:
748.
Colour and sound do not admit of being directly compared together
in any way, but both are referable to a higher formula, both are
derivable,[Pg 299] although each for itself, from this higher law. They are
like two rivers which have their source in one and the same mountain,
but subsequently pursue their way under totally different conditions
in two totally different regions, so that throughout the whole course
of both no two points can be compared. Both are general, elementary
effects acting according to the general law of separation and tendency
to union, of undulation and oscillation, yet acting thus in wholly
different provinces, in different modes, on different elementary
mediums, for different senses.—Note BB.
749.
Could some investigator rightly adopt the method in which we have
connected the doctrine of colours with natural philosophy generally,
and happily supply what has escaped or been missed by us, the theory
of sound, we are persuaded, might be perfectly connected with general
physics: at present it stands, as it were, isolated within the circle
of science.
750.
It is true it would be an undertaking of the greatest difficulty
to do away with the positive character which we are now accustomed
to attribute to music—a character resulting from the achievements
of practical skill, from accidental,[Pg 300] mathematical, æsthetical
influences—and to substitute for all this a merely physical inquiry
tending to resolve the science into its first elements. Yet considering
the point at which science and art are now arrived, considering the
many excellent preparatory investigations that have been made relative
to this subject, we may perhaps still see it accomplished.
CONCLUDING OBSERVATIONS ON TERMINOLOGY.
751.
We never sufficiently reflect that a language, strictly speaking, can
only be symbolical and figurative, that it can never express things
directly, but only, as it were, reflectedly. This is especially the
case in speaking of qualities which are only imperfectly presented
to observation, which might rather be called powers than objects,
and which are ever in movement throughout nature. They are not to be
arrested, and yet we find it necessary to describe them; hence we look
for all kinds of formulæ in order, figuratively at least, to define
them.
752.
Metaphysical formulæ have breadth as well as depth, but on this
very account they require a corresponding import; the danger
here is vagueness. Mathematical expressions may in many cases be
very conveniently and happily[Pg 301] employed, but there is always an
inflexibility in them, and we presently feel their inadequacy; for even
in elementary cases we are very soon conscious of an incommensurable
idea; they are, besides, only intelligible to those who are especially
conversant in the sciences to which such formulæ are appropriated. The
terms of the science of mechanics are more addressed to the ordinary
mind, but they are ordinary in other senses, and always have something
unpolished; they destroy the inward life to offer from without an
insufficient substitute for it. The formulæ of the corpuscular theories
are nearly allied to the last; through them the mutable becomes rigid,
description and expression uncouth: while, again, moral terms, which
undoubtedly can express nicer relations, have the effect of mere
symbols in the end, and are in danger of being lost in a play of wit.
753.
If, however, a writer could use all these modes of description and
expression with perfect command, and thus give forth the result of his
observations on the phenomena of nature in a diversified language;
if he could preserve himself from predilections, still embodying a
lively meaning in as animated an expression, we might look for much
instruction communicated in the most agreeable of forms.
[Pg 302]
754.
Yet, how difficult it is to avoid substituting the sign for the thing;
how difficult to keep the essential quality still living before us,
and not to kill it with the word. With all this, we are exposed in
modern times to a still greater danger by adopting expressions and
terminologies from all branches of knowledge and science to embody our
views of simple nature. Astronomy, cosmology, geology, natural history,
nay religion and mysticism, are called in in aid; and how often do
we not find a general idea and an elementary state rather hidden and
obscured than elucidated and brought nearer to us by the employment of
terms, the application of which is strictly specific and secondary.
We are quite aware of the necessity which led to the introduction and
general adoption of such a language, we also know that it has become in
a certain sense indispensable; but it is only a moderate, unpretending
recourse to it, with an internal conviction of its fitness, that can
recommend it.
755.
After all, the most desirable principle would be that writers should
borrow the expressions employed to describe the details of a given
province of investigation from the province itself; treating the
simplest phenomenon as an elementary[Pg 303] formula, and deriving and
developing the more complicated designations from this.
756.
The necessity and suitableness of such a conventional language where
the elementary sign expresses the appearance itself, has been duly
appreciated by extending, for instance, the application of the term
polarity, which is borrowed from the magnet to electricity, &c. The
plus and minus which may be substituted for this, have found as
suitable an application to many phenomena; even the musician, probably
without troubling himself about these other departments, has been
naturally led to express the leading difference in the modes of melody
by major and minor.
757.
For ourselves we have long wished to introduce the term polarity into
the doctrine of colours; with what right and in what sense, the present
work may show. Perhaps we may hereafter find room to connect the
elementary phenomena together according to our mode, by a similar use
of symbolical terms, terms which must at all times convey the directly
corresponding idea; we shall thus render more explicit what has been
here only alluded to generally, and perhaps too vaguely expressed.
EFFECT OF COLOUR WITH REFERENCE TO MORAL ASSOCIATIONS.
758.
Since colour occupies so important a place in the series of elementary
phenomena, filling as it does the limited circle assigned to it with
fullest variety, we shall not be surprised to find that its effects are
at all times decided and significant, and that they are immediately
associated with the emotions of the mind. We shall not be surprised
to find that these appearances presented singly, are specific, that
in combination they may produce an harmonious, characteristic, often
even an inharmonious effect on the eye, by means of which they act on
the mind; producing this impression in their most general elementary
character, without relation to the nature or form of the object on
whose surface they are apparent. Hence, colour considered as an element
of art, may be made subservient to the highest æsthetical ends.—Note CC.
759.
People experience a great delight in colour, generally. The eye
requires it as much as it requires light. We have only to remember
the[Pg 305] refreshing sensation we experience, if on a cloudy day the sun
illumines a single portion of the scene before us and displays its
colours. That healing powers were ascribed to coloured gems, may have
arisen from the experience of this indefinable pleasure.
760.
The colours which we see on objects are not qualities entirely
strange to the eye; the organ is not thus merely habituated to the
impression; no, it is always predisposed to produce colour of itself,
and experiences a sensation of delight if something analogous to its
own nature is offered to it from without; if its susceptibility is
distinctly determined towards a given state.
761.
From some of our earlier observations we can conclude, that general
impressions produced by single colours cannot be changed, that they act
specifically, and must produce definite, specific states in the living
organ.
762.
They likewise produce a corresponding influence on the mind. Experience
teaches us that particular colours excite particular states of feeling.
It is related of a witty Frenchman, "Il prétendoit que son ton de
conversation avec[Pg 306] Madame étoit changé depuis qu'elle avoit changé en
cramoisi le meuble de son cabinet, qui étoit bleu."
763.
In order to experience these influences completely, the eye should be
entirely surrounded with one colour; we should be in a room of one
colour, or look through a coloured glass. We are then identified with
the hue, it attunes the eye and mind in mere unison with itself.
764.
The colours on the plus side are yellow, red-yellow (orange),
yellow-red (minium, cinnabar). The feelings they excite are quick,
lively, aspiring.
YELLOW.
765.
This is the colour nearest the light. It appears on the slightest
mitigation of light, whether by semi-transparent mediums or faint
reflection from white surfaces. In prismatic experiments it extends
itself alone and widely in the light space, and while the two poles
remain separated from each other, before it mixes with blue to
produce green it is to be seen in its utmost purity and beauty. How
the chemical yellow developes itself in and upon the white, has been
circumstantially described in its proper place.
[Pg 307]
766.
In its highest purity it always carries with it the nature of
brightness, and has a serene, gay, softly exciting character.
767.
In this state, applied to dress, hangings, carpeting, &c., it is
agreeable. Gold in its perfectly unmixed state, especially when the
effect of polish is superadded, gives us a new and high idea of this
colour; in like manner, a strong yellow, as it appears on satin, has a
magnificent and noble effect.
768.
We find from experience, again, that yellow excites a warm and
agreeable impression. Hence in painting it belongs to the illumined and
emphatic side.
769.
This impression of warmth may be experienced in a very lively manner if
we look at a landscape through a yellow glass, particularly on a grey
winter's day. The eye is gladdened, the heart expanded and cheered, a
glow seems at once to breathe towards us.
770.
If, however, this colour in its pure and bright[Pg 308] state is agreeable
and gladdening, and in its utmost power is serene and noble, it is, on
the other hand, extremely liable to contamination, and produces a very
disagreeable effect if it is sullied, or in some degree tends to the
minus side. Thus, the colour of sulphur, which inclines to green, has
a something unpleasant in it.
771.
When a yellow colour is communicated to dull and coarse surfaces,
such as common cloth, felt, or the like, on which it does not appear
with full energy, the disagreeable effect alluded to is apparent. By
a slight and scarcely perceptible change, the beautiful impression
of fire and gold is transformed into one not undeserving the epithet
foul; and the colour of honour and joy reversed to that of ignominy
and aversion. To this impression the yellow hats of bankrupts and the
yellow circles on the mantles of Jews, may have owed their origin.
RED-YELLOW.
772.
As no colour can be considered as stationary, so we can very easily
augment yellow into reddish by condensing or darkening it. The colour
increases in energy, and appears in red-yellow more powerful and
splendid.
[Pg 309]
773.
All that we have said of yellow is applicable here in a higher
degree. The red-yellow gives an impression of warmth and gladness,
since it represents the hue of the intenser glow of fire, and of the
milder radiance of the setting sun. Hence it is agreeable around us,
and again, as clothing, in greater or less degrees is cheerful and
magnificent. A slight tendency to red immediately gives a new character
to yellow, and while the English and Germans content themselves
with bright pale yellow colours in leather, the French, as Castel
has remarked, prefer a yellow enhanced to red; indeed, in general,
everything in colour is agreeable to them which belongs to the active
side.
YELLOW-RED.
774.
As pure yellow passes very easily to red-yellow, so the deepening of
this last to yellow-red is not to be arrested. The agreeable, cheerful
sensation which red-yellow excites, increases to an intolerably
powerful impression in bright yellow-red.
775.
The active side is here in its highest energy, and it is not to
be wondered at that impetuous, robust, uneducated men, should be
especially[Pg 310] pleased with this colour. Among savage nations the
inclination for it has been universally remarked, and when children,
left to themselves, begin to use tints, they never spare vermilion and
minium.
776.
In looking steadfastly at a perfectly yellow-red surface, the colour
seems actually to penetrate the organ. It produces an extreme
excitement, and still acts thus when somewhat darkened. A yellow-red
cloth disturbs and enrages animals. I have known men of education to
whom its effect was intolerable if they chanced to see a person dressed
in a scarlet cloak on a grey, cloudy day.
777.
The colours on the minus side are blue, red-blue, and blue-red. They
produce a restless, susceptible, anxious impression.
BLUE.
778.
As yellow is always accompanied with light, so it may be said that blue
still brings a principle of darkness with it.
779.
This colour has a peculiar and almost indescribable[Pg 311] effect on the eye.
As a hue it is powerful, but it is on the negative side, and in its
highest purity is, as it were, a stimulating negation. Its appearance,
then, is a kind of contradiction between excitement and repose.
780.
As the upper sky and distant mountains appear blue, so a blue surface
seems to retire from us.
781.
But as we readily follow an agreeable object that flies from us, so we
love to contemplate blue, not because it advances to us, but because it
draws us after it.
782.
Blue gives us an impression of cold, and thus, again, reminds us of
shade. We have before spoken of its affinity with black.
783.
Rooms which are hung with pure blue, appear in some degree larger, but
at the same time empty and cold.
784.
The appearance of objects seen through a blue glass is gloomy and
melancholy.
[Pg 312]
785.
When blue partakes in some degree of the plus side, the effect is not
disagreeable. Sea-green is rather a pleasing colour.
RED-BLUE.
786.
We found yellow very soon tending to the intense state, and we observe
the same progression in blue.
787.
Blue deepens very mildly into red, and thus acquires a somewhat active
character, although it is on the passive side. Its exciting power is,
however, of a very different kind from that of the red-yellow. It may
be said to disturb rather than enliven.
788.
As augmentation itself is not to be arrested, so we feel an inclination
to follow the progress of the colour, not, however, as in the case of
the red-yellow, to see it still increase in the active sense, but to
find a point to rest in.
789.
In a very attenuated state, this colour is known to us under the name
of lilac; but even in this degree it has a something lively without
gladness.
[Pg 313]
790.
This unquiet feeling increases as the hue progresses, and it may be
safely assumed, that a carpet of a perfectly pure deep blue-red would
be intolerable. On this account, when it is used for dress, ribbons, or
other ornaments, it is employed in a very attenuated and light state,
and thus displays its character as above defined, in a peculiarly
attractive manner.
791.
As the higher dignitaries of the church have appropriated this unquiet
colour to themselves, we may venture to say that it unceasingly aspires
to the cardinal's red through the restless degrees of a still impatient
progression.
RED.
792.
We are here to forget everything that borders on yellow or blue. We
are to imagine an absolutely pure red, like fine carmine suffered to
dry on white porcelain. We have called this colour "purpur" by way
of distinction, although we are quite aware that the purple of the
ancients inclined more to blue.
793.
Whoever is acquainted with the prismatic[Pg 314] origin of red, will not think
it paradoxical if we assert that this colour partly actu, partly
potentiâ, includes all the other colours.
794.
We have remarked a constant progress or augmentation in yellow and
blue, and seen what impressions were produced by the various states;
hence it may naturally be inferred that now, in the junction of the
deepened extremes, a feeling of satisfaction must succeed; and thus, in
physical phenomena, this highest of all appearances of colour arises
from the junction of two contrasted extremes which have gradually
prepared themselves for a union.
795.
As a pigment, on the other hand, it presents itself to us already
formed, and is most perfect as a hue in cochineal; a substance which,
however, by chemical action may be made to tend to the plus or the
minus side, and may be considered to have attained the central point
in the best carmine.
796.
The effect of this colour is as peculiar as its nature. It conveys an
impression of gravity and dignity, and at the same time of grace and
attractiveness. The first in its dark deep state,[Pg 315] the latter in its
light attenuated tint; and thus the dignity of age and the amiableness
of youth may adorn itself with degrees of the same hue.
797.
History relates many instances of the jealousy of sovereigns with
regard to the quality of red. Surrounding accompaniments of this colour
have always a grave and magnificent effect.
798.
The red glass exhibits a bright landscape in so dreadful a hue as to
inspire sentiments of awe.
799.
Kermes and cochineal, the two materials chiefly employed in dyeing to
produce this colour, incline more or less to the plus or minus
state, and may be made to pass and repass the culminating point by
the action of acids and alkalis: it is to be observed that the French
arrest their operations on the active side, as is proved by the French
scarlet, which inclines to yellow. The Italians, on the other hand,
remain on the passive side, for their scarlet has a tinge of blue.
800.
By means of a similar alkaline treatment, the so-called crimson is
produced; a colour which the French must be particularly prejudiced[Pg 316]
against, since they employ the expressions—"Sot en cramoisi, méchant
en cramoisi," to mark the extreme of the silly and the reprehensible.
GREEN.
801.
If yellow and blue, which we consider as the most fundamental and
simple colours, are united as they first appear, in the first state of
their action, the colour which we call green is the result.
802.
The eye experiences a distinctly grateful impression from this colour.
If the two elementary colours are mixed in perfect equality so that
neither predominates, the eye and the mind repose on the result of this
junction as upon a simple colour. The beholder has neither the wish
nor the power to imagine a state beyond it. Hence for rooms to live in
constantly, the green colour is most generally selected.
COMPLETENESS AND HARMONY.
803.
We have hitherto assumed, for the sake of clearer explanation, that the
eye can be compelled to assimilate or identify itself with a single
colour; but this can only be possible for an instant.
[Pg 317]
804.
For when we find ourselves surrounded by a given colour which excites
its corresponding sensation on the eye, and compels us by its presence
to remain in a state identical with it, this state is soon found to be
forced, and the organ unwillingly remains in it.
805.
When the eye sees a colour it is immediately excited, and it is its
nature, spontaneously and of necessity, at once to produce another,
which with the original colour comprehends the whole chromatic scale.
A single colour excites, by a specific sensation, the tendency to
universality.
806.
To experience this completeness, to satisfy itself, the eye seeks for
a colourless space next every hue in order to produce the complemental
hue upon it.
807.
In this resides the fundamental law of all harmony of colours, of which
every one may convince himself by making himself accurately acquainted
with the experiments which we have described in the chapter on the
physiological colours.
[Pg 318]
808.
If, again, the entire scale is presented to the eye externally, the
impression is gladdening, since the result of its own operation is
presented to it in reality. We turn our attention therefore, in the
first place, to this harmonious juxtaposition.
809.
As a very simple means of comprehending the principle of this, the
reader has only to imagine a moveable diametrical index in the
colorific circle.[1] The index, as it revolves round the whole circle,
indicates at its two extremes the complemental colours, which, after
all, may be reduced to three contrasts.
810.
Yellow demands Red-blue,
Blue demands Red-yellow,
Red demands Green,
and contrariwise.
811.
In proportion as one end of the supposed index deviates from the
central intensity of the colours, arranged as they are in the natural
order, so the opposite end changes its place in the contrasted
gradation, and by such a simple[Pg 319] contrivance the complemental colours
may be indicated at any given point. A chromatic circle might be made
for this purpose, not confined, like our own, to the leading colours,
but exhibiting them with their transitions in an unbroken series.
This would not be without its use, for we are here considering a very
important point which deserves all our attention.[2]
812.
We before stated that the eye could be in some degree pathologically
affected by being long confined to a single colour; that, again,
definite moral impressions were thus produced, at one time lively and
aspiring, at another susceptible and anxious—now exalted to grand
associations, now reduced to ordinary ones. We now observe that the
demand for completeness, which is inherent in the organ, frees us from
this restraint; the eye relieves itself by producing the opposite
of the single colour forced upon it, and thus attains the entire
impression which is so satisfactory to it.
813.
Simple, therefore, as these strictly harmonious contrasts are, as
presented to us in the narrow circle, the hint is important, that
nature tends to emancipate the sense from confined[Pg 320] impressions by
suggesting and producing the whole, and that in this instance we have a
natural phenomenon immediately applicable to æsthetic purposes.
814.
While, therefore, we may assert that the chromatic scale, as given by
us, produces an agreeable impression by its ingredient hues, we may
here remark that those have been mistaken who have hitherto adduced
the rainbow as an example of the entire scale; for the chief colour,
pure red, is deficient in it, and cannot be produced, since in this
phenomenon, as well as in the ordinary prismatic series, the yellow-red
and blue-red cannot attain to a union.
815.
Nature perhaps exhibits no general phenomenon where the scale is in
complete combination. By artificial experiments such an appearance may
be produced in its perfect splendour. The mode, however, in which the
entire series is connected in a circle, is rendered most intelligible
by tints on paper, till after much experience and practice, aided by
due susceptibility of the organ, we become penetrated with the idea of
this harmony, and feel it present in our minds.
[Pg 321]
816.
Besides these pure, harmonious, self-developed combinations, which
always carry the conditions of completeness with them, there are
others which may be arbitrarily produced, and which may be most easily
described by observing that they are to be found in the colorific
circle, not by diameters, but by chords, in such a manner that an
intermediate colour is passed over.
817.
We call these combinations characteristic because they have all a
certain significancy and tend to excite a definite impression; an
impression, however, which does not altogether satisfy, inasmuch as
every characteristic quality of necessity presents itself only as a
part of a whole, with which it has a relation, but into which it cannot
be resolved.
818.
As we are acquainted with the impressions produced by the colours
singly as well as in their harmonious relations, we may at once
conclude that the character of the arbitrary combinations will be very
different from each other as regards their significancy. We proceed to
review them separately.
[Pg 322]
YELLOW AND BLUE.
819.
This is the simplest of such combinations. It may be said that it
contains too little, for since every trace of red is wanting in it,
it is defective as compared with the whole scale. In this view it
may be called poor, and as the two contrasting elements are in their
lowest state, may be said to be ordinary; yet it is recommended by
its proximity to green—in short, by containing the ingredients of an
ultimate state.
YELLOW AND RED.
820.
This is a somewhat preponderating combination, but it has a serene
and magnificent effect. The two extremes of the active side are seen
together without conveying any idea of progression from one to the
other. As the result of their combination in pigments is yellow-red, so
they in some degree represent this colour.
BLUE AND RED.
821.
The two ends of the passive side, with the excess of the upper end of
the active side. The effect of this juxtaposition approaches that of
the blue-red produced by their union.
[Pg 323]
YELLOW-RED AND BLUE-RED.
822.
These, when placed together, as the deepened extremes of both sides,
have something exciting, elevated: they give us a presentiment of red,
which in physical experiments is produced by their union.
823.
These four combinations have also the common quality of producing the
intermediate colour of our colorific circle by their union, a union
which actually takes place if they are opposed to each other in small
quantities and seen from a distance. A surface covered with narrow blue
and yellow stripes appears green at a certain distance.
824.
If, again, the eye sees blue and yellow next each other, it finds
itself in a peculiar disposition to produce green without accomplishing
it, while it neither experiences a satisfactory sensation in
contemplating the detached colours, nor an impression of completeness
in the two.
825.
Thus it will be seen that it was not without reason we called these
combinations characteristic; the more so, since the character of each[Pg 324]
combination must have a relation to that of the single colours of which
it consists.
COMBINATIONS NON-CHARACTERISTIC.
826.
We now turn our attention to the last kind of combinations. These are
easily found in the circle; they are indicated by shorter chords, for
in this case we do not pass over an entire intermediate colour, but
only the transition from one to the other.
827.
These combinations may justly be called non-characteristic, inasmuch
as the colours are too nearly alike for their impression to be
significant. Yet most of these recommend themselves to a certain
degree, since they indicate a progressive state, though its relations
can hardly be appreciable.
828.
Thus yellow and yellow-red, yellow-red and red, blue and blue-red,
blue-red and red, represent the nearest degrees of augmentation and
culmination, and in certain relations as to quantity may produce no
unpleasant effect.
829.
The juxtaposition of yellow and green has[Pg 325] always something ordinary,
but in a cheerful sense; blue and green, on the other hand, is ordinary
in a repulsive sense. Our good forefathers called these last fool's
colours.
RELATION OF THE COMBINATIONS TO LIGHT AND DARK.
830.
These combinations may be very much varied by making both colours light
or both dark, or one light and the other dark; in which modifications,
however, all that has been found true in a general sense is applicable
to each particular case. With regard to the infinite variety thus
produced, we merely observe:
831.
The colours of the active side placed next to black gain in energy,
those of the passive side lose. The active conjoined with white and
brightness lose in strength, the passive gain in cheerfulness. Red and
green with black appear dark and grave; with white they appear gay.
832.
To this we may add that all colours may be more or less broken or
neutralised, may to a certain degree be rendered nameless, and thus
combined partly together and partly with pure colours; but although the
relations may thus[Pg 326] be varied to infinity, still all that is applicable
with regard to the pure colours will be applicable in these cases.
CONSIDERATIONS DERIVED FROM THE EVIDENCE OF EXPERIENCE AND HISTORY.
833.
The principles of the harmony of colours having been thus far defined,
it may not be irrelevant to review what has been adduced in connexion
with experience and historical examples.
834.
The principles in question have been derived from the constitution of
our nature and the constant relations which are found to obtain in
chromatic phenomena. In experience we find much that is in conformity
with these principles, and much that is opposed to them.
835.
Men in a state of nature, uncivilised nations, children, have a great
fondness for colours in their utmost brightness, and especially for
yellow-red: they are also pleased with the motley. By this expression
we understand the juxtaposition of vivid colours without an harmonious
balance; but if this balance is observed, through instinct or accident,
an agreeable effect may be produced. I remember a Hessian officer,
returned[Pg 327] from America, who had painted his face with the positive
colours, in the manner of the Indians; a kind of completeness or due
balance was thus produced, the effect of which was not disagreeable.
836.
The inhabitants of the south of Europe make use of very brilliant
colours for their dresses. The circumstance of their procuring silk
stuffs at a cheap rate is favourable to this propensity. The women,
especially, with their bright-coloured bodices and ribbons, are always
in harmony with the scenery, since they cannot possibly surpass the
splendour of the sky and landscape.
837.
The history of dyeing teaches us that certain technical conveniences
and advantages have had great influence on the costume of nations.
We find that the Germans wear blue very generally because it is a
permanent colour in cloth; so in many districts all the country people
wear green twill, because that material takes a green dye well. If
a traveller were to pay attention to these circumstances, he might
collect some amusing and curious facts.
838.
Colours, as connected with particular frames[Pg 328] of mind, are again a
consequence of peculiar character and circumstances. Lively nations,
the French for instance, love intense colours, especially on the active
side; sedate nations, like the English and Germans, wear straw-coloured
or leather-coloured yellow accompanied with dark blue. Nations aiming
at dignity of appearance, the Spaniards and Italians for instance,
suffer the red colour of their mantles to incline to the passive side.
839.
In dress we associate the character of the colour with the character of
the person. We may thus observe the relation of colours singly, and in
combination, to the colour of the complexion, age, and station.
840.
The female sex in youth is attached to rose-colour and sea-green, in
age to violet and dark-green. The fair-haired prefer violet, as opposed
to light yellow, the brunettes, blue, as opposed to yellow-red, and
all on good grounds. The Roman emperors were extremely jealous with
regard to their purple. The robe of the Chinese Emperor is orange
embroidered with red; his attendants and the ministers of religion wear
citron-yellow.
[Pg 329]
841.
People of refinement have a disinclination to colours. This may be
owing partly to weakness of sight, partly to the uncertainty of taste,
which readily takes refuge in absolute negation. Women now appear
almost universally in white and men in black.
842.
An observation, very generally applicable, may not be out of place
here, namely, that man, desirous as he is of being distinguished, is
quite as willing to be lost among his fellows.
843.
Black was intended to remind the Venetian noblemen of republican
equality.
844.
To what degree the cloudy sky of northern climates may have gradually
banished colour may also admit of explanation.
845.
The scale of positive colours is obviously soon exhausted; on the
other hand, the neutral, subdued, so-called fashionable colours
present infinitely varying degrees and shades, most of which are not
unpleasing.
[Pg 330]
846.
It is also to be remarked that ladies, in wearing positive colours,
are in danger of making a complexion which may not be very bright
still less so, and thus to preserve a due balance with such brilliant
accompaniments, they are induced to heighten their complexions
artificially.
847.
An amusing inquiry might be made which would lead to a critique of
uniforms, liveries, cockades, and other distinctions, according to the
principles above hinted at. It might be observed, generally, that such
dresses and insignia should not be composed of harmonious colours.
Uniforms should be characteristic and dignified; liveries might be
ordinary and striking to the eye. Examples both good and bad would
not be wanting, since the scale of colours usually employed for such
purposes is limited, and its varieties have been often enough tried.[3]
ÆSTHETIC INFLUENCE.
848.
From the moral associations connected with the appearance of colours,
single or combined, their æsthetic influence may now be deduced[Pg 331] for
the artist. We shall touch the most essential points to be attended
to after first considering the general condition of pictorial
representation, light and shade, with which the appearance of colour is
immediately connected.
CHIARO-SCURO.
849.
We apply the term chiaro-scuro (Helldunkel) to the appearance of
material objects when the mere effect produced on them by light and
shade is considered.—Note DD.
850.
In a narrower sense a mass of shadow lighted by reflexes is often
thus designated; but we here use the expression in its first and more
general sense.
851.
The separation of light and dark from all appearance of colour is
possible and necessary. The artist will solve the mystery of imitation
sooner by first considering light and dark independently of colour, and
making himself acquainted with it in its whole extent.
852.
Chiaro-scuro exhibits the substance as substance, inasmuch as light and
shade inform us as to degrees of density.
[Pg 332]
853.
We have here to consider the highest light, the middle tint, and the
shadow, and in the last the shadow of the object itself, the shadow it
casts on other objects, and the illumined shadow or reflexion.
854.
The globe is well adapted for the general exemplification of the nature
of chiaro-scuro, but it is not altogether sufficient. The softened
unity of such complete rotundity tends to the vapoury, and in order to
serve as a principle for effects of art, it should be composed of plane
surfaces, so as to define the gradations more.
855.
The Italians call this manner "il piazzoso;" in German it might
be called "das Flächenhafte."[4] If, therefore, the sphere is a
perfect example of natural chiaro-scuro, a polygon would exhibit the
artist-like treatment in which all kinds of lights, half-lights,
shadows, and reflexions, would be appreciable.—Note EE.
856.
The bunch of grapes is recognised as a good example of a picturesque
completeness in chiaro-scuro, the more so as it is fitted, from its
form, to represent a principal group; but it is only[Pg 333] available for the
master who can see in it what he has the power of producing.
857.
In order to make the first idea intelligible to the beginner, (for
it is difficult to consider it abstractedly even in a polygon,) we
may take a cube, the three sides of which that are seen represent the
light, the middle tint, and the shadow in distinct order.
858.
To proceed again to the chiaro-scuro of a more complicated figure, we
might select the example of an open book, which presents a greater
diversity.
859.
We find the antique statues of the best time treated very much with
reference to these effects. The parts intended to receive the light
are wrought with simplicity, the portion originally in shade is, on
the other hand, in more distinct surfaces to make them susceptible
of a variety of reflexions; here the example of the polygon will be
remembered.—Note FF.
860.
The pictures of Herculaneum and the Aldobrandini marriage are examples
of antique painting in the same style.
[Pg 334]
861.
Modern examples may be found in single figures by Raphael, in entire
works by Correggio, and also by the Flemish masters, especially Rubens.
TENDENCY TO COLOUR.
862.
A picture in black and white seldom makes its appearance; some works
of Polidoro are examples of this kind of art. Such works, inasmuch as
they can attain form and keeping, are estimable, but they have little
attraction for the eye, since their very existence supposes a violent
abstraction.
863.
If the artist abandons himself to his feeling, colour presently
announces itself. Black no sooner inclines to blue than the eye demands
yellow, which the artist instinctively modifies, and introduces partly
pure in the light, partly reddened and subdued as brown, in the
reflexes, thus enlivening the whole.—Note GG.
864.
All kinds of camayeu, or colour on similar colour, end in the
introduction either of a complemental contrast, or some variety of hue.
Thus, Polidoro in his black and white frescoes[Pg 335] sometimes introduced a
yellow vase, or something of the kind.
865.
In general it may be observed that men have at all times instinctively
striven after colour in the practice of the art. We need only observe
daily, how soon amateurs proceed from colourless to coloured materials.
Paolo Uccello painted coloured landscapes to colourless figures.—Note HH.
866.
Even the sculpture of the ancients could not be exempt from the
influence of this propensity. The Egyptians painted their bas-reliefs;
statues had eyes of coloured stones. Porphyry draperies were added to
marble heads and extremities, and variegated stalactites were used
for the pedestals of busts. The Jesuits did not fail to compose the
statue of their S. Luigi, in Rome, in this manner, and the most modern
sculpture distinguishes the flesh from the drapery by staining the
latter.
KEEPING.
867.
If linear perspective displays the gradation of objects in their
apparent size as affected by distance, aërial perspective shows us
their gradation[Pg 336] in greater or less distinctness, as affected by the
same cause.
868.
Although from the nature of the organ of sight, we cannot see distant
objects so distinctly as nearer ones, yet aërial perspective is
grounded strictly on the important fact that all mediums called
transparent are in some degree dim.
869.
The atmosphere is thus always, more or less, semi-transparent. This
quality is remarkable in southern climates, even when the barometer is
high, the weather dry, and the sky cloudless, for a very pronounced
gradation is observable between objects but little removed from each
other.
870.
The appearance on a large scale is known to every one; the painter,
however, sees or believes he sees, the gradation in the slightest
varieties of distance. He exemplifies it practically by making a
distinction, for instance, in the features of a face according to their
relative position as regards the plane of the picture. The direction of
the light is attended to in like manner. This is considered to produce
a gradation from side to side, while keeping has reference to depth, to
the comparative distinctness of near and distant things.
[Pg 337]
871.
In proceeding to consider this subject, we assume that the painter is
generally acquainted with our sketch of the theory of colours, and that
he has made himself well acquainted with certain chapters and rubrics
which especially concern him. He will thus be enabled to make use of
theory as well as practice in recognising the principles of effect in
nature, and in employing the means of art.
COLOUR IN GENERAL NATURE.
872.
The first indication of colour announces itself in nature together
with the gradations of aërial perspective; for aërial perspective is
intimately connected with the doctrine of semi-transparent mediums. We
see the sky, distant objects and even comparatively near shadows, blue.
At the same moment, the illuminating and illuminated objects appear
yellow, gradually deepening to red. In many cases the physiological
suggestion of contrasts comes into the account, and an entirely
colourless landscape, by means of these assisting and counteracting
tendencies, appears to our eyes completely coloured.
[Pg 338]
873.
Local colours are composed of the general elementary colours; but these
are determined or specified according to the properties of substances
and surfaces on which they appear: this specification is infinite.
874.
Thus, there is at once a great difference between silk and wool
similarly dyed. Every kind of preparation and texture produces
corresponding modifications. Roughness, smoothness, polish, all are to
be considered.
875.
It is therefore one of the pernicious prejudices of art that the
skilful painter must never attend to the material of draperies,
but always represent, as it were, only abstract folds. Is not all
characteristic variety thus done away with, and is the portrait of Leo
X. less excellent because velvet, satin, and moreen, are imitated in
their relative effect?
876.
In the productions of nature, colours appear more or less modified,
specified, even individualised: this may be readily observed in
minerals[Pg 339] and plants, in the feathers of birds and the skins of beasts.
877.
The chief art of the painter is always to imitate the actual appearance
of the definite hue, doing away with the recollection of the elementary
ingredients of colour. This difficulty is in no instance greater than
in the imitation of the surface of the human figure.
878.
The colour of flesh, as a whole, belongs to the active side, yet the
bluish of the passive side mingles with it. The colour is altogether
removed from the elementary state and neutralised by organisation.
879.
To bring the colouring of general nature into harmony with the
colouring of a given object, will perhaps be more attainable for the
judicious artist after the consideration of what has been pointed out
in the foregoing theory. For the most fancifully beautiful and varied
appearances may still be made true to the principles of nature.
CHARACTERISTIC COLOURING.
880.
The combination of coloured objects, as well as the colour of
their ground, should depend on[Pg 340] considerations which the artist
pre-establishes for himself. Here a reference to the effect of colours
singly or combined, on the feelings, is especially necessary. On this
account the painter should possess himself with the idea of the general
dualism, as well as of particular contrasts, not forgetting what has
been adverted to with regard to the qualities of colours.
881.
The characteristic in colour may be comprehended under three leading
rubrics, which we here define as the powerful, the soft, and the
splendid.
882.
The first is produced by the preponderance of the active side, the
second by that of the passive side, and the third by completeness, by
the exhibition of the whole chromatic scale in due balance.
883.
The powerful impression is attained by yellow, yellow-red, and red,
which last colour is to be arrested on the plus side. But little violet
and blue, still less green, are admissible. The soft effect is produced
by blue, violet, and red, which in this case is arrested on the minus
side; a moderate addition of yellow and yellow-red, but much green may
be admitted.
[Pg 341]
884.
If it is proposed to produce both these effects in their full
significancy, the complemental colours may be excluded to a minimum,
and only so much of them may be suffered to appear as is indispensable
to convey an impression of completeness.
HARMONIOUS COLOURING.
885.
Although the two characteristic divisions as above defined may in some
sense be also called harmonious, the harmonious effect, properly so
called, only takes place when all the colours are exhibited together in
due balance.
886.
In this way the splendid as well as the agreeable may be produced; both
of these, however, have of necessity a certain generalised effect, and
in this sense may be considered the reverse of the characteristic.
887.
This is the reason why the colouring of most modern painters is without
character, for, while they follow their general instinctive feeling
only, the last result of such a tendency must be mere completeness;
this, they more or less attain, but thus at the same time neglect the
characteristic[Pg 342] impression which the subject might demand.
888.
But if the principles before alluded to are kept in view, it must be
apparent that a distinct style of colour may be adopted on safe grounds
for every subject. The application requires, it is true, infinite
modifications, which can only succeed in the hands of genius.
GENUINE TONE.
889.
If the word tone, or rather tune, is to be still borrowed in future
from music, and applied to colouring, it might be used in a better
sense than heretofore.
890.
For it would not be unreasonable to compare a painting of powerful
effect, with a piece of music in a sharp key; a painting of soft effect
with a piece of music in a flat key, while other equivalents might be
found for the modifications of these two leading modes.
FALSE TONE.
891.
The word tone has been hitherto understood to mean a veil of a
particular colour spread over[Pg 343] the whole picture; it was generally
yellow, for the painter instinctively pushed the effect towards the
powerful side.
892.
If we look at a picture through a yellow glass it will appear in this
tone. It is worth while to make this experiment again and again, in
order to observe what takes place in such an operation. It is a sort of
artificial light, deepening, and at the same time darkening the plus
side, and neutralising the minus side.
893.
This spurious tone is produced instinctively through uncertainty
as to the means of attaining a genuine effect; so that instead of
completeness, monotony is the result.
WEAK COLOURING.
894.
It is owing to the same uncertainty that the colours are sometimes so
much broken as to have the effect of a grey camayeu, the handling being
at the same time as delicate as possible.
895.
The harmonious contrasts are often found to be very happily felt in
such pictures, but without spirit, owing to a dread of the motley.
[Pg 344]
THE MOTLEY.
896.
A picture may easily become party-coloured or motley, when the colours
are placed next each other in their full force, as it were only
mechanically and according to uncertain impressions.
897.
If, on the other hand, weak colours are combined, even although they
may be dissonant, the effect, as a matter of course, is not striking.
The uncertainty of the artist is communicated to the spectator, who, on
his side, can neither praise nor censure.
898.
It is also important to observe that the colours may be disposed
rightly in themselves, but that a work may still appear motley, if they
are falsely arranged in relation to light and shade.
899.
This may the more easily occur as light and shade are already defined
in the drawing, and are, as it were, comprehended in it, while the
colour still remains open to selection.
DREAD OF THEORY.
900.
A dread of, nay, a decided aversion for all[Pg 345] theoretical views
respecting colour and everything belonging to it, has been hitherto
found to exist among painters; a prejudice for which, after all, they
were not to be blamed; for what has been hitherto called theory was
groundless, vacillating, and akin to empiricism. We hope that our
labours may tend to diminish this prejudice, and stimulate the artist
practically to prove and embody the principles that have been explained.
ULTIMATE AIM.
901.
But without a comprehensive view of the whole of our theory, the
ultimate object will not be attained. Let the artist penetrate himself
with all that we have stated. It is only by means of harmonious
relations in light and shade, in keeping, in true and characteristic
colouring, that a picture can be considered complete, in the sense we
have now learnt to attach to the term.
GROUNDS.
902.
It was the practice of the earlier artists to paint on light grounds.
This ground consisted of gypsum, and was thickly spread on linen or
panel, and then levigated. After the outline was drawn, the subject was
washed in with a[Pg 346] blackish or brownish colour. Pictures prepared in
this manner for colouring are still in existence, by Leonardo da Vinci,
and Fra Bartolomeo; there are also several by Guido.—Note II.
903.
When the artist proceeded to colour, and had to represent white
draperies, he sometimes suffered the ground to remain untouched.
Titian did this latterly when he had attained the greatest certainty
in practice, and could accomplish much with little labour. The whitish
ground was left as a middle tint, the shadows painted in, and the high
lights touched on.—Note KK.
904.
In the process of colouring, the preparation merely washed as it were
underneath, was always effective. A drapery, for example, was painted
with a transparent colour, the white ground shone through it and gave
the colour life, so the parts previously prepared for shadows exhibited
the colour subdued, without being mixed or sullied.
905.
This method had many advantages; for the painter had a light ground
for the light portions of his work and a dark ground for the shadowed
portions. The whole picture was prepared; the[Pg 347] artist could work with
thin colours in the shadows, and had always an internal light to give
value to his tints. In our own time painting in water colours depends
on the same principles.
906.
Indeed a light ground is now generally employed in oil-painting,
because middle tints are thus found to be more transparent, and are in
some degree enlivened by a bright ground; the shadows, again, do not so
easily become black.
907.
It was the practice for a time to paint on dark grounds. Tintoret
probably introduced them. Titian's best pictures are not painted on a
dark ground.
908.
The ground in question was red-brown, and when the subject was drawn
upon it, the strongest shadows were laid in; the colours of the lights
impasted very thickly in the bright parts, and scumbled towards the
shadows, so that the dark ground appeared through the thin colour as a
middle tint. Effect was attained in finishing by frequently going over
the bright parts and touching on the high lights.
[Pg 348]
909.
If this method especially recommended itself in practice on account
of the rapidity it allowed of, yet it had pernicious consequences.
The strong ground increased and became darker, and the light colours
losing their brightness by degrees, gave the shadowed portions more
and more preponderance. The middle tints became darker and darker, and
the shadows at last quite obscure. The strongly impasted lights alone
remained bright, and we now see only light spots on the painting. The
pictures of the Bolognese school, and of Caravaggio, afford sufficient
examples of these results.
910.
We may here in conclusion observe, that glazing derives its effect
from treating the prepared colour underneath as a light ground. By
this operation colours may have the effect of being mixed to the eye,
may be enhanced, and may acquire what is called tone; but they thus
necessarily become darker.
PIGMENTS.
911.
We receive these from the hands of the chemist and the investigator of
nature. Much has been recorded respecting colouring substances,[Pg 349] which
is familiar to all by means of the press. But such directions require
to be revised from time to time. The master meanwhile communicates his
experience in these matters to his scholar, and artists generally to
each other.
912.
Those pigments which according to their nature are the most permanent,
are naturally much sought after, but the mode of employing them also
contributes much to the duration of a picture. The fewest possible
colouring materials are to be employed, and the simplest methods of
using them cannot be sufficiently recommended.
913.
For from the multitude of pigments colouring has suffered much. Every
pigment has its peculiar nature as regards its effect on the eye;
besides this it has its peculiar quality, requiring a corresponding
technical method in its application. The former circumstance is a
reason why harmony is more difficult of attainment with many materials
than with few, the latter, why chemical action and re-action may take
place among the colouring substances.
914.
We may refer, besides, to some false tendencies[Pg 350] which the artists
suffer themselves to be led away with. Painters are always looking
for new colouring substances, and believe when such a substance is
discovered that they have made an advance in the art. They have a
great curiosity to know the practical methods of the old masters, and
lose much time in the search. Towards the end of the last century
we were thus long tormented with wax-painting. Others turn their
attention to the discovery of new methods, through which nothing new is
accomplished; for, after all, it is the feeling of the artist only that
informs every kind of technical process.
ALLEGORICAL, SYMBOLICAL, MYSTICAL APPLICATION OF COLOUR.
915.
It has been circumstantially shown above, that every colour produces
a distinct impression on the mind, and thus addresses at once the eye
and feelings. Hence it follows that colour may be employed for certain
moral and æsthetic ends.
916.
Such an application, coinciding entirely with nature, might be called
symbolical, since the colour would be employed in conformity with its
effect, and would at once express its meaning. If, for example, pure
red were assumed to[Pg 351] designate majesty, there can be no doubt that this
would be admitted to be a just and expressive symbol. All this has been
already sufficiently entered into.
917.
Another application is nearly allied to this; it might be called the
allegorical application. In this there is more of accident and caprice,
inasmuch as the meaning of the sign must be first communicated to us
before we know what it is to signify; what idea, for instance, is
attached to the green colour, which has been appropriated to hope?
918.
That, lastly, colour may have a mystical allusion, may be readily
surmised, for since every diagram in which the variety of colours may
be represented points to those primordial relations which belong both
to nature and the organ of vision, there can be no doubt that these may
be made use of as a language, in cases where it is proposed to express
similar primordial relations which do not present themselves to the
senses in so powerful and varied a manner. The mathematician extols
the value and applicability of the triangle; the triangle is revered
by the mystic; much admits of being expressed in it by diagrams, and,
among other things, the law[Pg 352] of the phenomena of colours; in this case,
indeed, we presently arrive at the ancient mysterious hexagon.
919.
When the distinction of yellow and blue is duly comprehended, and
especially the augmentation into red, by means of which the opposite
qualities tend towards each other and become united in a third; then,
certainly, an especially mysterious interpretation will suggest itself,
since a spiritual meaning may be connected with these facts; and when
we find the two separate principles producing green on the one hand and
red in their intenser state, we can hardly refrain from thinking in the
first case on the earthly, in the last on the heavenly, generation of
the Elohim.—Note LL.
920.
But we shall do better not to expose ourselves, in conclusion, to
the suspicion of enthusiasm; since, if our doctrine of colours finds
favour, applications and allusions, allegorical, symbolical, and
mystical, will not fail to be made, in conformity with the spirit of
the age.
CONCLUDING OBSERVATIONS.
In reviewing this labour, which has occupied me long, and which at
last I give but as a[Pg 353] sketch, I am reminded of a wish once expressed
by a careful writer, who observed that he would gladly see his works
printed at once as he conceived them, in order then to go to the task
with a fresh eye; since everything defective presents itself to us more
obviously in print than even in the cleanest manuscript. This feeling
may be imagined to be stronger in my case, since I had not even an
opportunity of going through a fair transcript of my work before its
publication, these pages having been put together at a time when a
quiet, collected state of mind was out of the question.[5]
Some of the explanations I was desirous of giving are to be found in
the introduction, but in the portion of my work to be devoted to the
history of the doctrine of colours, I hope to give a more detailed
account of my investigations and the vicissitudes they underwent. One
inquiry, however, may not be out of place here; the consideration,
namely, of the question, what can a man accomplish who cannot devote
his whole life to scientific pursuits? what can he perform as a
temporary guest on an estate not his own, for the advantage of the
proprietor?
When we consider art in its higher character, we might wish that
masters only had to do with[Pg 354] it, that scholars should be trained by
the severest study, that amateurs might feel themselves happy in
reverentially approaching its precincts. For a work of art should be
the effusion of genius, the artist should evoke its substance and form
from his inmost being, treat his materials with sovereign command, and
make use of external influences only to accomplish his powers.
But if the professor in this case has many reasons for respecting
the dilettante, the man of science has every motive to be still more
indulgent, since the amateur here is capable of contributing what may
be satisfactory and useful. The sciences depend much more on experiment
than art, and for mere experiment many a votary is qualified.
Scientific results are arrived at by many means, and cannot dispense
with many hands, many heads. Science may be communicated, the treasure
may be inherited, and what is acquired by one may be appropriated
by many. Hence no one perhaps ought to be reluctant to offer his
contributions. How much do we not owe to accident, to mere practice,
to momentary observation. All who are endowed only with habits of
attention, women, children, are capable of communicating striking and
true remarks.
In science it cannot therefore be required, that he who endeavours
to furnish something in[Pg 355] its aid should devote his whole life to it,
should survey and investigate it in all its extent; for this, in most
cases, would be a severe condition even for the initiated. But if we
look through the history of science in general, especially the history
of physics, we shall find that many important acquisitions have been
made by single inquirers, in single departments, and very often by
unprofessional observers.
To whatever direction a man may be determined by inclination or
accident, whatever class of phenomena especially strike him, excite
his interest, fix his attention, and occupy him, the result will still
be for the advantage of science: for every new relation that comes to
light, every new mode of investigation, even the imperfect attempt,
even error itself is available; it may stimulate other observers and is
never without its use as influencing future inquiry.
With this feeling the author himself may look back without regret
on his endeavours. From this consideration he can derive some
encouragement for the prosecution of the remainder of his task; and
although not satisfied with the result of his efforts, yet re-assured
by the sincerity of his intentions, he ventures to recommend his past
and future labours to the interest of his contemporaries and posterity.
Multi pertransibunt et augebitur scientia.
NOTE A.—Par. 18.
Leonardo da Vinci observes that "a light object relieved on a dark
ground appears magnified;" and again, "Objects seen at a distance
appear out of proportion; this is because the light parts transmit
their rays to the eye more powerfully than the dark. A woman's white
head-dress once appeared to me much wider than her shoulders, owing
to their being dressed in black."[1] "It is now generally admitted
that the excitation produced by light is propagated on the retina a
little beyond the outline of the image. Professor Plateau, of Ghent,
has devoted a very interesting special memoir to the description
and explanation of phenomena of this nature. See his 'Mémoire sur
l'Irradiation,' published in the 11th vol. of the Transactions of the
Royal Academy of Sciences at Brussels."[2]—S. F.
NOTE B.—Par. 23.
"The duration of ocular spectra produced by strongly exciting the
retina, may be conveniently measured by minutes and seconds; but to
ascertain the duration of more evanescent phenomena, recourse must be
had to other means. The Chevalier d'Arcy (Mém. de l'Acad. des Sc.[Pg 358]
1765,) endeavoured to ascertain the duration of the impression produced
by a glowing coal in the following manner. He attached it to the
circumference of a wheel, the velocity of which was gradually increased
until the apparent trace of the object formed a complete circle, and
then measured the duration of a revolution, which was obviously that
of the impression. To ascertain the duration of a revolution it is
sufficient merely to know the number of revolutions described in a
given time. Recently more refined experiments of the same kind have
been made by Professors Plateau and Wheatstone."—S. F.
NOTE C.—Par. 50.
Every treatise on the harmonious combination of colours contains the
diagram of the chromatic circle more or less elaborately constructed.
These diagrams, if intended to exhibit the contrasts produced by
the action and re-action of the retina, have one common defect. The
opposite colours are made equal in intensity; whereas the complemental
colour pictured on the retina is always less vivid, and always darker
or lighter than the original colour. This variety undoubtedly accords
more with harmonious effects in painting.
The opposition of two pure hues of equal intensity, differing only in
the abstract quality of colour, would immediately be pronounced crude
and inharmonious. It would not, however, be strictly correct to say
that such a contrast is too violent; on the contrary, it appears the
contrast is not carried far enough, for though differing in colour,
the two hues may be exactly similar in purity and intensity. Complete
contrast, on the other hand, supposes dissimilarity in all respects.
In addition to the mere difference of hue, the eye, it seems, requires
difference in the lightness or darkness of the hue. The spectrum of a
colour relieved as a dark on a light ground, is a light colour on a
dark ground, and vice versâ. Thus, if we look at a bright red wafer
on the whitest[Pg 359] surface, the complemental image will be still lighter
than the white surface; if the same wafer is placed on a black surface,
the complemental image will be still darker. The colour of both these
spectra may be called greenish, but it is evident that a colour must be
scarcely appreciable as such, if it is lighter than white and darker
than black. It is, however, to be remarked, that the white surface
round the light greenish image seems tinged with a reddish hue, and
the black surface round the dark image becomes slightly illuminated
with the same colour, thus in both cases assisting to render the image
apparent (58).
The difficulty or impossibility of describing degrees of colour in
words, has also had a tendency to mislead, by conveying the idea of
more positive hues than the physiological contrast warrants. Thus,
supposing scarlet to be relieved as a dark, the complemental colour is
so light in degree and so faint in colour, that it should be called a
pearly grey; whereas the theorists, looking at the quality of colour
abstractedly, would call it a green-blue, and the diagram would falsely
present such a hue equal in intensity to scarlet, or as nearly equal as
possible.
Even the difference of mass which good taste requires may be suggested
by the physiological phenomena, for unless the complemental image is
suffered to fall on a surface precisely as near to the eye as that on
which the original colour was displayed, it appears larger or smaller
than the original object (22), and this in a rapidly increasing
proportion. Lastly, the shape itself soon becomes changed (26).
That vivid colour demands the comparative absence of colour, either
on a lighter or darker scale, as its contrast, may be inferred again
from the fact that bright colourless objects produce strongly coloured
spectra. In darkness, the spectrum which is first white, or nearly
white, is followed by red: in light, the spectrum which is first black,
is followed by green (39-44). All colour, as the author observes
(259), is to be considered as half-light, inasmuch as it[Pg 360] is in every
case lighter than black and darker than white. Hence no contrast of
colour with colour, or even of colour with black or white, can be so
great (as regards lightness or darkness) as the contrast of black and
white, or light and dark abstractedly. This distinction between the
differences of degree and the differences of kind is important, since a
just application of contrast in colour may be counteracted by an undue
difference in lightness or darkness. The mere contrast of colour is
happily employed in some of Guido's lighter pictures, but if intense
darks had been opposed to his delicate carnations, their comparative
whiteness would have been unpleasantly apparent. On the other hand, the
flesh-colour in Giorgione, Sebastian del Piombo (his best imitator),
and Titian, was sometimes so extremely glowing[1] that the deepest
colours, and black, were indispensable accompaniments. The manner of
Titian as distinguished from his imitation of Giorgione, is golden
rather than fiery, and his biographers are quite correct in saying
that he was fond of opposing red (lake) and blue to his flesh[2]. The
correspondence of these contrasts with the physiological phenomena will
be immediately apparent, while the occasional practice of Rubens in
opposing bright red to a still cooler flesh-colour, will be seen to be
equally consistent.
The effect of white drapery (the comparative absence of colour) in
enhancing the glow of Titian's flesh-colour, has been frequently
pointed out:[3] the shadows of white thus opposed to flesh, often
present, again, the physiological contrast, however delicately,
according to the hue of the carnation.[Pg 361] The lights, on the other hand,
are not, and probably never were, quite white, but from the first,
partook of the quality of depth, a quality assumed by the colourists to
pervade every part of a picture more or less.[4]
It was before observed that the description of colours in words may
often convey ideas of too positive a nature, and it may be remarked
generally that the colours employed by the great masters are, in their
ultimate effect, more or less subdued or broken. The physiological
contrasts are, however, still applicable in the most comparatively
neutral scale.
Again, the works of the colourists show that these oppositions are
not confined to large masses (except perhaps in works to be seen only
at a great distance); on the contrary, they are more or less apparent
in every part, and when at last the direct and intentional operations
of the artist may have been insufficient to produce them in their
minuter degrees, the accidental results of glazing and other methods
may be said to extend the contrasts to infinity. In such productions,
where every smallest portion is an epitome of the whole, the eye
still appreciates the fascinating effect of contrast, and the work is
pronounced to be true and complete, in the best sense of the words.
The Venetian method of scumbling and glazing exhibits these minuter
contrasts within each other, and is thus generally considered more
refined than the system of breaking the colours, since it ensures a
fuller gradation of hues, and produces another class of contrasts,
those, namely, which result from degrees of transparence and opacity.
In some of the Flemish and Dutch masters, and sometimes in Reynolds,
the two methods are combined in great perfection.
[Pg 362]
The chromatic diagram does not appear to be older than the last
century. It is one of those happy adaptations of exacter principles to
the objects of taste which might have been expected from Leonardo da
Vinci. That its true principle was duly felt is abundantly evident from
the works of the colourists, as well as from the general observations
of early writers.[5] The more practical directions occasionally to be
met with in the treatises of Leon Battista Alberti, Leonardo da Vinci
and others, are conformable to the same system. Some Italian works,
not written by painters, which pretend to describe this harmony, are,
however, very imperfect.[6] A passage in Lodovico Dolce's Dialogue on
Colours is perhaps the only one worth quoting. "He," says that writer,
"who wishes to combine colours that are agreeable to the eye, will
put grey next dusky orange; yellow-green next rose-colour; blue next
orange; dark purple, black, next dark-green; white next black, and
white next flesh-colour."[7] The Dialogue on Painting, by the same
author, has the reputation of containing some of Titian's precepts:
if the above passage may be traced to the same source, it must be
confessed that it is almost the only one of the kind in the treatise
from which it is taken.
NOTE D.—Par. 66.
In some of these cases there can be no doubt that Goethe[Pg 363] attributes
the contrast too exclusively to the physiological cause, without
making sufficient allowance for the actual difference in the colour of
the lights. The purely physical nature of some coloured shadows was
pointed out by Pohlmann; and Dr. Eckermann took some pains to convince
Goethe of the necessity of making such a distinction. Goethe at first
adhered to his extreme view, but some time afterwards confessed to
Dr. Eckermann, that in the case of the blue shadows of snow (74), the
reflection of the sky was undoubtedly to be taken into the account.
"Both causes may, however, operate together," he observed, "and the
contrast which a warm yellow light demands may heighten the effect of
the blue." This was all his opponent contended.[1]
With a few such exceptions, the general theory of Goethe with regard
to coloured shadows is undoubtedly correct; the experiments with two
candles (68), and with coloured glass and fluids (80), as well as the
observations on the shadows of snow (75), are conclusive, for in all
these cases only one light is actually changed in colour, while the
other still assumes the complemental hue. "Coloured shadows," Dr. J.
Müller observes, "are usually ascribed to the physiological influence
of contrast; the complementary colour presented by the shadow being
regarded as the effect of internal causes acting on that part of the
retina, and not of the impression of coloured rays from without. This
explanation is the one adopted by Rumford, Goethe, Grotthuss, Brandes,
Tourtual, Pohlmann, and most authors who have studied the subject."[2]
In the Historical Part the author gives an account of a scarce French
work, "Observations sur les Ombres Colorées," Paris, 1782. The
writer[3] concludes that "the colour[Pg 364] of shadows is as much owing to
the light that causes them as to that which (more faintly) illumines
them."
NOTE E.—Par. 69.
This opinion of the author is frequently repeated (201, 312, 591), and
as it seems at first sight to be at variance with a received principle
of art, it may be as well at once to examine it.
In order to see the general proposition in its true point of view,
it will be necessary to forget the arbitrary distinctions of light
and shade, and to consider all such modifications between highest
brightness and absolute darkness only as so many lesser degrees of
light.[1] The author, indeed, by the word shadow, always understands a
lesser light.
The received notion, as stated by Du Fresnoy,[2] is much too positive
and unconditional, and is only true when we understand the "displaying"
light to comprehend certain degrees of half or reflected light, and the
"destroying" shade to mean the intensest degree of obscurity.
There are degrees of brightness which destroy colour as well as
degrees of darkness.[3] In general, colour resides in a mitigated
light, but a very little observation shows us that different colours
require different degrees of light to display them. Leonardo da Vinci
frequently inculcates the general principle above alluded to, but he
as frequently qualifies it; for he not only remarks that the highest
light may be comparative[Pg 365] privation of colour, but observes, with great
truth, that some hues are best displayed in their fully illumined
parts, some in their reflections, and some in their half-lights; and
again, that every colour is most beautiful when lit by reflections from
its own surface, or from a hue similar to its own.[4]
The Venetians went further than Leonardo in this view and practice;
and he seems to allude to them when he criticises certain painters,
who, in aiming at clearness and fulness of colour, neglected what, in
his eyes, was of superior importance, namely, gradation and force of
chiaro-scuro.[5]
That increase of colour supposes increase of darkness, as so often
stated by Goethe, may be granted without difficulty. To what extent, on
the other hand, increase of darkness, or rather diminution of light,
is accompanied by increase of colour, is a question which has been
variously answered by various schools. Examples of the total negation
of the principle are not wanting, nor are they confined to the infancy
of the art. Instances, again, of the opposite tendency are frequent
in Venetian and early Flemish pictures resembling the augmenting
richness of gems or of stained glass:[6][Pg 366] indeed, it is not impossible
that the increase of colour in shade, which is so remarkable in the
pictures alluded to, may have been originally suggested by the rich
and fascinating effect of stained glass; and the Venetians, in this as
in many other respects, may have improved on a hint borrowed from the
early German painters, many of whom painted on glass.[7]
At all events, the principle of still increasing in colour in certain
hues seems to have been adopted in Flanders and in Venice at an early
period;[8] while Giorgione, in carrying the style to the most daring
extent, still recommended it by corresponding grandeur of treatment in
other respects.
The same general tendency, except that the technical methods are
less transparent, is, however, very striking in some of the painters
of the school of Umbria, the instructors or early companions of
Raphael.[9] The influence of[Pg 367] these examples, as well as that of Fra
Bartolommeo, in Florence, is distinctly to be traced in the works of
the great artist just named, but neither is so marked as the effect
of his emulation of a Venetian painter at a later period. The glowing
colour, sometimes bordering on exaggeration, which Raphael adopted
in Rome, is undoubtedly to be attributed to the rivalry of Sebastian
del Piombo. This painter, the best of Giorgione's imitators, arrived
in Rome, invited by Agostini Chigi, in 1511, and the most powerful of
Raphael's frescoes, the Heliodorus and Mass of Bolsena, as well as
some portraits in the same style, were painted in the two following
years. In the hands of some of Raphael's scholars, again, this extreme
warmth was occasionally carried to excess, particularly by Pierino del
Vaga, with whom it often degenerated into redness. The representative
of the glowing manner in Florence was Fra Bartolommeo, and, in the
same quality, considered abstractedly, some painters of the school of
Ferrara were second to none.
In another Note (par. 177) some further considerations[Pg 368] are offered,
which may partly explain the prevalence of this style in the beginning
of the sixteenth century; here we merely add, that the conditions under
which the appearance itself is most apparent in nature are perhaps more
obvious in Venice than elsewhere. The colour of general nature may be
observed in all places with almost equal convenience, but with regard
to an important quality in living nature, namely, the colour of flesh,
perhaps there are no circumstances in which its effects at different
distances can be so conveniently compared as when the observer and the
observed gradually approach and glide past each other on so smooth an
element and in so undisturbed a manner as on the canals and in the
gondolas of Venice;[10] the complexions, from the peculiar mellow
carnations of the Italian women to the sun-burnt features and limbs
of the mariners, presenting at the same time the fullest variety in
another sense.
At a certain distance—the colour being always assumed to be unimpaired
by interposed atmosphere—the reflections appear kindled to intenser
warmth; the fiery glow of Giorgione is strikingly apparent; the colour
is seen in its largest relation; the macchia,[11] an expression so
emphatically used by Italian writers, appears in all its quantity, and
the reflections being the focus of warmth, the hue seems to deepen in
shade.
A nearer view gives the detail of cooler tints more perceptibly,[12]
and the forms are at the same time more distinct. Hence Lanzi is quite
correct when, in distinguishing the style of Titian from that of
Giorgione, he says that Titian's[Pg 369] was at once more defined and less
fiery.[13] In a still nearer observation the eye detects the minute
lights which Leonardo da Vinci says are incompatible with effects such
as those we have described[14] and which, accordingly, we never find
in Giorgione and Titian. This large impression of colour, which seems
to require the condition of comparative distance for its full effect,
was most fitly employed by the same great artists in works painted in
the open air or for large altar-pieces. Their celebrated frescoes on
the exterior of the Fondaco de' Tedeschi at Venice, to judge from their
faint remains and the descriptions of earlier writers, were remarkable
for extreme warmth in the shadows. The old frescoes in the open air
throughout Friuli have often the same character, and, owing to the
fulness of effect which this treatment ensures, are conspicuous at a
very great distance.[15]
In assuming that the Venetian painters may have acquired a taste for
this breadth[16] of colour under the circumstances above alluded to,
it is moreover to be remembered that the time for this agreeable
study was the evening; when the sun had already set behind the hills
of Bassano; when the light was glowing but diffused; when shadows[Pg 370]
were soft—conditions all agreeing with the character of their
colouring:[17] above all, when the hour invited the fairer portion of
the population to betake themselves in their gondolas to the lagunes.
The scene of this "promenade" was to the north of Venice, the quarter
in which Titian at one time lived. A letter exists written by Francesco
Priscianese, giving an account of his supping with the great painter in
company with Jacopo Nardi, Pietro Aretino, the sculptor Sansovino, and
others. The writer speaks of the beauty of the garden, where the table
was prepared, looking over the lagunes towards Murano, "which part of
the sea," he continues, "as soon as the sun was down, was covered with
a thousand gondolas, graced with beautiful women, and enlivened by the
harmony of voices and instruments, which lasted till midnight, forming
a pleasing accompaniment to our cheerful repast."[18]
To return to Goethe: perhaps the foregoing remarks may warrant the
conclusion that his idea of colour in shadow is not irreconcileable
with the occasional practice of the best painters. The highest examples
of the style thus defined are, or were, to be found in the works of
Giorgione[19] and Titian, and hence the style itself, though "within
that circle"[Pg 371] few "dare walk" is to be considered the grandest and
most perfect. Its possible defects or abuse are not to be dissembled:
in addition to the danger of exaggeration[20] it is seldom united
with the plenitude of light and shade, or with roundness; yet, where
fine examples of both modes of treatment may be compared, the charm
of colour has perhaps the advantage.[21] The difficulty of uniting
qualities so different in their nature, is proved by the very rare
instances in which it has been accomplished. Tintoret in endeavouring
to add chiaro-scuro to Venetian colour, in almost every instance fell
short of the glowing richness of Titian.[22]
[Pg 372]
Giacomo Bassan and his imitators, even in their dark effects, still had
the principle of the gem in view: their light, in certain hues, is the
minimum of colour, their lower tones are rich, their darks intense,
and all is sparkling.[23] Of the great painters who, beginning, on
the other hand, with chiaro-scuro, sought to combine with it the full
richness of colour, Correggio, in the opinion of many, approached
perfection nearest; but we may perhaps conclude with greater justice
that the desired excellence was more completely attained by Rembrandt
than by any of the Italians.
NOTE F.—Par. 83.
The author, in these instances, seems to be anticipating his
subsequent explanations on the effect of semi-transparent mediums.
For an explanation of the general view contained in these paragraphs
respecting the gradual increase of colour from high light, see the last
Note.
The anonymous French work before alluded to, among other interesting
examples, contains a chapter on shadows cast by the upper light of the
sky and coloured by the setting sun. The effect of this remarkable
combination is, that the light on a wall is most coloured immediately
under a projecting roof, and becomes comparatively neutralised in
proportion to its distance from the edge of the darkest shade.
NOTE G.—Par. 98.
"The simplest case of the phenomenon, which Goethe calls a subjective
halo, and one which at once explains its cause, is the following.
Regard a red wafer on a sheet of white paper, keeping the eye
stedfastly fixed on a point at[Pg 373] its center. When the retina is
fatigued, withdraw the head a little from the paper, and a green halo
will appear to surround the wafer. By this slight increase of distance
the image of the wafer itself on the retina becomes smaller, and the
ocular spectrum which before coincided with the direct image, being
now relatively larger, is seen as a surrounding ring."—S. F. Goethe
mentions cases of this kind, but does not class them with subjective
halos. See Par. 30.
NOTE H.—Par. 113.
"Cases of this kind are by no means uncommon. Several interesting
ones are related in Sir John Herschell's article on Light in the
Encyclopædia Metropolitana. Careful investigation has, however, shown
that this defect of vision arises in most, if not in all cases, from
an inability to perceive the red, not the blue rays. The terms are so
confounded by the individuals thus affected, that the comparison of
colours in their presence is the only criterion."—S. F.
NOTE I.—Par. 135.
The author more than once admits that this chapter on "Pathological
Colours" is very incomplete, and expresses a wish (Par. 734) that some
medical physiologists would investigate the subject further. This was
afterwards in a great degree accomplished by Dr. Johannes Müller, in
his memoir "Über die Phantastischen Gesichtserscheinungen." Coblentz,
1826. Similar phenomena have been also investigated with great labour
and success by Purkinje. For a collection of extraordinary facts of the
kind recorded by these writers, the reader may consult Scott's Letters
on Demonology and Witchcraft.[1] The instances adduced by Müller and
others are, however, intended to prove the inherent capacity of the
organ of vision to produce light and colours. In some maladies of the
eye, the patient, it seems,[Pg 374] suffers the constant presence of light
without external light. The exciting principle in this case is thus
proved to be within, and the conclusion of the physiologists is that
external light is only one of the causes which produce luminous and
coloured impressions. That this view was anticipated by Newton may be
gathered from the concluding "query" in the third book of his Optics.
NOTE K.—Par. 140.
"Catoptrical colours. The colours included under this head are
principally those of fibres and grooved surfaces; they can be produced
artificially by cutting parallel grooves on a surface of metal from
2000 to 10,000 in the inch. See 'Brewster's Optics,' p. 120. The
colours called by Goethe paroptical, correspond with those produced
by the diffraction or inflection of light in the received theory.—See
Brewster, p. 95. The phenomena included under the title 'Epoptical
Colours,' are generally known as the colours of thin plates. They vary
with the thickness of the film, and the colour seen by reflection
always differs from that seen by transmission. The laws of these
phenomena have been thoroughly investigated. See Nobili, and Brewster,
p. 100."—S. F.
The colours produced by the transmission of polarised light through
chrystalised mediums, were described by Goethe, in his mode,
subsequently to the publication of his general theory, under the name
of Entoptic Colours. See note to Par. 485.
NOTE L.—Par. 150.
We have in this and the next paragraph the outline of Goethe's system.
The examples that follow seem to establish the doctrine here laid
down, but there are many cases which it appears cannot be explained on
such principles: hence, philosophers generally prefer the theory of
absorption, according to which it appears that certain mediums "have
the property of absorbing some of the component[Pg 375] rays of white light,
while they allow the passage of others."[1]
Whether all the facts adduced by Goethe—for instance, that recorded
in Par. 172, are to be explained by this doctrine, we leave to the
investigators of nature to determine. Dr. Eckermann, in conversing with
Goethe, thus described the two leading phenomena (156, 158) as seen by
him in the Alps. "At a distance of eighteen or twenty miles at mid-day
in bright sunshine, the snow appeared yellow or even reddish, while the
dark parts of the mountain, free from snow, were of the most decided
blue. The appearances did not surprise me, for I could have predicted
that the mass of the interposed medium would give a deep yellow tone
to the white snow, but I was pleased to witness the effect, since it
so entirely contradicted the erroneous views of some philosophers,
who assert that the air has a blue-tinging quality. The observation,
said Goethe, is of importance, and contradicts the error you allude to
completely."[2]
The same writer has some observations to the same effect on the colour
of the Rhone at Geneva. A circumstance of an amusing nature which he
relates in confirmation of Goethe's theory, deserves to be inserted.
"Here (at Strasburg), passing by a shop, I saw a little glass bust
of Napoleon, which, relieved as it was against the dark interior[Pg 376] of
the room, exhibited every gradation of blue, from milky light blue
to deep violet. I foresaw that the bust seen from within the shop
with the light behind it, would present every degree of yellow, and I
could not resist walking in and addressing the owner, though perfectly
unknown to me. My first glance was directed to the bust, in which, to
my great joy, I saw at once the most brilliant colours of the warmer
kind, from the palest yellow to dark ruby red. I eagerly asked if I
might be allowed to purchase the bust; the owner replied that he had
only lately brought it with him from Paris, from a similar attachment
to the emperor to that which I appeared to feel, but, as my ardour
seemed far to surpass his, I deserved to possess it. So invaluable
did this treasure seem in my eyes, that I could not help looking at
the good man with wonder as he put the bust into my hands for a few
franks. I sent it, together with a curious medal which I had bought
in Milan, as a present to Goethe, and when at Frankfort received the
following letter from him." The letter, which Dr. Eckermann gives
entire, thus concludes—"When you return to Weimar you shall see the
bust in bright sunshine, and while the transparent countenance exhibits
a quiet blue,[3] the thick mass of the breast and epaulettes glows with
every gradation of warmth, from the most powerful ruby-red downwards;
and as the granite statue of Memnon uttered harmonious sounds, so the
dim glass image displays itself in the pomp of colours. The hero is
victorious still in supporting the Farbenlehre."[4]
One effect of Goethe's theory has been to invite the attention of
scientific men to facts and appearances which had before been unnoticed
or unexplained. To the above cases may be added the very common, but
very important, fact in painting, that a light warm colour, passed in
a semi-transparent[Pg 377] state over a dark one, produces a cold, bluish
hue, while the operation reversed, produces extreme warmth. On the
judicious application of both these effects, but especially of the
latter, the richness and brilliancy of the best-coloured pictures
greatly depends. The principle is to be recognised in the productions
of schools apparently opposite in their methods. Thus the practice
of leaving the ground, through which a light colour is apparent, as
a means of ensuring warmth and depth, is very common among the Dutch
and Flemish painters. The Italians, again, who preferred a solid
under-painting, speak of internal light as the most fascinating quality
in colour. When the ground is entirely covered by solid painting, as
in the works of some colourists, the warmest tints in shadows and
reflections have been found necessary to represent it. This was the
practice of Rembrandt frequently, and of Reynolds universally, but the
glow of their general colour is still owing to its being repeatedly
or ultimately enriched on the above principle. Lastly, the works of
those masters who were accustomed to paint on dark grounds are often
heavy and opaque; and even where this influence of the ground was
overcome, the effects of time must be constantly diminishing the warmth
of their colouring as the surface becomes rubbed and the dark ground
more apparent through it. The practice of painting on dark grounds was
intended by the Carracci to compel the students of their school to
aim at the direct imitation of the model, and to acquire the use of
the brush; for the dark ground could only be overcome by very solid
painting. The result answered their expectations as far as dexterity of
pencil was concerned, but the method was fatal to brilliancy of colour.
An intelligent writer of the seventeenth century[5] relates that Guido
adopted his extremely light style from seeing the rapid change in some
works of the Carracci soon after they were done. It[Pg 378] is important,
however, to remark, that Guido's remedy was external rather than
internal brilliancy; and it is evident that so powerless a brightness
as white paint can only acquire the splendour of light by great
contrast, and, above all, by being seen through external darkness. The
secret of Van Eyck and his contemporaries is always assumed to consist
in the vehicle (varnish or oils) he employed; but a far more important
condition of the splendour of colour in the works of those masters was
the careful preservation of internal light by painting thinly, but
ultimately with great force, on white grounds. In some of the early
Flemish pictures in the Royal Gallery at Munich, it may be observed,
that wherever an alteration was made by the painter, so that a light
colour is painted over a dark one, the colour is as opaque as in any
of the more modern pictures which are generally contrasted with such
works. No quality in the vehicle could prevent this opacity under such
circumstances; and on the other hand, provided the internal splendour
is by any means preserved, the vehicle is comparatively unimportant.
It matters not (say the authorities on these points) whether the effect
in question is attained by painting thinly over the ground, in the
manner of the early Flemish painters and sometimes of Rubens, or by
painting a solid light preparation to be afterwards toned to richness
in the manner of the Venetians. Among the mechanical causes of the
clearness of colours superposed on a light preparation may be mentioned
that of careful grinding. All writers on art who have descended to
practical details have insisted on this. From the appearance of some
Venetian pictures it may be conjectured that the colours of the
solid under-painting were sometimes less perfectly ground than the
scumbling colours (the light having to pass through the one and to
be reflected from the other). The Flemish painters appear to have
used carefully-ground pigments universally. This is very evident in
Flemish copies from Raphael, which, though[Pg 379] equally impasted with
the originals, are to be detected, among other indications, by the
finely-ground colours employed.
NOTE M.—Par. 177.
Without entering further into the scientific merits or demerits of
this chapter on the "First Class of Dioptrical Colours," it is to be
observed that several of the examples correspond with the observations
of Leonardo da Vinci, and again with those of a much older authority,
namely, Aristotle. Goethe himself admits, and it has been remarked by
others, that his theory, in many respects, closely resembles that of
Aristotle: indeed he confesses[1] that at one time he had an intention
of merely paraphrasing that philosopher's Treatise on Colours.[2]
We have already remarked (Note on par. 150) that Goethe's notion with
regard to the production of warm colours, by the interposition of dark
transparent mediums before a light ground, agrees with the practice of
the best schools in colouring; and it is not impossible that the same
reasons which may make this part of the doctrine generally acceptable
to artists now, may have recommended the very similar theory of
Aristotle to the painters of the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries:
at all events, it appears that the ancient theory was known to those
painters.
It is unnecessary to dwell on the fact that the doctrines of Aristotle
were enthusiastically embraced and generally inculcated at the period
in question;[3] but it has not been[Pg 380] observed that the Italian writers
who translated, paraphrased, and commented on Aristotle's Treatise
on Colours in particular, were in several instances the personal
friends of distinguished painters. Celio Calcagnini[4] had the highest
admiration for Raphael; Lodovico Dolce[5] was the eulogist of Titian;
Portius,[6] whose amicable relations with the Florentine painters may
be inferred from various circumstances, lectured at Florence on the
Aristotelian doctrines early in the sixteenth century. The Italian
translations were later, but still prove that these studies were
undertaken with reference to the arts, for one of them is dedicated to
the painter Cigoli.[7]
[Pg 381]
The writers on art, from Leon Battista Alberti to Borghini, without
mentioning later authorities, either tacitly coincide with the
Aristotelian doctrine, or openly profess to explain it. It is true this
is not always done in the clearest manner, and some of these writers
might say with Lodovico Dolce, "I speak of colours, not as a painter,
for that would be the province of the divine Titian."
Leonardo da Vinci in his writings, as in everything else, appears as
an original genius. He now and then alludes generally to opinions
of "philosophers," but he quotes no authority ancient or modern.
Nevertheless, a passage on the nature of colours, particularly where
he speaks of the colours of the elements, appears to be copied from
Leon Battista Alberti,[8] and from the mode in which some of Leonardo's
propositions are stated, it has been supposed[9] that he had been
accustomed at Florence to the form of the Aristotelian philosophy. At
all events, some of the most important of his observations respecting
light and colours, have a great analogy with those contained in the
treatise in question. The following examples will be sufficient to
prove this coincidence; the corresponding passages in Goethe are
indicated, as usual, by the numbers of the paragraphs; the references
to Leonardo's treatise are given at the bottom of the page.
ARISTOTLE.
"A vivid and brilliant red appears when the weak rays of the
sun are tempered by subdued and shadowy white,"—154.
LEONARDO
"The air which is between the sun and the earth at sun-rise[Pg 382]
or sun-set, always invests what is beyond it more than any
other (higher) portion of the air: this is because it is
whiter."[10]
A bright object loses its whiteness in proportion to its
distance from the eye much more when it is illuminated by
the sun, for it partakes of the colour of the sun mingled
with the colour (tempered by the mass) of the air interposed
between the eye and the brightness.[11]
ARISTOTLE.
"If light is overspread with much obscurity, a red colour
appears; if the light is brilliant and vivid, this red
changes to a flame-colour."[12]—150, 160.
LEONARDO.
"This (the effect of transparent colours on various grounds)
is evident in smoke, which is blue when seen against black,
but when it is opposed to the (light) blue sky, it appears
brownish and reddening."[13]
ARISTOTLE.
"White surfaces as a ground for colours, have the effect of
making the pigments[14] appear in greater splendour."—594,
902.
[Pg 383]
LEONARDO.
"To exhibit colours in their beauty, the whitest ground
should be prepared. I speak of colours that are (more or
less) transparent."[15]
ARISTOTLE.
"The air near us appears colourless; but when seen in depth,
owing to its thinness it appears blue;[16] for where the
light is deficient (beyond it), the air is affected by the
darkness and appears blue: in a very accumulated state,
however, it appears, as is the case with water, quite
white."—155, 158.
LEONARDO.
"The blue of the atmosphere is owing to the mass of
illuminated air interposed between the darkness above and
the earth. The air in itself has no colour, but assumes
qualities according to the nature of the objects which are
beyond it. The blue of the atmosphere will be the more
intense in proportion to the degree of darkness beyond it:"
elsewhere—"if the air had not darkness beyond it, it would
be white."[17]
ARISTOTLE.
"We see no colour in its pure state, but every hue is
variously intermingled with others: even when it is
uninfluenced by other colours, the effect of light and
shade modifies it in various ways, so that it undergoes
alterations and appears unlike itself. Thus, bodies seen in
shade or in[Pg 384] light, in more pronounced or softer sun-shine,
with their surfaces inclined this way or that, with every
change exhibit a different colour."
LEONARDO.
"No substance will ever exhibit its own hue unless the light
which illumines it is entirely similar in colour. It very
rarely happens that the shadows of opaque bodies are really
similar (in colour) to the illumined parts. The surface of
every substance partakes of as many hues as are reflected
from surrounding objects."[18]
Aristotle.
"So, again, with regard to the light of fire, of the moon,
or of lamps, each has a different colour, which is variously
combined with differently coloured objects."
LEONARDO.
"We can scarcely ever say that the surface of illumined
bodies exhibits the real colour of those bodies. Take a
white band and place it in the dark, and let it receive
light by means of three apertures from the sun, from fire,
and from the sky: the white band will be tricoloured."[19]
ARISTOTLE.
"When the light falls on any object and assumes (for
example) a red or green tint, it is again reflected on other
substances, thus undergoing a new change. But this effect,
though it really takes place, is not appreciable by the
eye: though the light thus reflected to the eye is composed
of a variety of colours, the principal of these only are
distinguishable."
LEONARDO.
"No colour reflected on the surface of another colour,
tinges that surface with its own colour (merely), but will
be[Pg 385] mixed with various other reflections impinging on the
same surface:" but such effects, he observes elsewhere, "are
scarcely, if at all, distinguishable in a very diffused
light."[20]
ARISTOTLE.
"Thus, all combinations of colours are owing to three
causes: the light, the medium through which the light
appears, such as water or air, and lastly the local colour
from which the light happens to be reflected."
LEONARDO.
"All illumined objects partake of the colour of the light
they receive.
"Every opaque surface partakes of the colour of the
intervening transparent medium, according to the density of
such medium and the distance between the eye and the object.
"The medium is of two kinds; either it has a surface, like
water, &c., or it is without a common surface, like the
air."[21]
In the observations on trees and plants more points of resemblance
might be quoted; the passages corresponding with Goethe's views are
much more numerous.
It is remarkable that Leonardo, in opposition, it seems to some
authorities,[22] agrees with Aristotle in reckoning black and white
as colours, placing them at the beginning and end of the scale.[23]
Like Aristotle, again, he frequently makes use of the term black, for
obscurity; he even goes further,[Pg 386] for he seems to consider that blue
may be produced by the actual mixture of black and white, provided they
are pure.[24] The ancient author, however, explains himself on this
point as follows—"We must not attempt to make our observations on
these effects by mixing colours as painters mix them, but by remarking
the appearances as produced by the rays of light mingling with each
other."[25]
When we consider that Leonardo's Treatise professes to embrace the
subject of imitation in painting, and that Aristotle's briefly examines
the physical nature and appearance of colours, it must be admitted
that the latter sustains the above comparison with advantage; and it
is somewhat extraordinary that observations indicating so refined a
knowledge of nature, as regards the picturesque, should not have been
taken into the account, for such appears to be the fact, in the various
opinions and conjectures that have been expressed from time to time on
the painting of the Greeks. The treatise in question must have been
written when Apelles painted, or immediately before; and as a proof[Pg 387]
that Aristotle's remarks on the effect of semi-transparent mediums were
not lost on the artists of his time, the following passage from Pliny
is subjoined, for, though it is well known, it acquires additional
interest from the foregoing extracts.
"He (Apelles) passed a dark colour over his pictures when finished, so
thin that it increased the splendour of the tints, while it protected
the surface from dust and dirt: it could only be seen on looking into
the picture. The effect of this operation, judiciously managed, was to
prevent the colours from being too glaring, and to give the spectator
the impression of looking through a transparent crystal. At the same
time it seemed almost imperceptibly to add a certain dignity of tone to
colours that were too florid." "This," says Reynolds, "is a true and
artist-like description of glazing or scumbling, such as was practised
by Titian and the rest of the Venetian painters."
The account of Pliny has, in this instance, internal evidence
of truth, but it is fully confirmed by the following passage in
Aristotle:—"Another mode in which the effect of colours is exhibited
is when they appear through each other, as painters employ them when
they glaze (ἐπαλειφοντες)[26] a (dark) colour over a lighter one; just
as the sun, which is in itself white, assumes a red colour when seen
through darkness and smoke. This operation also ensures a variety of
colours, for there will be a certain ratio between those which are on
the surface and those which are in depth."—De Sensu et Sensili.
Aristotle's notion respecting the derivation of colours from white and
black may perhaps be illustrated by the following opinion on the very
similar theory of Goethe.
"Goethe and Seebeck regard colour as resulting from the mixture of
white and black, and ascribe to the different[Pg 388] colours a quality
of darkness (σκιερὸν), by the different degrees of which they are
distinguished, passing from white to black through the gradations
of yellow, orange, red, violet, and blue, while green appears to be
intermediate again between yellow and blue. This remark, though it has
no influence in weakening the theory of colours proposed by Newton,
is certainly correct, having been confirmed experimentally by the
researches of Herschell, who ascertained the relative intensity of the
different coloured rays by illuminating objects under the microscope by
their means, &c.
"Another certain proof of the difference in brightness of the different
coloured rays is afforded by the phenomena of ocular spectra. If, after
gazing at the sun, the eyes are closed so as to exclude the light, the
image of the sun appears at first as a luminous or white spectrum upon
a dark ground, but it gradually passes through the series of colours to
black, that is to say, until it can no longer be distinguished from the
dark field of vision; and the colours which it assumes are successively
those intermediate between white and black in the order of their
illuminating power or brightness, namely, yellow, orange, red, violet,
and blue. If, on the other hand, after looking for some time at the
sun we turn our eyes towards a white surface, the image of the sun is
seen at first as a black spectrum upon the white surface, and gradually
passes through the different colours from the darkest to the lightest,
and at last becomes white, so that it can no longer be distinguished
from the white surface"[27]—See par 40, 44.
It is not impossible that Aristotle's enumeration of the colours may
have been derived from, or confirmed by, this very experiment. Speaking
of the after-image of colours he says, "The impression not only exists
in the sensorium in the act of perceiving, but remains when the organ
is at rest. Thus if we look long and intently on any object,[Pg 389] when
we change the direction of the eyes a responding colour follows. If
we look at the sun, or any other very bright object, and afterwards
shut our eyes, we shall, as if in ordinary vision, first see a colour
of the same kind; this will presently be changed to a red colour,
then to purple, and so on till it ends in black and disappears."—De
Insomniis.
NOTE N.—Par. 246.
"The appearance of white in the centre, according to the Newtonian
theory, arises from each line of rays forming its own spectrum.
These spectra, superposing each other on all the middle part, leave
uncorrected (unneutralised) colours only at the two edges."—S.F.[1]
NOTE O.—Par. 252.
These experiments with grey objects, which exhibit different colours
as they are on dark or light grounds, were suggested, Goethe tells
us, by an observation of Antonius Lucas, of Lüttich, one of Newton's
opponents, and, in the opinion of the author, one of the few who made
any well-founded objections. Lucas remarks, that the sun acts merely
as a circumscribed image in the prismatic experiments, and that if the
same sun had a lighter background than itself, the colours of the prism
would be reversed. Thus in Goethe's experiments, when the grey disk is
on a dark ground, it is edged with blue on being magnified; when on a
light ground it is edged with yellow. Goethe acknowledges that Lucas
had in some measure anticipated his own theory.—Vol. ii. p. 440.
NOTE P.—Par. 284.
The earnestness and pertinacity with which Goethe insisted[Pg 390] that
the different colours are not subject to different degrees of
refrangibility are at least calculated to prove that he was himself
convinced on the subject, and, however extraordinary it may seem, his
conviction appears to have been the result of infinite experiments
and the fullest ocular evidence. He returns to the question in the
controversial division of his work, in the historical part, and again
in the description of the plates. In the first he endeavours to show
that Newton's experiment with the blue and red paper depends entirely
on the colours being so contrived as to appear elongated or curtailed
by the prismatic borders. "If," he says, "we take a light-blue instead
of a dark one, the illusion (in the latter case) is at once evident.
According to the Newtonian theory the yellow-red (red) is the least
refrangible colour, the violet the most refrangible. Why, then, does
Newton place a blue paper instead of a violet next the red? If the
fact were as he states it, the difference in the refrangibility of
the yellow-red and violet would be greater than in the case of the
yellow-red and blue. But here comes in the circumstance that a violet
paper conceals the prismatic borders less than a dark-blue paper, as
every observer may now easily convince himself," &c.—Polemischer
Theil, par. 45. Desaguliers, in repeating the experiment, confessed
that if the ground of the colours was not black, the effect did
not take place so well. Goethe adds, "not only not so well, but
not at all."—Historischer Theil, p. 459. Lucas of Lüttich, one of
Newton's first opponents, denied that two differently-coloured silks
are different in distinctness when seen in the microscope. Another
experiment proposed by him, to show the unsoundness of the doctrine of
various refrangibility, was the following:—Let a tin plate painted
with the prismatic colours in stripes be placed in an empty cubical
vessel, so that from the spectator's point of view the colours may be
just hidden by the rim. On pouring water into this vessel, all the
colours become visible in the same degree; whereas, it was contended,
if the Newtonian doctrine were true, some[Pg 391] colours would be apparent
before others.—Historischer Theil, p. 434.
Such are the arguments and experiments adduced by Goethe on this
subject; they have all probably been answered. In his analysis of
Newton's celebrated Experimentum Crucis, he shows again that by
reversing the prismatic colours (refracting a dark instead of a
light object), the colours that are the most refrangible in Newton's
experiment become the least so, and vice versâ.
Without reference to this objection, it is now admitted that "the
difference of colour is not a test of difference of refrangibility, and
the conclusion deduced by Newton is no longer admissible as a general
truth, that to the same degree of refrangibility ever belongs the
same colour, and to the same colour ever belongs the same degree of
refrangibility."—Brewster's Optics, p. 72.
NOTE Q—Par. 387.
With the exception of two very inconclusive letters to Sulpice
Boisserée, and some incidental observations in the conclusion of the
historical portion under the head of entoptic colours, Goethe never
returned to the rainbow. Among the plates he gave the diagram of
Antonius de Dominis. An interesting chapter on halos, parhelia, and
paraselenæ, will be found in Brewster's Optics, p. 270.
NOTE R.—Par. 478.
The most complete exhibition of the colouring or mantling of metals
was attained by the late Cav. Nobili, professor of physical science in
Florence. The general mode in which these colours are produced is thus
explained by him:[1]—
"A point of platinum is placed vertically at the distance of about
half a line above a lamina of the same metal laid[Pg 392] horizontally at the
bottom of a vessel of glass or porcelain. Into this vessel a solution
of acetate of lead is poured so as to cover not only the lamina of
platinum, but two or three lines of the point as well. Lastly, the
point is put in communication with the negative pole of a battery, and
the lamina with the positive pole. At the moment in which the circuit
is completed a series of coloured rings is produced on the lamina
under the point similar to those observed by Newton in lenses pressed
together."
The scale of colours thus produced corresponds very nearly with that
observed by Newton and others in thin plates and films, but it is
fuller, for it extends to forty-four tints. The following list, as
given by Nobili, is divided by him into four series to agree with
those of Newton: the numbers in brackets are those of Newton's scale.
The Italian terms are untranslated, because the colours in some cases
present very delicate transitions.[2]
| First Series. |
|---|
| 1. | Biondo argentino (4)[3]
. | 6. | Fulvo acceso. |
| 2. | Biondo. | 7. | Rosso di rame (6). |
| 3. | Biondo d'oro. | 8. | Ocria. |
| 4. | Biondo acceso (5). | 9. | Ocria violacea. |
| 5. | Fulvo. | 10. | Rosso violaceo (7). |
| Second Series. |
|---|
| 11. | Violetto (8). | 20. | Giallo acceso. |
| 12. | Indaco (10). | 21. | Giallo-rancio. |
| 13. | Blu carico. | 22. | Rancio (13). |
| 14. | Blu. | 23. | Rancio-rossiccio. |
| 15. | Blu chiaro (11) | 24. | Rancio-rosso. |
| 16. | Celeste. | 25. | Rosso-rancio. |
| 17. | Celeste giallognolo. | 26. | Lacca-rancia (14). |
| 18. | Giallo chiarissimo (12). | 27. | Lacca. |
| 19. | Giallo. | 28. | Lacca accesa (15). |
| Third Series.[Pg 393] |
|---|
| 29. | Lacca-purpurea (16). | 34. | Verde-giallo (20). |
| 30. | Lacca-turchiniccia (17). | 35. | Verde-rancio. |
| 31. | Porpora-verdognola (18). | 36. | Rancio-verde (21). |
| 32. | Verde (19). | 37. | Rancio-roseo. |
| 33. | Verde giallognolo. | 38. | Lacca-rosea (22). |
| Fourth Series. |
|---|
| 39. | Lacca-violacea (24). | 43. | Verde-giallo rossiccio (28). |
| 40. | Violaceo-verdognolo (25). | 44. | Lacca-rosea (30). |
| 41. | Verde (26). |
| 42. | Verde-giallo (27). |
"These tints," Professor Nobili observes, "are disposed according to
the order of the thin mantlings which occasion them; the colour of
the thinnest film is numbered 1; then follow in order those produced
by a gradual thickening of the medium. I cannot deceive myself in
this arrangement, for the thin films which produce the colours are
all applied with the same electro-chemical process. The battery, the
solution, the distances, &c., are always the same; the only difference
is the time the effect is suffered to last. This is a mere instant for
the colour of No. 1, a little longer for No. 2, and so on, increasing
for the succeeding numbers. Other criterions, however, are not wanting
to ascertain the place to which each tint belongs."
The scale differs from that of Newton, inasmuch as there is no blue in
Nobili's first series and no green in the second: green only appears in
the third and fourth series. "The first series," says the Professor,
"is remarkable for the fire and metallic appearance of its tints, the
second for clearness and brilliancy, the third and fourth for force and
richness." The fourth, he observes, has the qualities of the third in a
somewhat lesser degree, but the two greens are very nearly alike.
It is to be observed, that red and green are the principal[Pg 394] ingredients
in the third and fourth series, blue and yellow in the second and first.
NOTE S.—Par. 485.
A chapter on entoptic colours, contained in the supplement to Goethe's
works, was translated with the intention of inserting it among the
notes, but on the whole it was thought most advisable to omit it. Like
many other parts of the "Doctrine of Colours" it might have served as
a specimen of what may be achieved by accurate observation unassisted
by a mathematical foundation. The whole theory of the polarization of
light has, however, been so fully investigated since Goethe's time,
that the chapter in question would probably have been found to contain
very little to interest scientific readers, for whom it seems chiefly
to have been intended. One observation occurs in it which indeed has
more reference to the arts; in order to make this intelligible, the
leading experiment must be first described, and for this purpose the
following extracts may serve.
3.[1]
"The experiment, in its simplest form, is to be made as follows:—let
a tolerably thick piece of plate-glass be cut into several squares of
an inch and a half; let these be heated to a red heat and then suddenly
cooled. The squares of glass which do not split in this operation are
now fit to produce the entoptic colours.
4.
"In our mode of exhibiting the phenomenon, the observer is, above all,
to betake himself, with his apparatus to the open air. All dark rooms,
all small apertures[Pg 395] (foramina exigua),[2] are again to be given up. A
pure, cloudless sky is the source whence we are derive a satisfactory
insight into the appearances.
5.
"The atmosphere being clear, let the observer lay the squares above
described on a black surface, so placing them that two sides may
be parallel with the plane of vision. When the sun is low, let him
hold the squares so as to reflect to the eye that portion of the sky
opposite to the sun, and he will then perceive four dark points in
the four corners of a light space. If, after this, he turn towards
the quarters of the sky at right angles with that where his first
observation was made, he will see four bright points on a dark ground:
between the two regions the figures appear to fluctuate.
6.
"From this simple reflection we now proceed to another, which, but
little more complicated, exhibits the appearance much more distinctly.
A solid cube of glass, or in its stead a cube composed of several
plates, is placed on a black mirror, or held a little inclined
above it, at sun-rise or sun-set. The reflection of the sky being
now suffered to fall through the cube on the mirror, the appearance
above described will appear more distinctly. The reflection of the
sky opposite to the sun presents four dark points on a light ground;
the two lateral portions of the sky present the contrary appearance,
namely, four light points on a dark ground. The space not occupied by
the corner points appears in the first case as a white cross, in the
other as a black cross, expressions hereafter employed in describing
the phenomena. Before sun-rise or after sun-set, in a very[Pg 396] subdued
light, the white cross appears on the side of the sun also.[3]
"We thus conclude that the direct reflection of the sun produces a
light figure, which we call a white cross; the oblique reflection gives
a dark figure, which we call a black cross. If we make the experiment
all round the sky, we shall find that a fluctuation takes place in the
intermediate regions."
We pass over a variety of observations on the modes of exhibiting this
phenomenon, the natural transparent substances which exhibit it best,
and the detail of the colours seen within[4] them, and proceed to an
instance where the author was enabled to distinguish the "direct" from
the "oblique" reflection by means of the entoptic apparatus, in a
painter's study.
40.
"An excellent artist, unfortunately too soon taken from us, Ferdinand
Jagemann, who, with other qualifications, had a fine eye for light and
shade, colour and keeping, had built himself a painting-room for large
as well as small works. The single high window was to the north, facing
the most open sky, and it was thought that all necessary requisites had
been sufficiently attended to.
"But after our friend had worked for some time, it appeared to him,
in painting portraits, that the faces he copied were not equally well
lighted at all hours of the day, and yet his sitters always occupied
the same place, and the serenity of the atmosphere was unaltered.
"The variations of the favourable and unfavourable light had their
periods during the day. Early in the morning the light appeared most
unpleasantly grey and unsatisfactory;[Pg 397] it became better, till at last,
about an hour before noon, the objects had acquired a totally different
appearance. Everything presented itself to the eye of the artist in its
greatest perfection, as he would most wish to transfer it to canvas.
In the afternoon this beautiful appearance vanished—the light became
worse, even in the brightest day, without any change having taken place
in the atmosphere.
"As soon as I heard of this circumstance, I at once connected it in
my own mind with the phenomena which I had been so long observing,
and hastened to prove, by a physical experiment, what a clear-sighted
artist had discovered entirely of himself, to his own surprise and
astonishment.
"I had the second[5] entoptic apparatus brought to the spot, and the
effect on this was what might be conjectured from the above statement.
At mid-day, when the artist saw his model best lighted, the north,
direct reflection gave the white cross; in the morning and evening, on
the other hand, when the unfavourable oblique light was so unpleasant
to him, the cube showed the black cross; in the intermediate hours the
state of transition was apparent."
The author proceeds to recall to his memory instances where works of
art had struck him by the beauty of their appearance owing to the light
coming from the quarter opposite the sun, in "direct reflection," and
adds, "Since these decided effects are thus traceable to their cause,
the friends of art, in looking at and exhibiting pictures, may enhance
the enjoyment to themselves and others by attending to a fortunate
reflection."
NOTE T.—Par. 496.
"Since Goethe wrote, all the earths have been decomposed, and have
been shown to be metallic bases united with oxygen; but this does not
invalidate his statement."—S. F.
NOTE U.—Par. 502.
The cold nature of black and its affinity to blue are assumed by the
author throughout; if the quality is opaque, and consequently greyish,
such an affinity is obvious, but in many fine pictures, intense black
seems to be considered as the last effect of heat, and in accompanying
crimson and orange may be said rather to present a difference of
degree than a difference of kind. In looking at the great picture
of the globe, we find this last result produced in climates where
the sun has greatest power, as we find it the immediate effect of
fire. The light parts of black animals are often of a mellow colour;
the spots and stripes on skins and shells are generally surrounded
by a warm hue, and are brown before they are absolutely black. In
combustion, the blackness which announces the complete ignition, is
preceded always by the same mellow, orange colour. The representation
of this process was probably intended by the Greeks in the black and
subdued orange of their vases: indeed, the very colours may have been
first produced in the kiln. But without supposing that they were
retained merely from this accident, the fact that the combination
itself is extremely harmonious, would be sufficient to account for
its adoption. Many of the remarks of Aristotle[1] and Theophrastus[2]
on the production of black, are derived from the observation of the
action of fire, and on one occasion, the former distinctly alludes to
the terracotta kiln. That the above opinion as to the nature of black
was prevalent in the sixteenth century, may be inferred[Pg 399] from Lomazzo,
who observes,—"Quanto all' origine e generazione de' colori, la
frigidità è la madre della bianchezza: il calore è padre del nero."[3]
The positive coldness of black may be said to begin when it approaches
grey. When Leonardo da Vinci says that black is most beautiful in
shade, he probably means to define its most intense and transparent
state, when it is furthest removed from grey.
NOTE V.—Par. 555.
The nature of vehicles or liquid mediums to combine with the substance
of colours, has been frequently discussed by modern writers on art,
and may perhaps be said to have received as much attention as it
deserves. Reynolds smiles at the notion of our not having materials
equal to those of former times, and indeed, although the methods of
individuals will always differ, there seems no reason to suppose that
any great technical secret has been lost. In these inquiries, however,
which relate merely to the mechanical causes of bright and durable
colouring, the skill of the painter in the adequate employment of the
higher resources of his art is, as if by common consent, left out of
the account, and without departing from this mode of considering the
question, we would merely repeat a conviction before expressed, viz.
that the preservation of internal brightness, a quality compatible with
various methods, has had more to do with the splendour and durability
of finely coloured pictures than any vehicle. The observations that
follow are therefore merely intended to show how far the older
written authorities on this subject agree with the results of modern
investigation, without at all assuming that the old methods, if known,
need be implicitly followed.
On a careful examination of the earlier pictures, it is said[Pg 400] that
a resinous substance appears to have been mingled with the colours
together with the oil; that the fracture of the indurated pigment is
shining, and that the surface resists the ordinary solvents.[1] This
admixture of resinous solutions or varnishes with the solid is not
alluded to, as far as we have seen, by any of the writers on Italian
practice, but as the method corresponds with that now prevalent in
England, the above hypothesis is not likely to be objected to for the
present.
Various local circumstances and relations might seem to warrant the
supposition that the Venetian painters used resinous substances. An
important branch of commerce between the mountains of Friuli and Venice
still consists in the turpentine or fir-resin.[2] Similar substances
produced from various trees, and known under the common name of
balsams,[3] were imported from the East through Venice, for general
use, before the American balsams[4] in some degree superseded them;
and a Venetian painter, Marco Boschini, in his description of the
Archipelago, does not omit to speak of the abundance of mastic produced
in the island of Scio.[5]
The testimonies, direct or indirect, against the employment[Pg 401] of any
such substances by the Venetian painters, in the solid part of their
work, seem, notwithstanding, very conclusive; we begin with the writer
just named. In his principal composition, a poem[6] describing the
practice and the productions of the Venetian painters, Boschini speaks
of certain colours which they shunned, and adds:—"In like manner
(they avoided) shining liquids and varnishes, which I should rather
call lackers;[7] for the surface of flesh, if natural and unadorned,
assuredly does not shine, nature speaks as to this plainly." After
alluding to the possible alteration of this natural appearance by
means of cosmetics, he continues: "Foreign artists set such great
store by these varnishes, that a shining surface seems to them the
only desirable quality in art. What trash it is they prize! fir-resin,
mastic, and sandarach, and larch-resin (not to say treacle), stuff fit
to polish boots.[8] If those great painters of ours had to represent
armour, a gold vase, a mirror, or anything of the kind, they made it
shine with (simple) colours."[9]
This writer so frequently alludes to the Flemish painters, of whose
great reputation he sometimes seems jealous, that the above strong
expression of opinion may have been pointed at them. On the other hand
it is to be observed that the term forestieri, strangers, does not
necessarily mean transalpine foreigners, but includes those Italians
who were[Pg 402] not of the Venetian state.[10] The directions given by
Raphael Borghini,[11] and after him by Armenini,[12] respecting the use
and preparation of varnishes made from the very materials in question,
may thus have been comprehended in the censure, especially as some of
these recipes were copied and republished in Venice by Bisagno,[13] in
1642—that is, only six years before Boschini's poem appeared.
Ridolfi's Lives of the Venetian Painters[14] (1648) may be mentioned
with the two last. His only observation respecting the vehicle is, that
Giovanni Bellini, after introducing himself by an artifice into the
painting-room of Antonello da Messina, saw that painter dip his brush
from time to time in linseed oil. This story, related about two hundred
years after the supposed event, is certainly not to be adduced as very
striking evidence in any way.[15]
Among the next writers, in order of time prior to Bisagno, may be
mentioned Canepario[16] (1619). His work, "De Atramentis" contains
a variety of recipes for different purposes: one chapter, De
atramentis diversicoloribus, has a more direct reference to painting.
His observations under this head are by no means confined to the
preparation of transparent colours, but he says little on the subject
of[Pg 403] varnishes. After describing a mode of preserving white of egg,
he says, "Others are accustomed to mix colours in liquid varnish and
linseed, or nut-oil; for a liquid and oily varnish binds the (different
layers of) colours better together, and thus forms a very fit glazing
material."[17] On the subject of oils he observes, that linseed oil was
in great request among painters; who, however, were of opinion that
nut-oil-excelled it "in giving brilliancy to pictures, in preserving
them better, and in rendering the colours more vivid."[18]
Lomazzo (a Milanese) says nothing on the subject of vehicles in his
principal work, but in his "Idea del Tempio della Pittura,"[19] he
speaks of grinding the colours "in nut-oil, and spike-oil, and other
things," the "and" here evidently means or, and by "other things" we
are perhaps to understand other oils, poppy oil, drying oils, &c.
The directions of Raphael Borghini and Vasari[20] cannot certainly be
considered conclusive as to the practice of the Venetians, but they are
very clear on the subject of varnish. These writers may be considered
the earliest Italian authorities who have entered much into practical
methods. In the few observations on the subject of vehicles in Leonardo
da Vinci's treatise, "there is nothing," as M. Merimée observes, "to
show that he was in the habit of mixing varnish with his colours."
Cennini says but little on the subject[Pg 404] of oil-painting; Leon Battista
Alberti is theoretical rather than practical, and the published
extracts of Lorenzo Ghiberti's MS. chiefly relate to sculpture.
Borghini and Vasari agree in recommending nut-oil in preference to
linseed-oil; both recommend adding varnish to the colours in painting
on walls in oil, "because the work does not then require to be
varnished afterwards," but in the ordinary modes of painting on panel
or cloth, the varnish is omitted. Borghini expressly says, that oil
alone (senza più) is to be employed; he also recommends a very sparing
use of it.
The treatise of Armenini (1587) was published at Ravenna, and he
himself was of Faenza, so that his authority, again, cannot be
considered decisive as to the Venetian practice. After all, he
recommends the addition of "common varnish" only for the ground or
preparation, as a consolidating medium, for the glazing colours,
and for those dark pigments which are slow in drying. Many of his
directions are copied from the writers last named; the recipes for
varnishes, in particular, are to be found in Borghini. Christoforo
Sorte[21] (1580) briefly alludes to the subject in question. After
speaking of the methods of distemper, he observes that the same colours
may be used in oil, except that instead of mixing them with size, they
are mixed on the palette with nut-oil, or (if slow in drying) with
boiled linseed-oil: he does not mention varnish. The Italian writers
next in order are earlier than Vasari, and may therefore be considered
original, but they are all very concise.
[Pg 405]
The treatise of Michael Angelo Biondo[22] (1549), remarkable for
its historical mistakes, is not without interest in other respects.
The list of colours he gives is, in all probability, a catalogue of
those in general use in Venice at the period he wrote. With regard
to the vehicle, he merely mentions oil and size as the mediums for
the two distinct methods of oil-painting and distemper, and does not
speak of varnish. The passages in the Dialogue of Doni[23] (1549),
which relate to the subject in question, are to the same effect. "In
colouring in oil," he observes, "the most brilliant colours (that we
see in pictures) are prepared by merely mixing them with the end of a
knife on the palette." Speaking of the perishable nature of works in
oil-painting as compared with sculpture, he says, that the plaster of
Paris (gesso) and mastic, with other ingredients of which the ground
is prepared, are liable to decay, &c.; and elsewhere, in comparing
painting in general with mosaic, that in the former the colours "must
of necessity be mixed with various things, such as oils, gums, white
or yolk of egg, and juice of figs, all which tend to impair the beauty
of the tints." This catalogue of vehicles is derived from all kinds of
painting to enforce the argument, and is by no means to be understood
as belonging to one and the same method.
An interesting little work,[24] still in the form of a dialogue (Fabio
and Lauro), appeared a year earlier; the author, Paolo Pino, was a
Venetian painter. In speaking of the practical methods Fabio observes,
as usual, that oil-painting is of all modes of imitation the most
perfect, but his reasons for this opinion seem to have a reference
to the Venetian[Pg 406] practice of going over the work repeatedly. Lauro
asks whether it is not possible to paint in oil on the dry wall, as
Sebastian del Piombo did. Fabio answers, "the work cannot last, for the
solidity of the plaster is impenetrable, and the colours, whether in
oil or distemper, cannot pass the surface." This might seem to warrant
the inference that absorbent grounds were prepared for oil-painting,
but there are proofs enough that resins as well as oil were used with
the gesso to make the preparation compact. See Doni, Armenini, &c.
This writer, again, does not speak of varnish. These appear to be the
chief Venetian and Italian authorities[25] of the sixteenth and part of
the following century; and although Boschini wrote latest, he appears
to have had his information from good sources, and more than once
distinctly quotes Palma Giovane.
In all these instances it will be seen that there is no allusion to the
immixture of varnishes with the solid colours, except in painting on
walls in oil, and that the processes of distemper and oil are always
considered as separate arts.[26][Pg 407] On the other hand, the prohibition
of Boschini cannot be understood to be universal, for it is quite
certain that the Venetians varnished their pictures when done.[27]
After Titian had finished his whole-length portrait of Pope Paul III.
it was placed in the sun to be varnished.[28] Again, in the archives of
the church of S. Niccolo at Treviso a sum is noted (Sept. 21, 1521 ),
"per far la vernise da invernisar la Pala dell' altar grando," and the
same day a second entry appears of a payment to a painter, "per esser
venuto a dar la vernise alla Pala," &c.[29] It is to be observed that
in both these cases the pictures were varnished as soon as done;[30]
the varnish employed was perhaps the thin compound of naphtha (oglio di
sasso) and melted turpentine (oglio d'abezzo), described by Borghini,
and after him by Armenini: the last-named writer remarks that he had
seen[Pg 408] this varnish used by the best painters in Lombardy, and had heard
that it was preferred by Correggio. The consequence of this immediate
varnishing may have been that the warm resinous liquid, whatever it
was, became united with the colours, and thus at a future time the
pigment may have acquired a consistency capable of resisting the
ordinary solvents. Not only was the surface of the picture required to
be warm, but the varnish was applied soon after it was taken from the
fire.[31]
Many of the treatises above quoted contain directions for making the
colours dry:[32] some of these recipes, and many in addition, are to be
found in Palomino, who, however defective as an historian,[33] has left
very copious practical details, evidently of ancient date. His drying
recipes are numerous, and although sugar of lead does not appear,
cardenillo (verdigris), which is perhaps as objectionable, is admitted
to be the best of all dryers. It may excite some surprise that the
Spanish painters should have bestowed so much attention on this subject
in a climate like theirs, but the rapidity of their execution must have
often required such an assistance.[34]
One circumstance alluded to by Palomino, in his very minute practical
directions, deserves to be mentioned. After[Pg 409] saying what colours should
be preserved in their saucers under water, and what colours should be
merely covered with oiled paper because the water injures them, he
proceeds to communicate "a curious mode of preserving oil-colours," and
of transporting them from place to place. The important secret is to
tie them in bladders, the mode of doing which he enters into with great
minuteness, as if the invention was recent. It is true, Christoforo
Sorte, in describing his practice in water-colour drawing, says he was
in the habit of preserving a certain vegetable green with gum-water in
a bladder; but as the method was obviously new to Palomino, there seems
sufficient reason to believe that oil-colours, when once ground, had,
up to his time, been kept in saucers and preserved under water.[35]
Among the items of expense in the Treviso document before alluded to,
we find "a pan and saucers for the painters."[36] This is in accordance
with Cennini's directions, and the same system appears to have been
followed till after 1700.[37]
The Flemish accounts of the early practice of oil-painting are all
later than Vasari. Van Mander, in correcting the Italian historian in
his dates, still follows his narrative in other respects verbatim. If
Vasari's story is to be accepted as true, it might be inferred that
the Flemish secret consisted in an oil varnish like copal.[38] Vasari
says, that Van[Pg 410] Eyck boiled the oils with other ingredients; that the
colours, when mixed with this kind of oil, had a very firm consistence;
that the surface of the pictures so executed had a lustre, so that they
needed no varnish when done; and that the colours were in no danger
from water.[39]
Certain colours, as is well known, if mixed with oil alone, may be
washed off after a considerable time. Leonardo da Vinci remarks, that
verdigris may be thus removed. Carmine, Palomino observes, may be
washed off after six years. It is on this account the Italian writers
recommend the use of varnish with certain colours, and it appears the
Venetians, and perhaps the Italians generally, employed it solely in
such cases. But it is somewhat extraordinary that Vasari should teach
a mode of painting in oil so different in its results (inasmuch as the
work thus required varnish at last) from the Flemish method which he so
much extols—a method which he says the Italians long endeavoured to
find out in vain. If they knew it, it is evident, assuming his account
to be correct, that they did not practice it.
NOTE W.—Par. 608.
In the second volume Goethe gives the nomenclature of the Greeks and
Romans at some length. The general notions of the ancients with regard
to colours are thus described:—"The ancients derive all colours from
white and black, from light and darkness. They say, all colours are
between white and black, and are mixed out of these. We must not,
however, suppose that they understand by this a mere atomic mixture,
although they occasionally use the word μίξις;[1] for in the remarkable
passages, where they wish to express a kind of reciprocal (dynamic)
action of the two contrasting principles, they employ the words κρᾶσις,
union, σύγκρισις, combination; thus, again, the mutual influence of
light and darkness, and of colours among each[Pg 411] other, is described by
the word κεράννυστας, an expression of similar import.
"The varieties of colours are differently enumerated; some mention
seven, others twelve, but without giving the complete list. From a
consideration of the terminology both of the Greeks and Romans, it
appears that they sometimes employed general for specific terms, and
vice versâ.
"Their denominations of colours are not permanently and precisely
defined, but mutable and fluctuating, for they are employed even with
regard to similar colours both on the plus and minus side. Their
yellow, on the one hand, inclines to red, on the other to blue; the
blue is sometimes green, sometimes red; the red is at one time yellow,
at another blue. Pure red (purpur) fluctuates between warm red and
blue, sometimes inclining to scarlet, sometimes to violet.
"Thus the ancients not only seem to have looked upon colour as a
mutable and fleeting quality, but appear to have had a presentiment of
the (physical and chemical) effects of augmentation and re-action. In
speaking of colours they make use of expressions which indicate this
knowledge; they make yellow redden, because its augmentation tends to
red; they make red become yellow, for it often returns thus to its
origin.
"The hues thus specified undergo new modifications. The colours
arrested at a given point are attenuated by a stronger light darkened
by a shadow, nay, deepened and condensed in themselves. For the
gradations which thus arise the name of the species only is often
given, but the more generic terms are also employed. Every colour, of
whatever kind, can, according to the same view, be multiplied into
itself, condensed, enriched, and will in consequence appear more or
less dark. The ancients called colour in this state," &c. Then follow
the designations of general states of colour and those of specific hues.
Another essay on the notions of the ancients respecting[Pg 412] the origin
and nature of colour generally, shows how nearly Goethe himself has
followed in the same track. The dilating effect of light objects,
the action and reaction of the retina, the coloured after-image, the
general law of contrast, the effect of semi-transparent mediums in
producing warm or cold colours as they are interposed before a dark or
light background—all this is either distinctly expressed or hinted
at; "but," continues Goethe, "how a single element divides itself into
two, remained a secret for them. They knew the nature of the magnet,
in amber, only as attraction; polarity was not yet distinctly evident
to them. And in very modern times have we not found that scientific
men have still given their almost exclusive attention to attraction,
and considered the immediately excited repulsion only as a mere
after-action?"
An essay on the Painting of the Ancients[2] was contributed by Heinrich
Meyer.
NOTE X.—Par. 670.
This agrees with the general recommendation so often given by high
authorities in art, to avoid a tinted look in the colour of flesh. The
great example of Rubens, whose practice was sometimes an exception
to this, may however show that no rule of art is to be blindly or
exclusively adhered to. Reynolds, nevertheless, in the midst of his
admiration for this great painter, considered the example dangerous,
and more than once expresses himself to this effect, observing on one
occasion that Rubens, like Baroccio, is sometimes open to the criticism
made on an ancient painter, namely, that his figures looked as if they
fed on roses.
Lodovico Dolce, who is supposed to have given the vivâ voce precepts
of Titian in his Dialogue,[1] makes Aretino[Pg 413] say: "I would generally
banish from my pictures those vermilion cheeks with coral lips; for
faces thus treated look like masks. Propertius, reproving his Cynthia
for using cosmetics, desires that her complexion might exhibit the
simplicity and purity of colour which is seen in the works of Apelles."
Those who have written on the practice of painting have always
recommended the use of few colours for flesh. Reynolds and others quote
even ancient authorities as recorded by Pliny, and Boschini gives
several descriptions of the method of the Venetians, and particularly
of Titian, to the same effect. "They used," he says, "earths more than
any other colour, and at the utmost only added a little vermilion,
minium, and lake, abhorring as a pestilence biadetti, gialli santi,
smaltini, verdi-azzurri, giallolini."[2] Elsewhere he says,[3] "Earths
should be used rather than other colours:" after repeating the above
prohibited list he adds, "I speak of the imitation of flesh, for in
other things every colour is good;" again, "Our great Titian used to
say that he who wishes to be a painter should be acquainted with three
colours, white, black, and red."[4] Assuming this[Pg 414] account to be a
little exaggerated, it is still to be observed that the monotony to
which the use of few colours would seem to tend, is prevented by the
nature of the Venetian process, which was sufficiently conformable to
Goethe's doctrine; the gradations being multiplied, and the effect
of the colours heightened by using them as semi-opaque mediums.
Immediately after the passage last quoted we read, "He also gave this
true precept, that to produce a lively colouring in flesh it is not
possible to finish at once."[5] As these particulars may not be known
to all, we add some further abridged extracts explaining the order and
methods of these different operations.
"The Venetian painters," says this writer,[6] "after having drawn in
their subject, got in the masses with very solid colour, without making
use of nature or statues. Their great object in this stage of their
work was to distinguish the advancing and retiring portions, that the
figures might be relieved by means of chiaro-scuro—one of the most
important departments of colour and form, and indeed of invention.
Having decided on their scheme of effect, when this preparation was
dry, they consulted nature and the antique; not servilely, but with the
aid of a few lines on paper (quattro segni in carta) they corrected
their figures without any other model. Then returning to their brushes,
they began to paint smartly on this preparation, producing the colour
of flesh." The passage before quoted follows, stating that they used
earths chiefly, that they carefully avoided certain colours, "and
likewise varnishes and whatever produces a shining surface.[7] When
this second painting was dry, they proceeded to scumble over this or
that figure with a low tint to make the one next it come forward,
giving another, at the same time, an additional light—for example,[Pg 415] on
a head, a hand, or a foot, thus detaching them, so to speak, from the
canvas." (Tintoret's Prigionia di S. Rocco is here quoted.) "By thus
still multiplying these well-understood retouchings where required, on
the dry surface, (à secco) they reduced the whole to harmony. In this
operation they took care not to cover entire figures, but rather went
on gemming them (gioielandole) with vigorous touches. In the shadows,
too, they infused vigour frequently by glazing with asphaltum, always
leaving great masses in middle-tint, with many darks, in addition to
the partial glazings, and few lights."
The introduction to the subject of Venetian colouring, in the poem by
the same author, is also worth transcribing, but as the style is quaint
and very concise, a translation is necessarily a paraphrase.[8]
"The art of colouring has the imitation of qualities for its object;
not all qualities, but those secondary ones which are appreciable by
the sense of sight. The eye especially sees colours, the imitation
of nature in painting is therefore justly called colouring; but the
painter arrives at his end by indirect means. He gives the varieties
of tone in masses;[9][Pg 416] he smartly impinges lights, he clothes his
preparation with more delicate local hues, he unites, he glazes: thus
everything depends on the method, on the process. For if we look
at colour abstractedly, the most positive may be called the most
beautiful, but if we keep the end of imitation in view, this shallow
conclusion falls to the ground. The refined Venetian manner is very
different from mere direct, sedulous imitation. Every one who has
a good eye may arrive at such results, but to attain the manner of
Paolo, of Bassan, of Palma, Tintoret, or Titian, is a very different
undertaking."[10]
The effects of semi-transparent mediums in some natural productions
seem alluded to in the following passage—"Nature sometimes
accidentally imitates figures in stones and other substances, and
although they are necessarily incomplete in form, yet the principle
of effect (depth) resembles the Venetian practice." In a passage that
follows there appears to be an allusion to the production of the
atmospheric colours by semi-transparent mediums.[11]
NOTE Y.—Par. 672.
The author's conclusion here is unsatisfactory, for the colour of
the black races may be considered at least quite as negative as that
of Europeans. It would be safer to say that the white skin is more
beautiful than the black, because it is more capable of indications
of life, and indications of emotion. A degree of light which would
fail to exhibit the finer varieties of form on a dark surface, would
be sufficient to display them on a light one; and the delicate
mantlings[Pg 417] of colour, whether the result of action or emotion, are more
perceptible for the same reason.
NOTE Z.—Par. 690.
The author appears to mean that a degree of brightness which the organ
can bear at all, must of necessity be removed from dazzling, white
light. The slightest tinge of colour to this brightness, implies that
it is seen through a medium, and thus, in painting, the lightest,
whitest surface should partake of the quality of depth. Goethe's view
here again accords, it must be admitted, with the practice of the best
colourists, and with the precepts of the highest authorities.—See Note C.
NOTE AA.—Par. 732.
Ample details respecting the opinions of Louis Bertrand Castel, a
Jesuit, are given in the historical part. The coincidence of some
of his views with those of Goethe is often apparent: he objects,
for instance, to the arbitrary selection of the Newtonian spectrum;
observing that the colours change with every change of distance between
the prism and the recipient surface.—Farbenl. vol. ii. p. 527.
Jeremias Friedrich Gülich was a dyer in the neighbourhood of Stutgardt:
he published an elaborate work on the technical details of his own
pursuit.—Farbenl. vol. ii. p. 630.
NOTE BB.—Par. 748.
Goethe, in his account of Castel, suppresses the learned Jesuit's
attempt at colorific music (the claveçin oculaire), founded on the
Newtonian doctrine. Castel was complimented, perhaps ironically, on
having been the first to remark that there were but three principal
colours. In asserting his claim to the discovery, he admits that there
is nothing new. In fact, the notion of three colours is to be found in
Aristotle; for that philosopher enumerates no[Pg 418] more in speaking of the
rainbow,[1] and Seneca calls them by their right names.[2] Compare with
Dante, Parad. c. 33. The relation between colours and sounds is in like
manner adverted to by Aristotle; he says—"It is possible that colours
may stand in relation to each other in the same manner as concords
in music, for the colours which are (to each other) in proportions
corresponding with the musical concords, are those which appear to
be the most agreeable."[3] In the latter part of the 16th century,
Arcimboldo, a Milanese painter, invented a colorific music; an account
of his principles and method will be found in a treatise on painting
which appeared about the same time. "Ammaestrato dal quai ordine Mauro
Cremonese dalla viola, musico dell' Imperadore Ridolfo II. trovò sul
gravicembalo tutte quelle consonanze che dall' Arcimboldo erano segnate
coi colori sopra una carta."[4]
NOTE CC.—Par. 758.
The moral associations of colours have always been a more favourite
subject with poets than with painters. This is to be traced to the
materials and means of description as distinguished from those of
representation. An image is more distinct for the mind when it is
compared with something that resembles it. An object is more distinct
for the eye when it is compared with something that differs from it.
Association is the auxiliary in the one case, contrast in the[Pg 419] other.
The poet, of necessity, succeeds best in conveying the impression
of external things by the aid of analogous rather than of opposite
qualities: so far from losing their effect by this means, the images
gain in distinctness. Comparisons that are utterly false and groundless
never strike us as such if the great end is accomplished of placing
the thing described more vividly before the imagination. In the common
language of laudatory description the colour of flesh is like snow
mixed with vermilion: these are the words used by Aretino in one of
his letters in speaking of a figure of St. John, by Titian. Similar
instances without end might be quoted from poets: even a contrast can
only be strongly conveyed in description by another contrast that
resembles it.[1] On the other hand it would be easy to show that
whenever poets have attempted the painter's method of direct contrast,
the image has failed to be striking, for the mind's eye cannot see the
relation between two colours.
Under the same category of effect produced by association may be
classed the moral qualities in which poets have judiciously taken
refuge when describing visible forms and colours, to avoid competition
with the painters' elements, or rather to attain their end more
completely. But a little examination would show that very pleasing
moral associations may be connected with colours which would be far
from agreeable to the eye. All light, positive colours, light-green,
light-purple, white, are pleasing to the mind's eye, and no degree
of dazzling splendour is offensive. The moment, however, we have to
do with the actual sense of vision, the susceptibility of the eye
itself is to be considered, the law of comparison is reversed, colours
become striking by being opposed to what they are not, and their moral
associations are not owing to the colours themselves,[Pg 420] but to the
modifications such colours undergo in consequence of what surrounds
them. This view, so naturally consequent on the principles the author
has himself arrived at, appears to be overlooked in the chapter under
consideration, the remarks in which, in other respects, are acute and
ingenious.
NOTE DD.—Par. 849.
According to the usual acceptation of the term chiaro-scuro in the
artist world, it means not only the mutable effects produced by light
and shade, but also the permanent differences in brightness and
darkness which are owing to the varieties of local colour.
NOTE EE.—Par. 855.
The mannered treatment of light and shade here alluded to by the
author is very seldom to be met with in the works of the colourists;
the taste may have first arisen from the use of plaster-casts, and
was most prevalent in France and Italy in the early part of the last
century. Piazzetta represented it in Venice, Subleyras in Rome. In
France "Restout taught his pupils that a globe ought to be represented
as a polyhedron. Greuze most implicitly adopted the doctrine, and in
practice showed that he considered the round cheeks of a young girl or
an infant as bodies cut into facettes."[1]
NOTE FF.—Par. 859.
All this was no doubt suggested by Heinrich Meyer, whose chief
occupation in Rome, at one time, was making[Pg 421] sepia drawings from
sculpture (see Goethe's Italiänische Reise). It is hardly necessary to
say that the observation respecting the treatment of the surface in the
antique statues is very fanciful.
NOTE GG.—Par. 863.
This observation might have been suggested by the drawings of Claude,
which, with the slightest means, exhibit an harmonious balance of warm
and cold.
NOTE HH.—Par. 865.
The colouring of Paolo Uccello, according to Vasari's account of him,
was occasionally so remarkable that he might perhaps have been fairly
included among the instances of defective vision given by the author.
His skill in perspective, indicating an eye for gradation, may be also
reckoned among the points of resemblance (see Par. 105).
NOTE II.—Par. 902.
The quotation before given from Boschini shows that the method
described by the author, and which is true with regard to some of the
Florentine painters, was not practised by the Venetians, for their
first painting was very solid. It agrees, however, with the manner
of Rubens, many of whose works sufficiently corroborate the account
of his process given by Descamps. "In the early state of Rubens's
pictures," says that writer,[1] "everything appeared like a thin wash;
but although he often made use of the ground in producing his tones,
the canvas was entirely covered more or less with colour." In this
system of leaving the shadows transparent from the first, with the
ground shining through them, it would have been obviously destructive
of richness to use white mixed with the darks, the brightness, in
fact, already existed underneath. Hence the[Pg 422] well-known precept of
Rubens to avoid white in the shadows, a precept, like many others,
belonging to a particular practice, and involving all the conditions of
that practice.[2] Scarmiglione, whose Aristotelian treatise on colour
was published in Germany when Rubens was three-and-twenty, observes,
"Painters, with consummate art, lock up the bright colours with dark
ones, and, on the other hand, employ white, the poison of a picture,
very sparingly." (Artificiosissimè pictores claros obscuris obsepiant
et contra candido picturarum veneno summè parcentes, &c.)
NOTE KK.—Par. 903.
The practice here alluded to is more frequently observable in slight
works by Paul Veronese. His ground was often pure white, and in some
of his works it is left as such. Titian's white ground was covered
with a light warm colour, probably at first, and appears to have
been similar to that to which Armenini gives the preference, namely,
"quella che tira al color di carne chiarissima con un non so che di
fiammeggiante."[1]
NOTE LL.—Par. 919.
The notion which the author has here ventured to express may have
been suggested by the remarkable passage in the last canto of Dante's
"Paradiso"—
"Nella profonda e chiara sussistenza,
Dell' alto lume parremi tre giri
Di tre colori e d'una continenza," &c.
After the concluding paragraph the author inserts a letter from a
landscape-painter, Philipp Otto Runge, which is intended to show that
those who imitate nature may arrive at principles analogous to those of
the "Farbenlehre."
THE END.
To learn how to paint in watercolor, enroll now
Watercolor Academy Online Course
A self-study, self-paced course where you can learn how to paint in watercolor by watching video lessons and doing assignments
- Unlimited access to 80 watercolor painting video lessons
- Lifetime membership without deadlines
- Unlimited support from the Academy tutors
- Constructive critique of your artworks
- Member access to the Academy's Art community
- Place in the Academy's Students Gallery
- Exclusive members-only newsletter and bonuses
- Watercolor Academy Diploma of Excellence in your name
One-time payment - Lifetime membership
$297 USD
ENROLL NOW
Personal Tutoring online + Online Course
One-to-one, unlimited and custom-tailored to your skills and needs Personal Tutoring by the Watercolor Academy teachers
- Everything in Online Course, plus:
- Dedicated team of art tutors
- Assessment of your current level of art skills
- Personalized curriculum tailored to your skills and goals
- Up to 100 art tasks with by-task assessment
- Unlimited one-to-one personal coaching with detailed per-task instructions and feedback
- Artwork critiques and results-oriented guidance
One-time payment - Lifetime membership
$997 USD
ENROLL NOW









